Bulletin of Botanical Research ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (5): 722-730.doi: 10.7525/j.issn.1673-5102.2025.05.007
• Original Paper • Previous Articles Next Articles
Shang LIU, Jinhua WANG, Hasi YU, Chang LIU( )
)
Received:2025-04-30
Online:2025-09-20
Published:2025-09-28
Contact:
Chang LIU
E-mail:changliu0110@163.com
CLC Number:
Shang LIU, Jinhua WANG, Hasi YU, Chang LIU. Effects of Constitutive Overexpression of PagPYL4 Gene on Drought Tolerance and Growth of 84K poplar[J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2025, 45(5): 722-730.
Table 1
Primer sequence
引物名称 Primer name | 序列(5′→3′) Sequence(5′→3′) | 应用 Application |
|---|---|---|
| 84KPYL4-F | CAGGTCGACTCTAGAGGATCCATGCCTGCTAATCCTCCGAG | PCR/Identification |
| 84KPYL4-R | GGGAAATTCGAGCTCGGTACCTCACGATGATGATTTATTATTGCGTC | PCR |
| Semi-PagPYL4-F | CGGTGGTCTCCTCTACCACGC | Semi-quantitative PCR |
| Semi-PagPYL4-R | GCTCATCGTCGAGGATCTCGAGG | Semi-quantitative PCR |
| UBQ7-F | CCTAACTGGCAAGACCATCAC | Semi-quantitative PCR |
| UBQ7-R | AGCCTCAGAACCAGATGCAGT | Semi-quantitative PCR |
| NOSR | CATCGCAAGACCGGCAACAG | Identification |

Fig.1
Identification of 84K poplar PagPYL4 gene and phenotype analysis of the transgenic linesA. Phylogenetic tree analysis of PYL4; B. Semi-quantitative PCR electrophoretogram of transgenic 84K poplar; C. Plant height statistics; D. Ground diameter statistics; E. Phenotypic diagram of transgenic 84K poplar. In Figs. 1C and D, two-way analysis of variance(ANOVA) was used. Data were expressed as mean±SE; the error line represented the standard error of three biological replicates, different lowercase letters indicated significant differences between lines at P<0.05.
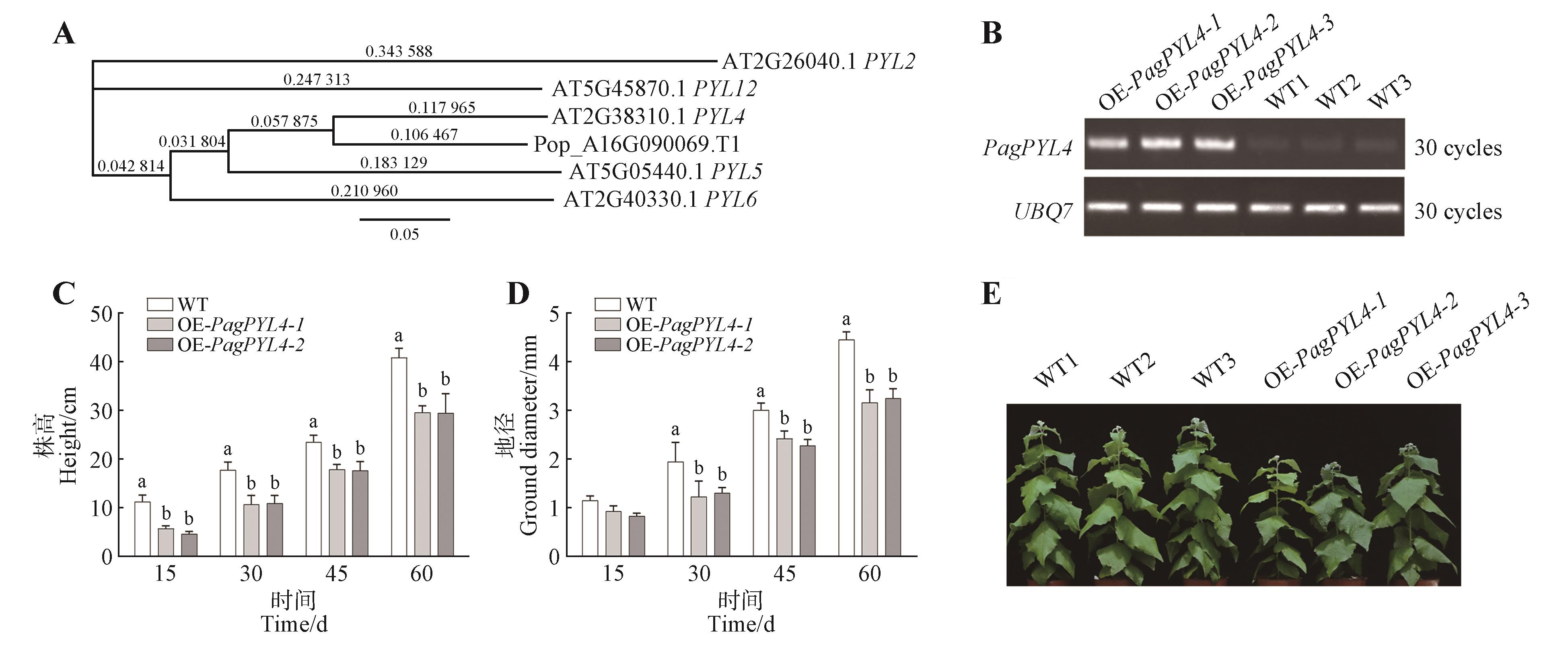
Fig.3
Stomatal aperture indexs of different lines under different ABA concentrationsA. The stomatal opening before and after ABA treatment; B. Stomatal aperture after 5 µmol·L-1 ABA treatment for 0 and 2 h; C. Stomatal aperture after 10 µmol·L-1 ABA treatment for 0 and 2 h. OS. Open solution buffer.Different lowercase letters indicated significant differences between lines at P<0.05.
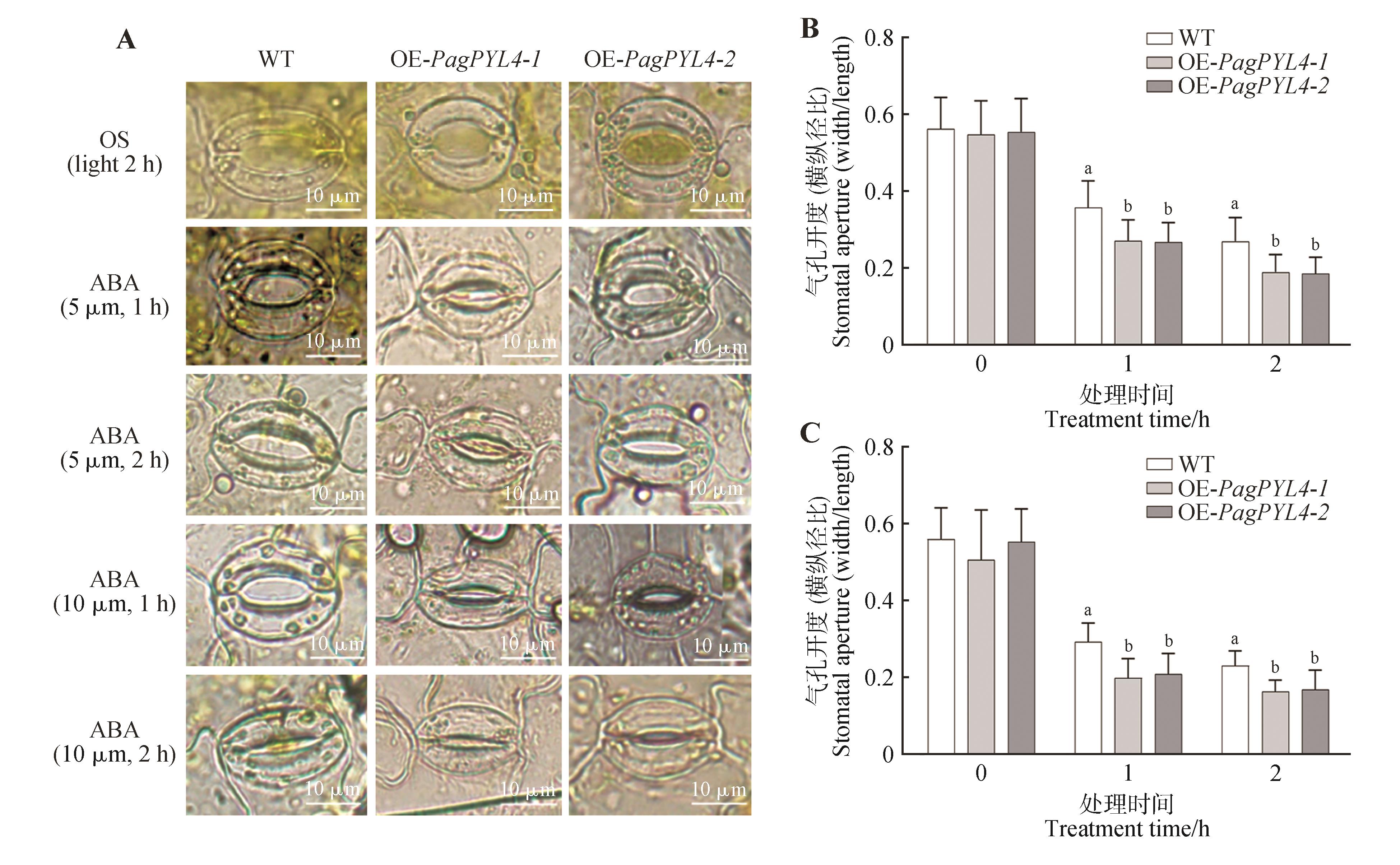

Fig.4
Analysis of drought-resistant physiological indices of 84K poplar linesA. Determination of the water loss rate of detached leaves; B. DAB staining under mannitol treatment; C. The level of DAB staining under mannitol treatment. Different lowercase letters indicated significant differences between 84K poplar lines at P<0.05.
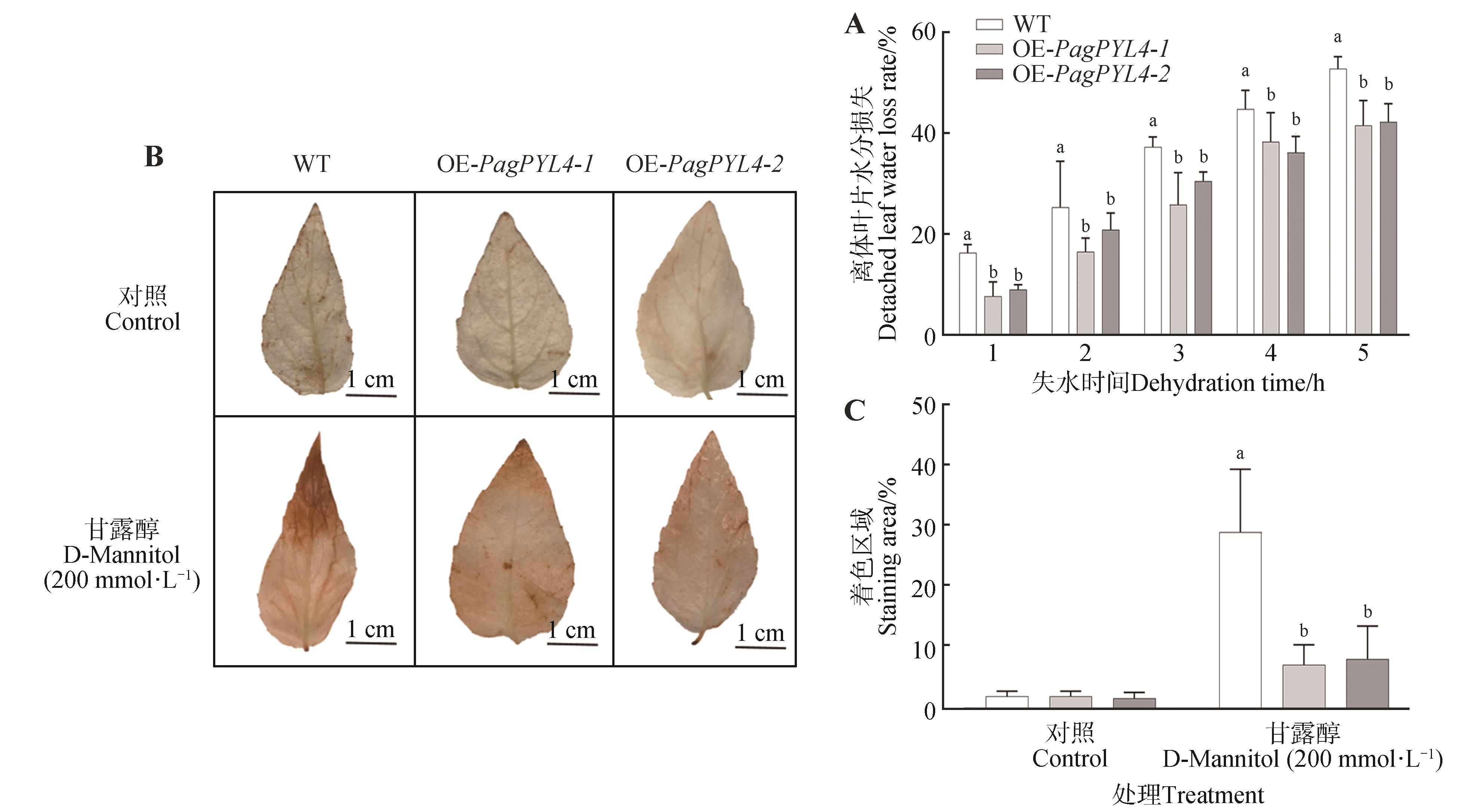
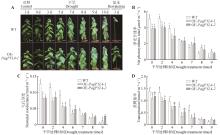
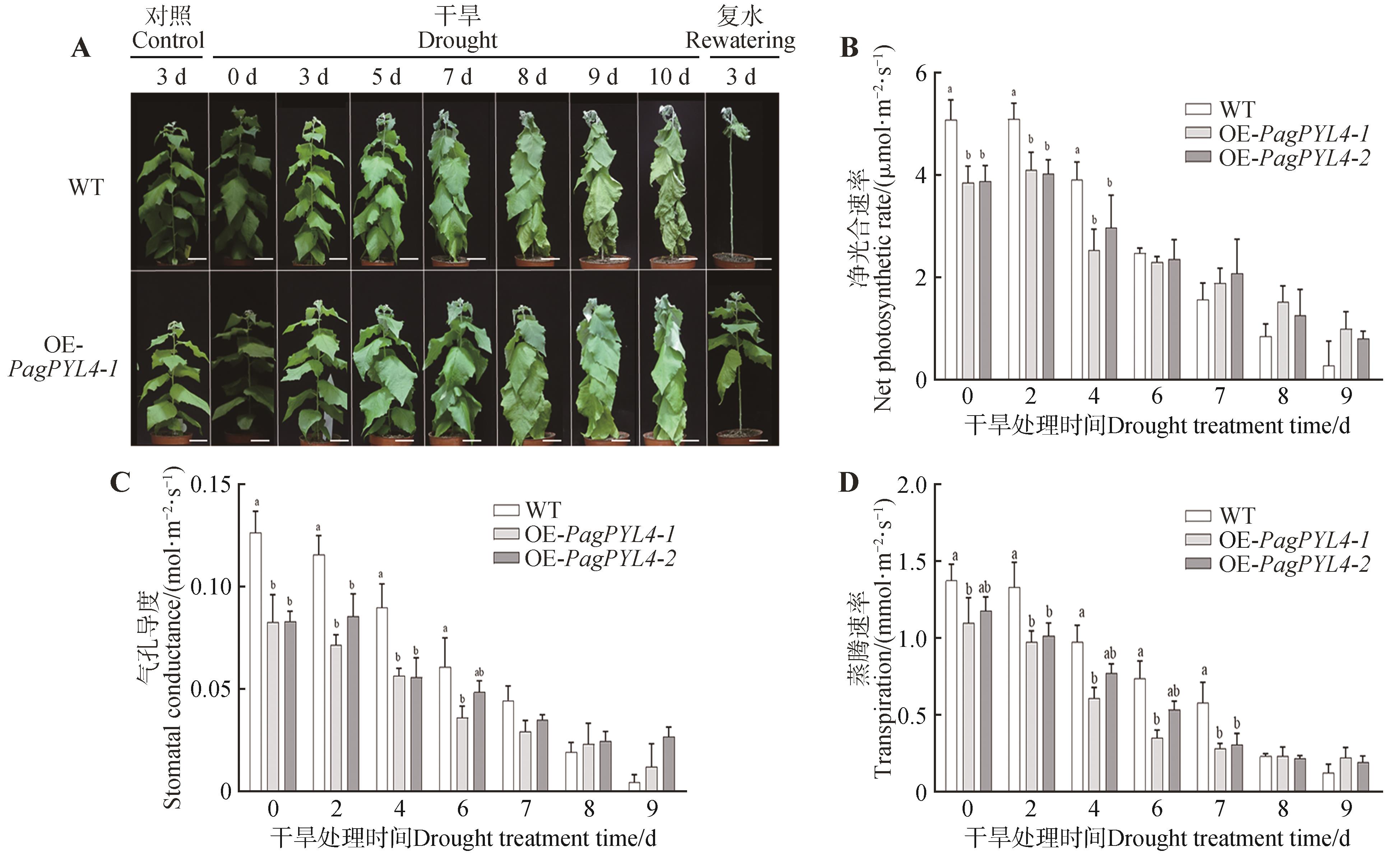
Fig.5
Photosynthetic parameters and phenotypic analysis of 84K poplar lines under short-term drought stressA. Phenotypic observation under short-term drought stress; B. Net photosynthetic rate; C. Stomatal conductance; D. Transpiration rate. Different lowercase letters indicated significant differences between 84K poplar lines at P<0.05.
| [1] | AITKEN S N, YEAMAN S, HOLLIDAY J A,et al.Adaptation,migration or extirpation: climate change outcomes for tree populations[J].Evolutionary Application,2008,1(1):95-111. |
| [2] | SCHNABEL F, PURRUCKER S, SCHMITT L,et al.Cumulative growth and stress responses to the 2018—2019 drought in a European floodplain forest[J].Global Change Biology,2022,28(5):1870-1883. |
| [3] | 安元强,郑勇奇,林富荣,等.林木种质资源调查技术规程研制[J].林业调查规划,2016,41(3):1-6. |
| AN Y Q, ZHENG Y Q, LIN F Q,et al.Development of technical regulations for forest tree germplasm resources investigation[J].Forest Inventory and Planning,2016,41(3):1-6. | |
| [4] | 顾万春.中国林木遗传(种质)资源保存与研究现状[J].世界林业研究,1999(2):50-57. |
| GU W C.Current situation of conservation and research on forest tree genetic (germplasm) resources in China[J].World Forestry Research,1999(2):50-57. | |
| [5] | MATSUI A, ISHIDA J, MOROSAWA T,et al. Arabidopsis transcriptome analysis under drought,cold,high-salinity and ABA treatment conditions using a tiling array[J].Plant Cell Physiology,2008,49(8):1135-1149. |
| [6] | YANG Y, LI H G, WANG J,et al. ABF3 enhances drought tolerance via promoting ABA-induced stomatal closure by directly regulating ADF5 in Populus euphratica [J].Journal of Experimental Botany,2020,71(22):7270-7285. |
| [7] | SOON F F, NG L M, ZHOU X E,et al.Molecular mimicry regulates ABA signaling by SnRK2 kinases and PP2Cphosphatases[J].Science,2012,335(6064):85-88. |
| [8] | CUTLER S R, RODRIGUEZ P L, FINKELSTEIN R R,et al.Abscisic acid:emergence of a core signaling network[J].Annual Review of Plant Biology,2010,61:651-679. |
| [9] | PIZZIO G A, RODRIGUEZ L, ANTONI R,et al.The PYL4 A194T mutant uncovers a key role of PYR1-LIKE4/PROTEIN PHOSPHATASE 2CA interaction for abscisic acid signaling and plant drought resistance[J].Plant Physiology,2013,163(1):441-455. |
| [10] | PARK S Y, FUNG P, NISHIMURA N,et al.Abscisic acid inhibits type 2C protein phosphatases via the PYR/PYL family of START proteins[J].Science,2009,324(5930):1068-1071. |
| [11] | WANG S, FAN Y, DU S,et al. PtaERF194 inhibits plant growth and enhances drought tolerance in poplar[J].Tree Physiology,2022,42(8):1678-1692. |
| [12] | TUNG S A, SMEETON R, WHITE C A,et al.Over-expression of LeNCED1 in tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) with the rbcS3C promoter allows recovery of lines that accumulate very high levels of abscisic acid and exhibit severe phenotypes[J].Plant Cell & Environment,2008,31(7):968-981. |
| [13] | ZHAO Y, CHAN Z L, GAO J H,et al.ABA receptor PYL9 promotes drought resistance and leaf senescence[J].Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America,2016,113(7):1949-1954. |
| [14] | LI Q, SHEN C, ZHANG Y,et al. PePYL4 enhances drought tolerance by modulating water-use efficiency and ROS scavenging in Populus [J].Tree Physiology,2023,43(1):102-117. |
| [15] | HE F, WANG H L, LI H G,et al.PeCHYR1,a ubiquitin E3 ligase from Populus euphratica,enhances drought tolerance via ABA-induced stomatal closure by ROS production in Populus [J].Plant Biotechnology Journal,2018,16(8):1514-1528. |
| [16] | WEN S S, GE X L, WANG R,et al.An efficient agrobacterium-mediated transformation method for hybrid poplar 84K (Populus alba × P.glandulosa) using calli as explants[J].International Journal of Molecular Sciences,2022,23(4):2216. |
| [17] | 金思雨,彭祚登,张舒乐.不同程度干旱胁迫和复水处理对刺槐苗木生理指标的影响[J].东北林业大学学报,2024,52(10):27-39. |
| JIN S Y, PENG Z D, ZHANG S L.Effects of drought stress at different levels and rewatering treatments on the physiological indexes of Robinia pseudoacacia seedlings[J].Journal of Northeast Forestry University,2024,52(10):27-39. | |
| [18] | VAHISALU T, KOLLIST H, WANG Y F,et al.SLAC1 is required for plant guard cell S-type anion channel function in stomatal signalling[J].Nature,452(7186):487-491. |
| [19] | TAN YQ, YANG Y, SHEN X,et al.Multiple cyclic nucleotide-gated channels function as ABA-activated Ca2+ channels required for ABA-induced stomatal closure in Arabidopsis [J].Plant Cell,2023,35(1):239-259. |
| [20] | CRUZ DE CARVALHO M H.Drought stress and reactive oxygen species:production,scavenging and signaling[J].Plant Signal & Behavior,2008,3(3):156-165. |
| [21] | CHEN Q, HU T, LI X,et al.Phosphorylation of SWEET sucrose transporters regulates plant root:shoot ratio under drought.Nature Plants,2022,8(1):68-77. |
| [22] | Braun D M.Plant science.SWEET! The pathway is complete.Science,2012,335(6065):173-174. |
| [23] | GAO J, ZHANG Y, XU C,et al.Abscisic acid collaborates with lignin and flavonoid to improve pre-silking drought tolerance by tuning stem elongation and ear development in maize (Zea mays L.).Plant Journal,2023,114(2):437-454. |
| [24] | DONG N Q, LIN H X.Contribution of phenylpropanoid metabolism to plant development and plant-environment interactions.Journal of Integrative Plant Biology,2021,63(1):180-209. |
| [25] | LIU H, GAO X, FAN W,et al.Optimizing carbon and nitrogen metabolism in plants:from fundamental principles to practical applications.Journal of Integrative Plant Biology,2025,67(6):1447-1466. |
| [26] | CHEN X, YAO Q, GAO X,et al.Shoot-to-root mobile transcription factor HY5 coordinates plant carbon and nitrogen acquisition.Current Biology,2016,26(5):640-646. |
| [1] | Xinyi HU, Liming XU, Botao QIN, Yidong AN, Guofeng JIANG. Distinct Water Supply and Consumption Characteristics in Leaves between Nymphaeaceae and Terrestrial Herbs [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2025, 45(5): 675-685. |
| [2] | Fang WANG, Yelei YANG, Changhua YUAN, Jun WANG, Wei WEI, Lin WU, Kuiyou LI, Kuiquan LI, Zhimin LU, Yuanxing WANG, Yuchun YANG. Variation Analysis of Growth Traits of Offspring and Superior Materials Selection of Pinus koraiensis [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2025, 45(5): 816-826. |
| [3] | Min ZHAO, Feng WANG, Jianan WANG, Qi YU, Hanguo ZHANG, Lei ZHANG. Selection of Superior Families of Larch Resistant to Pine Wood Nematode Disease [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2025, 45(5): 827-836. |
| [4] | Minwei CHAI, Yifan WU, Ruili LI, Lin ZHOU, Xiaoxue SHEN. The Influence of Cadmium, Microplastics, and Their Combination on the Growth and Photosynthetic Characteristics of Kandelia obovata [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2025, 45(4): 603-613. |
| [5] | Wu LIU, Yaying YANG, Ning GONG, Ziwei ZOU, Yi WANG, Baodong CHEN, Qiong WANG, Wei LIU. Growth and Physiological Responses of Ancient Celtis sinensis Seedlings to the Inoculation of Indigenous Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungi [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2025, 45(3): 393-405. |
| [6] | Yanyan PAN, Xiaoguang LI, Lijun LIU, Hong LI, Xin ZHONG, Yifei ZHANG. Response of Pinus Koraiensis Growth and Rhizosphere Soil Enzyme Activity to Lepista nuda Inoculation [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2025, 45(3): 460-470. |
| [7] | Baojie TONG, Dongying DAN, Jiawei LI. Research Progress on Heat Tolerance and Regulatory Strategies of Plant Leaves [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2025, 45(2): 171-180. |
| [8] | Ziteng SUN, Xinyu WANG, Lili HOU, Yueying LIU, Zhimin ZHENG. Identification and Preliminary Functional Analysis of the BpGRFs Gene in Betula Platyphylla [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2025, 45(2): 191-201. |
| [9] | Yanli ZENG, Yanhui GUAN, Lujing QIAO, Yating CHEN, Cunyong JU, Tijiu CAI. Effects of Neighborhood Structure on Radial Growth of Larix olgensis and Quercus mongolica with Different Diameter Classes [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2025, 45(2): 254-265. |
| [10] | Xiao LI, Hanshi WANG, Hongxing WANG, Luping JIANG, Zhongyi PANG, Yanhui PENG, Xiyang ZHAO. Effects of Irrigation and Fertilization on Growth and Photosynthetic Physiological Characteristics of Populus cathayana × canadansis ‘Xinlin1’ [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2025, 45(1): 77-87. |
| [11] | Xiaopeng MU, Xiaoyan MOU, Xinliang QI, Jing WANG, Yu YANG, Jiancheng ZHANG, Pengfei WANG. Effects of Different Growth Retardant Treatments on Rooting of Prunus humilis Rhizome Cuttings [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2025, 45(1): 88-97. |
| [12] | Ting LIU, Mingyue LI, Meiru ZHU, Hao XIN, Bowen DONG, Peng ZHANG. Differences in Seed Dormancy Among Different Clones of Fraxinus mandshurica [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2024, 44(5): 711-720. |
| [13] | Xuhong JIN, Cong YU, Tingyao ZHANG, Songtong LÜ, Yang LIU, Le CHEN, Sheng LONG, Huaizhi MU. Preliminary Selection of Half-sib Family in Betula costata Based on Seed Vigor and Sapling Growth [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2024, 44(5): 763-773. |
| [14] | Xuelai WANG, Xiaoting LIU, Liran WANG, Shitong LI, Taijin ZHANG, Jiafeng ZHANG, Jinghua XU, Guanzheng QU, Xiyang ZHAO. Coupling Evaluation of Growth and Wood Properties of Pinus koraiensis Half-sib Families [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2024, 44(4): 554-564. |
| [15] | Jing XU, Ying CUI, Fusen WANG, Kailong LI, Guanzheng QU, Xiyang ZHAO. Growth and Wood Character Variation of Populus pseudo-cathyana×Populus deltoids Plantation with Different Thinning Intensity in Northeast China [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2024, 44(2): 248-258. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||