Bulletin of Botanical Research ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (2): 191-201.doi: 10.7525/j.issn.1673-5102.2025.02.005
• Original Paper • Previous Articles
Ziteng SUN, Xinyu WANG, Lili HOU, Yueying LIU, Zhimin ZHENG( )
)
Received:2024-12-11
Online:2025-03-20
Published:2025-04-07
Contact:
Zhimin ZHENG
E-mail:zmzheng@nefu.edu.cn
CLC Number:
Ziteng SUN, Xinyu WANG, Lili HOU, Yueying LIU, Zhimin ZHENG. Identification and Preliminary Functional Analysis of the BpGRFs Gene in Betula Platyphylla[J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2025, 45(2): 191-201.
Table 1
Primers for qRT-PCR of the BpGRF gene family
基因名称 Gene name | 引物序列(5′→3′) Primer sequences (5′→3′) |
|---|---|
| BpGRF1-F | AGATCATCTTCAGGGACCTTTGAAGAT |
| BpGRF1-R | GAGGTTCTGATTTGGGGGAAGAG |
| BpGRF2-F | GATGATGATGGTTATGCCACATCATGA |
| BpGRF2-R | TCAGAGTCTTTGGCACCATTGCA |
| BpGRF3-F | CTCAGTGGCAAGAGCTTGAACA |
| BpGRF3-R | GCAAGTAGTTCCAGCCAATATGTGG |
| BpGRF4-F | GTCTGGGCCTGCTGAAGATGA |
| BpGRF4-R | ATCCTTGCTGAGAAAGGGAACCT |
| BpGRF5-F | ACTCAGTGGCAAGAGCTTGAACA |
| BpGRF5-R | CTGCCATATCCCATCTCAAAACATGT |
| BpGRF6-F | AGAGGATGTCTGACGAGGAGGA |
| BpGRF6-R | TCCTTGAAGCTCATGCGACTGAG |
| BpGRF7-F | ATGTTGTTGCTGCTGCTTGTTCT |
| BpGRF7-R | GCTTGTCTCTCAAGCTCTTTCCAC |
| BpGRF8-F | ATGAACAGTGGTGGAGCTGGC |
| BpGRF8-R | ATGAGAAATGGACTCAAAGCTTTTCTGAAT |
| BpGRF9-F | ATGGACTTCCATCTGAAGCAATGGA |
| BpGRF9-R | ATCCTGGGAAATCTGGTGGGTG |
| BpTubulin-F | TCAACCGCCTTGTCTCTCAGG |
| BpTubulin-R | TGGCTCGAATGCACTGTTGG |
Table 2
Analysis of the physicochemical properties of the GRF gene family in birch
基因名称 Gene name | 基因ID Gene ID | 染色体 Chromosome | 基因位置 Gene location | 氨基酸数目 Number of amino acids/aa | 相对分子质量 Molecular weight/Da | 等电点 Isoelectricpoint | 总平均亲水性 Total average hydrophilicity | 亚细胞定位 Subcellular location |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BpGRF1 | Chr01G01531 | 1 | 20095262~20098378 | 606 | 65 788.05 | 8.67 | -0.662 | 细胞核Nuclear |
| BpGRF2 | Chr02G01459 | 2 | 17218445~17220195 | 462 | 50 533.66 | 7.54 | -0.610 | 细胞核Nuclear |
| BpGRF3 | Chr03G01749 | 3 | 21418731~21420189 | 375 | 42 955.78 | 8.11 | -0.918 | 细胞核Nuclear |
| BpGRF4 | Chr06G00029 | 6 | 331582~334410 | 600 | 64 353.25 | 6.52 | -0.582 | 细胞核Nuclear |
| BpGRF5 | Chr06G01222 | 6 | 11256167~11257412 | 316 | 36 045.05 | 8.71 | -0.879 | 细胞核Nuclear |
| BpGRF6 | Chr06G02041 | 6 | 23869844~23872981 | 503 | 54 207.00 | 9.57 | -0.608 | 细胞核Nuclear |
| BpGRF7 | Chr08G00312 | 8 | 2742946~2745353 | 528 | 56 979.17 | 6.28 | -0.585 | 细胞核Nuclear |
| BpGRF8 | Chr08G00421 | 8 | 3587787~3591990 | 327 | 35 993.60 | 7.75 | -0.783 | 细胞核Nuclear |
| BpGRF9 | Chr14G02157 | 14 | 25355104~25357316 | 389 | 42 098.12 | 8.64 | -0.559 | 细胞核Nuclear |

Fig.1
Bioinformatics analysis of the BpGRF gene family in birchA.GRF phylogenetic trees of birch,rice,Arabidopsis,soybean and Populus tomentosa(Bp. Birch, Loc. Rice, At. Arabidopsis, Gly. Soybean, GR. Zea mays, Potri. Populus tomentosa); B. Conservative domain analysis of BpGRF gene family in birch; red boxes were WRC and QLQ structural domains; C. Gene structure analysis of the GRF gene family in birch; D. Analysis of cis acting elements in the promoter of the GRF gene in birch.
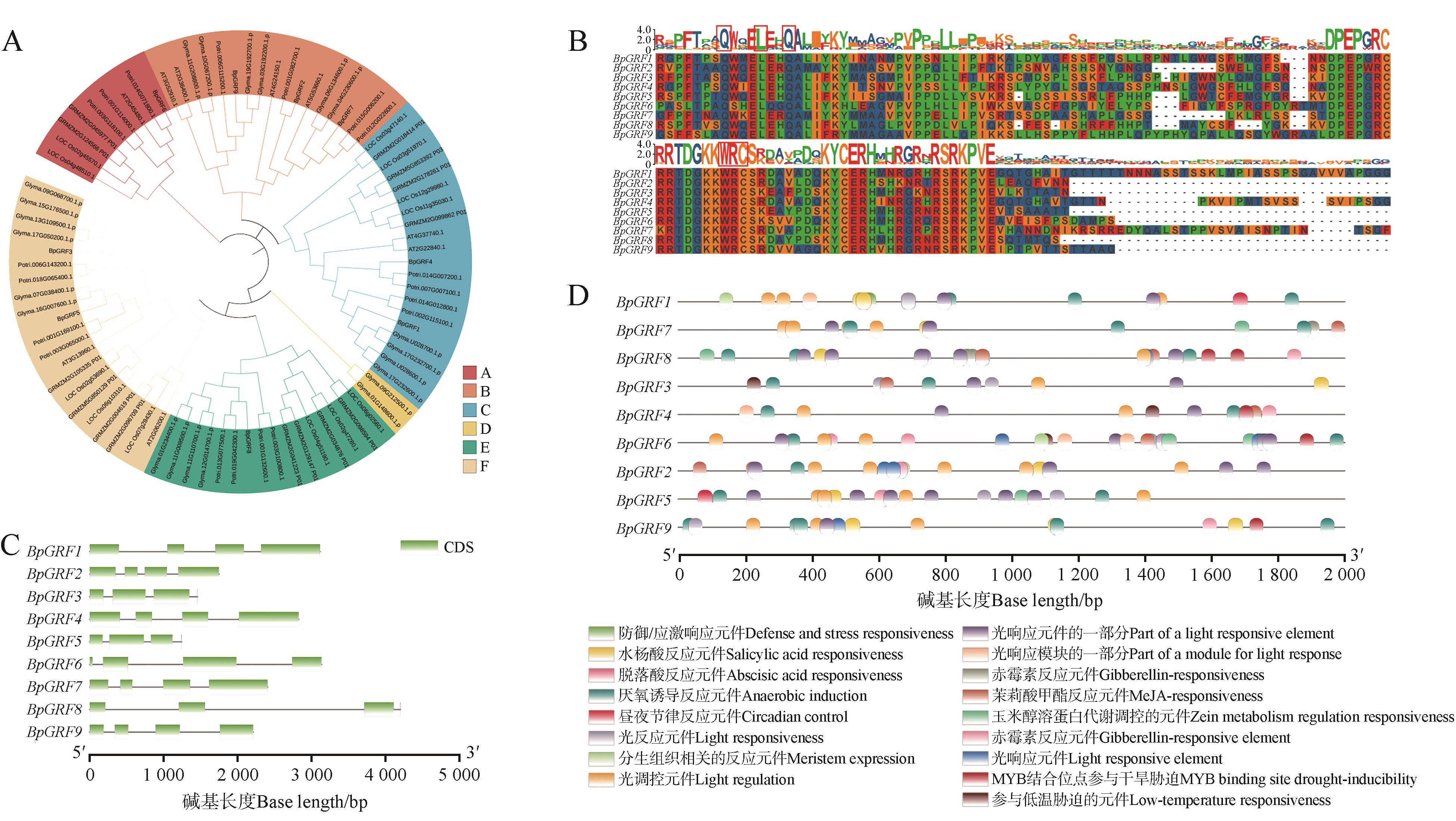

Fig.3
Phenotypic statistics of overexpressed BpGRF4 transgenic linesA.Relative expression of transgenic birch; B.Transgenic birch phenotypes; C.Plant height statistics; D.Internode number statistics; E.Internode length statistics; F.Branch number statistics; G.Branch length statistics. WT represented the wild-type strain; OE-1,OE-2 and OE-3 represented three overexpression lines; ns represented no significant difference; the error line represented the standard error of three biological replicates(*.P<0.05, **.P<0.01,***.P<0.001).
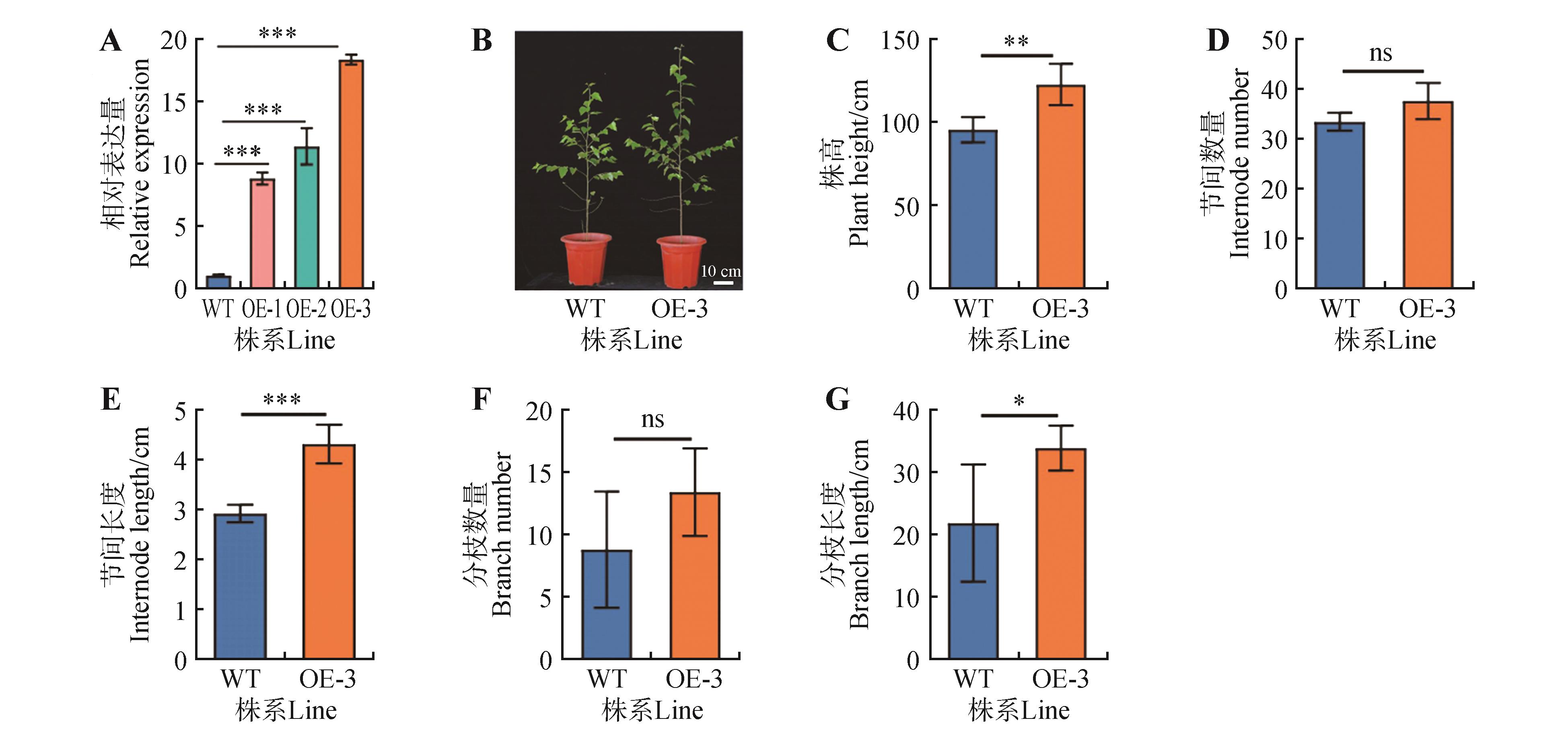
Fig.4
Stem phenotypic statistics of OE-3 transgenic linesA.WT stem transverse paraffin sections; B.OE-3 stem transverse paraffin sections; C.Ground diameter statistics; D.Stem cross-sectional area statistics; E.Cortex area statistics; F.Phloem area statistics; G.Xylem area statistics; H.Pith centre area statistics. WT represented the wild-type strain; OE-3 represented the third overexpression line; ns represented no significant difference; the error line represented the standard error of three biological replicates (**. P<0.01, ***. P<0.001).
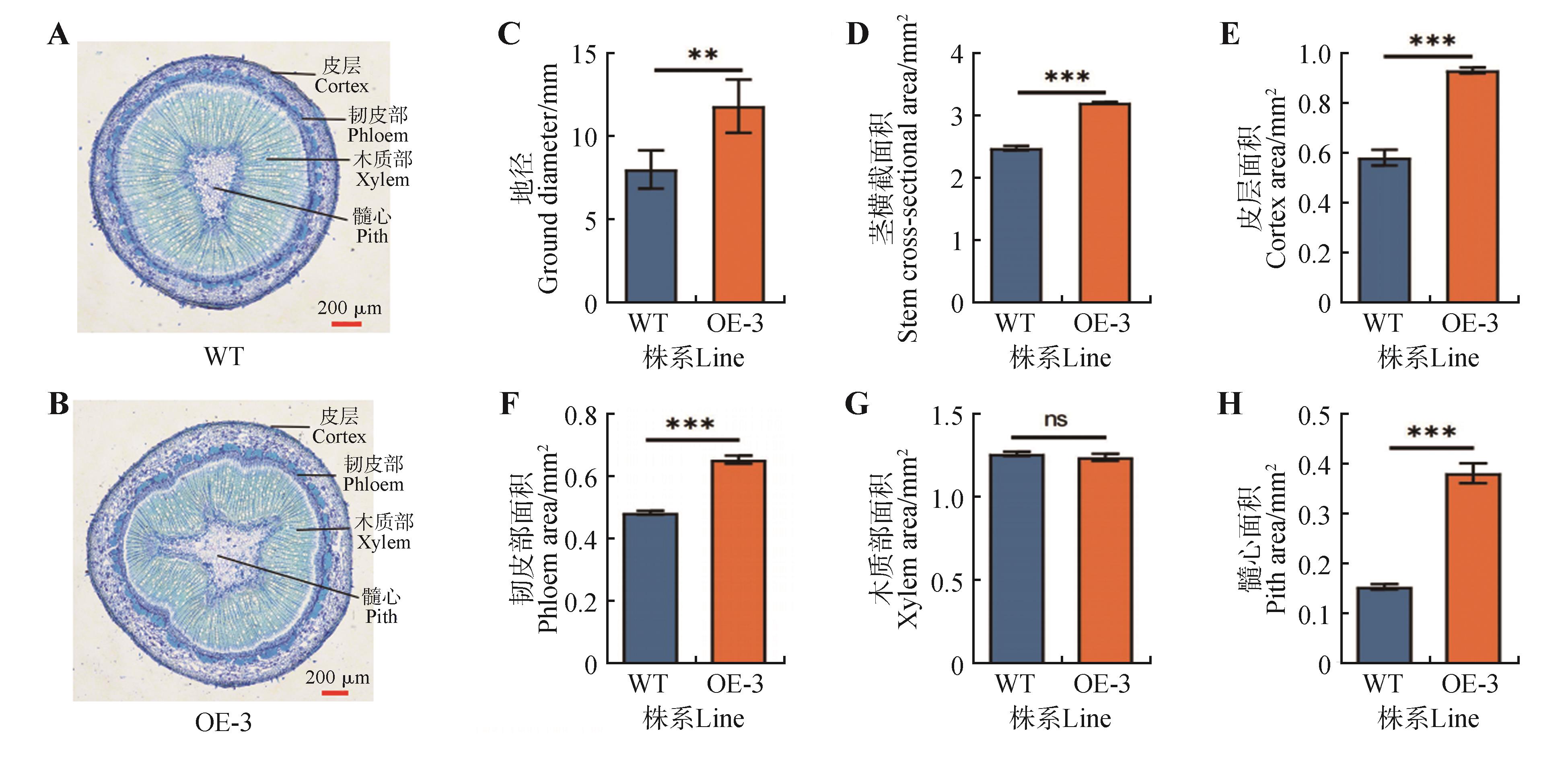

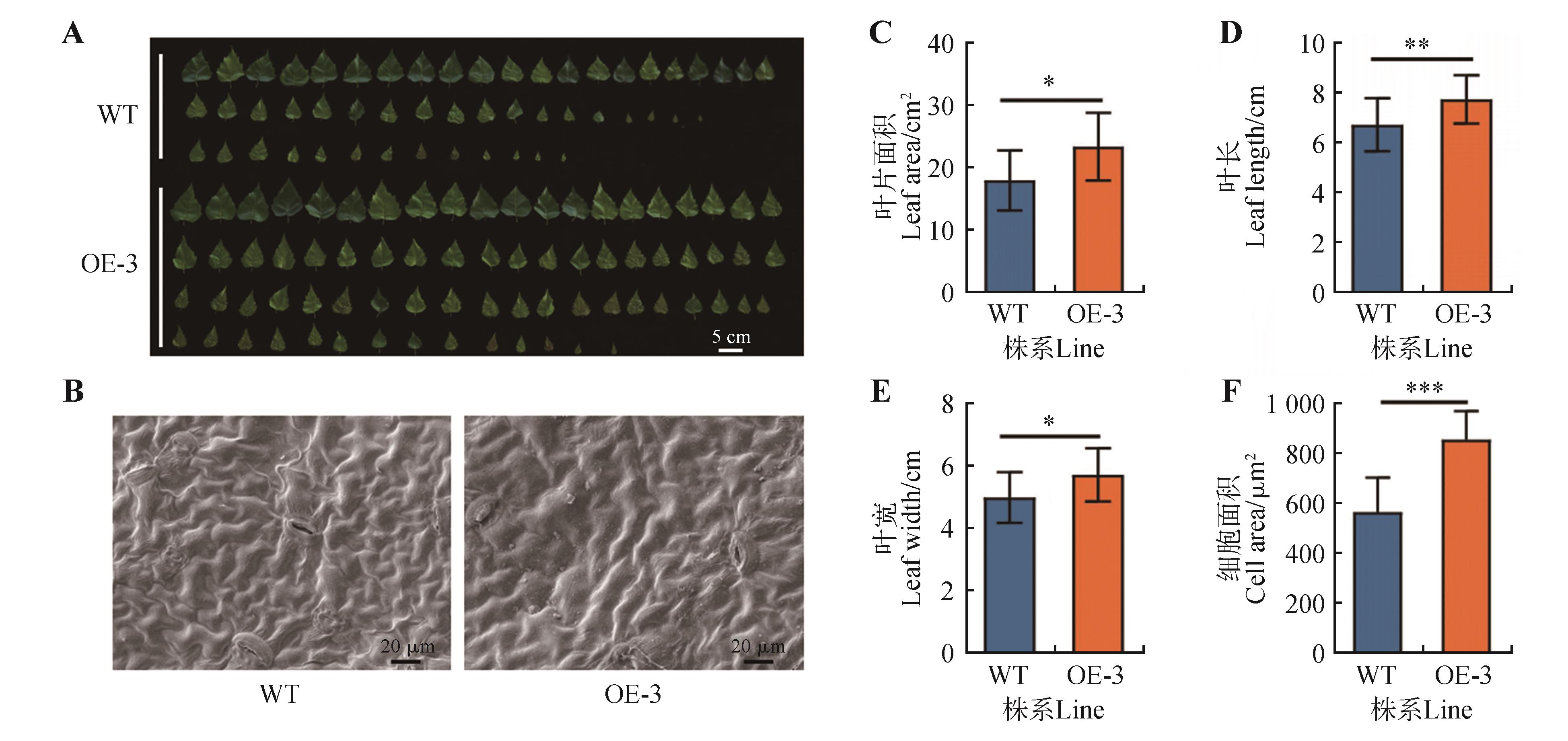
Fig.5
Leaf phenotypic statistics of OE-3 transgenic linesA.Transgenic birch leaf phenotype; B.Leaf scanning electron microscopy; C.Leaf area statistics; D.Leaf length statistics; E.Leaf width statistics; F.Cell area statistics. WT represented the wild-type strain; OE-3 represented the third overexpression line; ns represented no significant difference; the error line represented the standard error of three biological replicates(*.P<0.05,**.P<0.01,***.P<0.001).
| 1 | KIM J H.Biological roles and an evolutionary sketch of the GRF-GIF transcriptional complex in plants[J].BMB Reports,2019,52(4):227-238. |
| 2 | LIEBSCH D, PALATNIK F J.MicroRNA miR396,GRF transcription factors and GIF co-regulators:a conserved plant growth regulatory module with potential for breeding and biotechnology[J].Current Opinion in Plant Biology,2020,53:31-42. |
| 3 | KIM J H, CHOI D, KENDE H.The AtGRF family of putative transcription factors is involved in leaf and cotyledon growth in Arabidopsis [J].The Plant Journal,2003,36(1):94-104. |
| 4 | KIM J S, MIZOI J, KIDOKORO S,et al. Arabidopsis growth-regulating factor7 functions as a transcriptional repressor of abscisic acid- and osmotic stress-responsive genes,including DREB2A [J].The Plant Cell,2012,24(8):3393-3405. |
| 5 | CHEN L, LUAN Y S, ZHAI J M.Sp-miR396a-5p acts as a stress-responsive genes regulator by conferring tolerance to abiotic stresses and susceptibility to Phytophthora nicotianae infection in transgenic tobacco[J].Plant Cell Reports,2015,34(12):2013-2025. |
| 6 | WANG M, WANG Q L, ZHANG B H.Response of miRNAs and their targets to salt and drought stresses in cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.)[J].Gene,2013,530(1):26-32. |
| 7 | YUAN S R, ZHAO J M, LI Z G,et al.MicroRNA396-mediated alteration in plant development and salinity stress response in creeping bentgrass[J].Horticulture Research,2019,6(1):48. |
| 8 | RODRIGUEZ R E, MECCHIA M A, DEBERNARDI J M,et al.Control of cell proliferation in Arabidopsis thaliana by microRNA miR396[J].Development,2010,137(1):103-112. |
| 9 | DEBERNARDI J M, MECCHIA M A, VERCRUYSSEN L,et al.Post-transcriptional control of GRF transcription factors by microRNA miR396 and GIF co-activator affects leaf size and longevity[J].The Plant Journal,2014,79(3):413-426. |
| 10 | BELTRAMINO M, ERCOLI M F, DEBERNARDI J M,et al.Robust increase of leaf size by Arabidopsis thaliana GRF3-like transcription factors under different growth conditions[J].Scientific Reports,2018,8(1):13447. |
| 11 | HORIGUCHI G, KIM G T, TSUKAYA H.The transcription factor AtGRF5 and the transcription coactivator AN3 regulate cell proliferation in leaf primordia of Arabidopsis thaliana [J].The Plant Journal,2005,43(1):68-78. |
| 12 | VERCRUYSSEN L, TOGNETTI V B, GONZALEZ N,et al.GROWTH REGULATING FACTOR5 stimulates Arabidopsis chloroplast division,photosynthesis,and leaf longevity[J].Plant Physiology,2015,167(3):817-832. |
| 13 | VERCRUYSSE J, BAEKELANDT A, GONZALEZ N,et al.Molecular networks regulating cell division during Arabidopsis leaf growth[J].Journal of Experimental Botany,2020,71(8):2365-2378. |
| 14 | CHANDRAN V, WANG H, GAO F,et al.miR396-OsGRFs module balances growth and rice blast disease-resistance[J].Frontiers in Plant Science,2019,9:1999. |
| 15 | CHEN S, WANG Y C, YU L L,et al.Genome sequence and evolution of Betula platyphylla [J].Horticulture Research,2021,8(1):37. |
| 16 | 吴迪.白桦BpDof4基因的抗旱调控机制[D].沈阳:沈阳农业大学,2023. |
| WU D.Drought resistance regulation mechanism of BpDof4 gene in Betula platyphylla [D].Shenyang:Shenyang Agricultural University,2023. | |
| 17 | 张杰,顾宸瑞,李慧玉,等.白桦四倍体半同胞家系生长和材性性状的变异及选择[J].东北林业大学学报,2024,52(10):7-14,26. |
| ZHANG J, GU C R, LI H Y,et al.Variation and selection of growth and wood properties of tetraploid half-sib families of Betula platyphylla [J].Journal of Northeast Forestry University,2024,52(10):7-14,26. | |
| 18 | 邓长贺.大兴安岭的白桦树资源开发与利用[J].林业科技情报,2023,55(3):52-54. |
| DENG C H.Development and utilization of birch resources in Greater Khingan[J].Forestry Science and Technology Information,2023,55(3):52-54. | |
| 19 | WANG M, ZHAO Y H, ZHEN Z,et al.Individual-tree diameter growth model for Korean pine plantations based on optimized interpolation of meteorological variables[J].Journal of Forestry Research,2021,32(4):1535-1552. |
| 20 | CHEN C J, WU Y, LI J W,et al.TBtools-Ⅱ:a “one for all,all for one” bioinformatics platform for biological big-data mining[J].Molecular Plant,2023,16(11):1733-1742. |
| 21 | SONG Q X, LI Q T, LIU Y F,et al.Soybean GmbZIP123 gene enhances lipid content in the seeds of transgenic Arabidopsis plants[J].Journal of Experimental Botany,2013,64(14):4329-4341. |
| 22 | CHENG D W, LIU Y Y, WANG Y,et al.Establishment of high-efficiency genome editing in white birch (Betula platyphylla Suk.)[J].Plant Biotechnology Journal,2024,22(1):7-9. |
| 23 | GENG W L, LI Y Y, SUN D Q,et al.Prediction of the potential geographical distribution of Betula platyphylla Suk.in China under climate change scenarios[J].PLoS One,2022,17(3):e0262540. |
| 24 | CHI Y, WANG Z H, CHEN S Z,et al.Identification of BpEXP family genes and functional characterization of the BpEXPA1 gene in the stems development of Betula platyphylla [J].Journal of Plant Physiology,2024,303:154361. |
| 25 | YAN B, LI F R, MA Q,et al.The miR156-SPL4/SPL9 module regulates leaf and lateral branch development in Betula platyphylla [J].Plant Science,2024,338:111869. |
| 26 | JIA Y Q, ZHAO H M, NIU Y N,et al.Long noncoding RNA from Betula platyphylla,BplncSIR1,confers salt tolerance by regulating BpNAC2 to mediate reactive oxygen species scavenging and stomatal movement[J].Plant Biotechnology Journal,2024,22(1):48-65. |
| 27 | TAN Z L, WEN X J, WANG Y C. Betula platyphylla BpHOX2 transcription factor binds to different cis-acting elements and confers osmotic tolerance[J].Journal of Integrative Plant Biology,2020,62(11):1762-1779. |
| 28 | CHENG Z H, WEN S Q, WU Y K,et al.Comparatively evolution and expression analysis of GRF transcription factor genes in seven plant species[J].Plants,2023, 12(15):2790. |
| 29 | LANTZOUNI O, ALKOFER A, FALTER-BRAUN P,et al.GROWTH-REGULATING FACTORS interact with DELLAs and regulate growth in cold stress[J].The Plant Cell,2020,32(4):1018-1034. |
| 30 | OMIDBAKHSHFARD M A, PROOST S, FUJIKURA U,et al.Growth-Regulating Factors(GRFs):a small transcription factor family with important functions in plant biology[J].Molecular Plant,2015,8(7):998-1010. |
| 31 | LIU Y T, GUO P, WANG J,et al.Growth-regulating factors:conserved and divergent roles in plant growth and development and potential value for crop improvement[J].The Plant Journal,2022,113(6):1122-1145. |
| 32 | PIYA S, LIU J Y, BURCH-SMITH T,et al.A role for Arabidopsis growth-regulating factors 1 and 3 in growth-stress antagonism[J].Journal of Experimental Botany,2020,71(4):1402-1417. |
| 33 | KUIJT S J H, GRECO R, AGALOU A,et al.Interaction between the GROWTH-REGULATING FACTOR and KNOTTED1-LIKE HOMEOBOX families of transcription factors[J].Plant Physiology,2014,164(4):1952-1966. |
| 34 | OMIDBAKHSHFARD M A, FUJIKURA U, OLAS J J,et al.GROWTH-REGULATING FACTOR 9 negatively regulates Arabidopsis leaf growth by controlling ORG3 and restricting cell proliferation in leaf primordia[J].PLoS Genetics,2018,14(7):e1007484. |
| 35 | PAJORO A, MADRIGAL P, MUIÑO J M,et al.Dynamics of chromatin accessibility and gene regulation by MADS-domain transcription factors in flower development[J].Genome Biology,2014,15(3):R41. |
| 36 | JATHAR V, SAINI K, CHAUHAN A,et al.Spatial control of cell division by GA-OsGRF7/8 module in a leaf explaining the leaf length variation between cultivated and wild rice[J].New Phytologist,2022,234(3):867-883. |
| 37 | YIN X H, YUAN Y, HAN X W,et al.Genome-wide identification,characterization,and expression profiling of TaDUF668 gene family in Triticum aestivum [J].Agronomy,2023,13(8):2178. |
| 38 | WALTHER D, BRUNNEMANN R, SELBIG J.The regulatory code for transcriptional response diversity and its relation to genome structural properties in A.thaliana [J].PLoS Genetics,2007,3(2):e11. |
| 39 | XIE D W, WANG X N, FU L S,et al.Identification of the trehalose-6-phosphate synthase gene family in winter wheat and expression analysis under conditions of freezing stress[J].Journal of Genetics,2015,94(1):55-65. |
| 40 | GUO J F, LI W, SHANG L G,et al. OsbHLH98 regulates leaf angle in rice through transcriptional repression of OsBUL1 [J].New Phytologist,2021,230(5):1953-1966. |
| 41 | SHI C L, YANG S H, CUI Y,et al.Oxidative burst causes loss of tapetal Ubisch body and male sterility in rice[J].New Phytologist,2024,244(1):10-15. |
| 42 | YANG R, SUN Y, ZHU X L,et al.The tuber-specific StbHLH93 gene regulates proplastid-to-amyloplast development during stolon swelling in potato[J].New Phytologist,2024,241(4):1676-1689. |
| 43 | LIU Y R, YAN J P, WANG K X,et al.MiR396-GRF module associates with switchgrass biomass yield and feedstock quality[J].Plant Biotechnology Journal,2021,19(8):1523-1536. |
| 44 | WERADUWAGE S M, CHEN J, ANOZIE F C,et al.The relationship between leaf area growth and biomass accumulation in Arabidopsis thaliana [J].Frontiers in Plant Science,2015,6:167. |
| 45 | WANG J N, ZHOU H J, ZHAO Y Q,et al.Characterization of poplar growth-regulating factors and analysis of their function in leaf size control[J].BMC Plant Biology,2020,20(1):509. |
| 46 | LAZZARA F E, RODRIGUEZ R E, PALATNIK J F.Molecular mechanisms regulating GROWTH-REGULATING FACTORS activity in plant growth,development,and environmental responses[J].Journal of Experimental Botany,2024,75(14):4360-4372. |
| 47 | WANG X Y, YU S, LI B X,et al.A microRNA396b-growth regulating factor module controls castor seed size by mediating auxin synthesis[J].Plant Physiology,2024,196(2):916-930. |
| 48 | LIU Z Y, ZHANG T Q, XU R T,et al. BpGRP1 acts downstream of BpmiR396c/BpGRF3 to confer salt tolerance in Betula platyphylla [J].Plant Biotechnology Journal,2024,22(1):131-147. |
| [1] | Xinyi YU, Huiyue JI, Pingping LU, Jiayu ZHOU, Hai LIAO. The Bioinformatic Analysis on the Plant Isopentenyl Pyrophosphate Isomerase [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2024, 44(5): 774-782. |
| [2] | Shanshan WANG, Rui WANG, Erqin FAN, Pengyue FU, Guanzheng QU, Nan WANG. Bioinformatics Analysis of CbuDELLAs Gene Family and Functional Analysis of CbuGRAS9 [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2024, 44(1): 139-151. |
| [3] | Zhanmin ZHENG, Yubing SHANG, Guangbo ZHOU, Di XIAO, Yi LIU, Xiangling YOU. Genetic Transformation and Function Analysis of PsnHB13 and PsnHB15 of Populus simonii × Populus nigra [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2023, 43(3): 340-350. |
| [4] | Senyao LIU, Fenglin JIA, Qing GUO, Gaofeng FAN, Boru ZHOU, Tingbo JIANG. Response Analysis of Transcription Factor PsnbHLH162 Gene in Populus simonii × P. nigra under Salt Stress and Low Temperature Stress [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2023, 43(2): 300-310. |
| [5] | Shixian LIAO, Yuting WANG, Liben DONG, Yongmei GU, Fenglin JIA, Tingbo JIANG, Boru ZHOU. Function Analysis of the Transcription Factor PsnbZIP1 of Populus simonii×P. nigra in Response to Salt Stress [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2023, 43(2): 288-299. |
| [6] | Denggao LI, Rui LIN, Qinghui MU, Na ZHOU, Yanru ZHANG, Wei BAI. Identification and Analysis of the Potato StCRKs Gene Family and Expression Patterns in Response to Stress Signals [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2022, 42(6): 1033-1043. |
| [7] | Huafeng CHEN, Longjun DAI, Mingyang LIU, Bingbing GUO, Hong YANG, Lifeng WANG. Stress Tolerance Functional Analysis of the High Expression Heat Shock Protein HbHSP90.4 Gene from the Latex of Hevea brasiliensis [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2022, 42(6): 1023-1032. |
| [8] | Anying HUANG, Dean XIA, Yang ZHANG, Dongchen NA, Qing YAN, Zhigang WEI. Cloning and Drought Tolerance Expression Analysis of PtrWRKY51 Gene in Populus trichocarpa [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2022, 42(6): 1005-1013. |
| [9] | Mingyang LIU, Huaxing XIAO, Lifeng WANG, Xiaoxu LIANG, Yu ZHANG, Meng WANG. Cloning and Functional Analysis of Heat Shock Protein HbHSP90.8-1 from Hevea brasiliensis Müll. Arg. [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2022, 42(5): 811-820. |
| [10] | He CHENG, Shuanghui TIAN, Yang ZHANG, Cong LIU, De’an XIA, Zhigang WEI. Genome-wide Identification and Expression Analysis of nsLTP Gene Family in Populus trichocarpa [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2022, 42(3): 412-423. |
| [11] | Qian Sun, Yuhang Wu, Yaxuan Zhang, Jingdan Cao, Jingjing Shi, Chao Wang. Bioinformatic Analysis and Expression Pattern of LTP Family Genes in Populus davidiana × P. alba var. pyramidalis [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2022, 42(2): 211-223. |
| [12] | Jiaming Zhao, Erqin Fan, Yi Liu, Zhi Wang, Junhui Wang, Guanzheng Qu. Cloning and Bioinformatics Analysis of CbuATX1,CbuATX1-like and CbuATX2 Genes from Catalpa bungei [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2022, 42(1): 47-61. |
| [13] | Shuang Ma, Boya Wang, Ying Cao, Shanglian Hu, Zhimin Gao. Identification and Expression Analysis of Expansin Genes in Moso Bamboo (Phyllostachys edulis) [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2022, 42(1): 29-38. |
| [14] | Yuning Yang, Hao Dong, Shiwei Dong, Nairui Wang, Yue Song, Hanguo Zhang, Shujuan Li. Cloning and Expression Analysis of Transcription Factor LobHLH34 from Larix olgensis [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2022, 42(1): 112-120. |
| [15] | Dong-Lin LÜ, Teng LI, Yi-Wen GUO, Jing JIANG, Hai-Jiao HUANG. Determination of Seed Vigor and Genetic Analysis of Foreign Genes in Different Transgenic Birch Hybrids [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2021, 41(4): 564-572. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||