Bulletin of Botanical Research ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (3): 460-470.doi: 10.7525/j.issn.1673-5102.2025.03.015
• Original Paper • Previous Articles
Yanyan PAN1, Xiaoguang LI2, Lijun LIU3, Hong LI1, Xin ZHONG1, Yifei ZHANG1( )
)
Received:2025-02-20
Online:2025-05-20
Published:2025-05-23
Contact:
Yifei ZHANG
E-mail:yifeii@hotmail.com
CLC Number:
Yanyan PAN, Xiaoguang LI, Lijun LIU, Hong LI, Xin ZHONG, Yifei ZHANG. Response of Pinus Koraiensis Growth and Rhizosphere Soil Enzyme Activity to Lepista nuda Inoculation[J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2025, 45(3): 460-470.
Table 1
Colonization rate and growth characteristics of Pinus koraiensis seedlings under different inoculation treatments
处理 Treatment | 苗高 Height of seedling/cm | 地径 Diameter at ground level/cm | 鲜质量 Fresh weight/g | 干质量 Dry weight/g | 干鲜质量比 Ratio of dry weight to fresh weight | 侵染率 Colonization rate/% | 根系活力 Root viability/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 16.41±1.35c | 4.71±0.37b | 4.14±0.72c | 1.95±0.31c | 0.47±0.05b | 4.38±0.78c | 44.56±4.76c |
| M1 | 18.91±1.11b | 5.64±0.20a | 4.84±0.63b | 2.43±0.21b | 0.51±0.05a | 60.13±5.04b | 62.11±3.71a |
| M2 | 19.44±1.27b | 5.74±0.14a | 5.29±0.35a | 2.64±0.36b | 0.50±0.05a | 67.50±9.21ab | 59.30±6.22a |
| M3 | 21.18±1.87a | 5.92±0.46a | 5.72±0.39a | 3.07±0.22a | 0.54±0.06a | 72.27±5.12a | 60.76±6.76a |
| M4 | 21.15±1.25a | 5.91±0.27a | 5.17±0.27a | 3.05±0.21a | 0.53±0.04a | 72.25±2.85a | 55.02±4.33b |
Table 2
Soil nutrient mass fraction under different inoculation treatments
处理 Treatment | 有机质 Soil organic matter/ (g·kg-1) | 碱解氮 Alkali-hydrolyzable nitrogen/ (mg·kg-1) | 全氮 Total nitrogen/ (g·kg-1) | 全磷 Total phosphorus/ (g·kg-1) | 速效磷 Available phosphorous/ (mg·kg-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 21.69±1.26c | 122.19±1.73b | 7.92±0.15b | 0.18±0.01b | 5.18±0.07b |
| M1 | 28.34±2.36b | 124.48±2.86b | 8.25±0.17b | 0.20±0.01b | 5.96±0.44b |
| M2 | 33.63±1.76a | 155.83±4.66a | 9.92±0.07a | 0.26±0.01a | 6.87±0.27a |
| M3 | 34.85±0.68a | 160.63±3.73a | 10.71±0.42a | 0.31±0.01a | 7.04±0.24a |
| M4 | 34.35±1.15a | 158.36±3.56a | 10.52±025a | 0.28±0.02a | 6.79±0.25a |
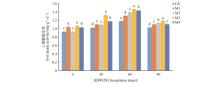
Fig.1
Urease activity in rhizosphere soil under different inoculation treatmentsCK. Control; M1. 50 g⋅plant-1; M2. 100 g⋅plant-1; M3. 150 g⋅plant-1; M4. 200 g⋅plant-1. Different lowercase letters indicated significant differences in soil urease activity between different treatments in the same inoculation time(P<0.05).
Fig.2
Sucrase activities in rhizosphere soil under different inoculation treatmentsCK. Control; M1. 50 g⋅plant-1; M2. 100 g⋅plant-1; M3. 150 g⋅plant-1; M4. 200 g⋅plant-1. Different lowercase letters indicated significant differences in soil sucrase activity between different treatments in the same inoculation time (P<0.05).
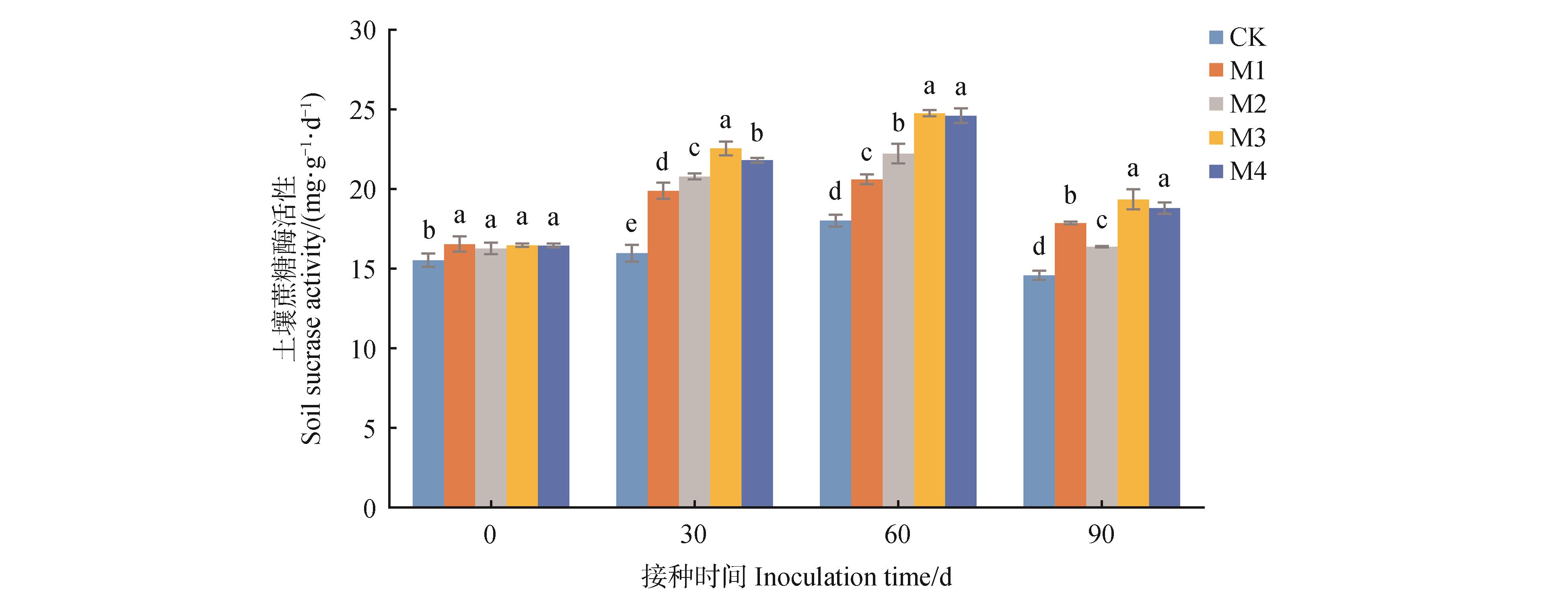
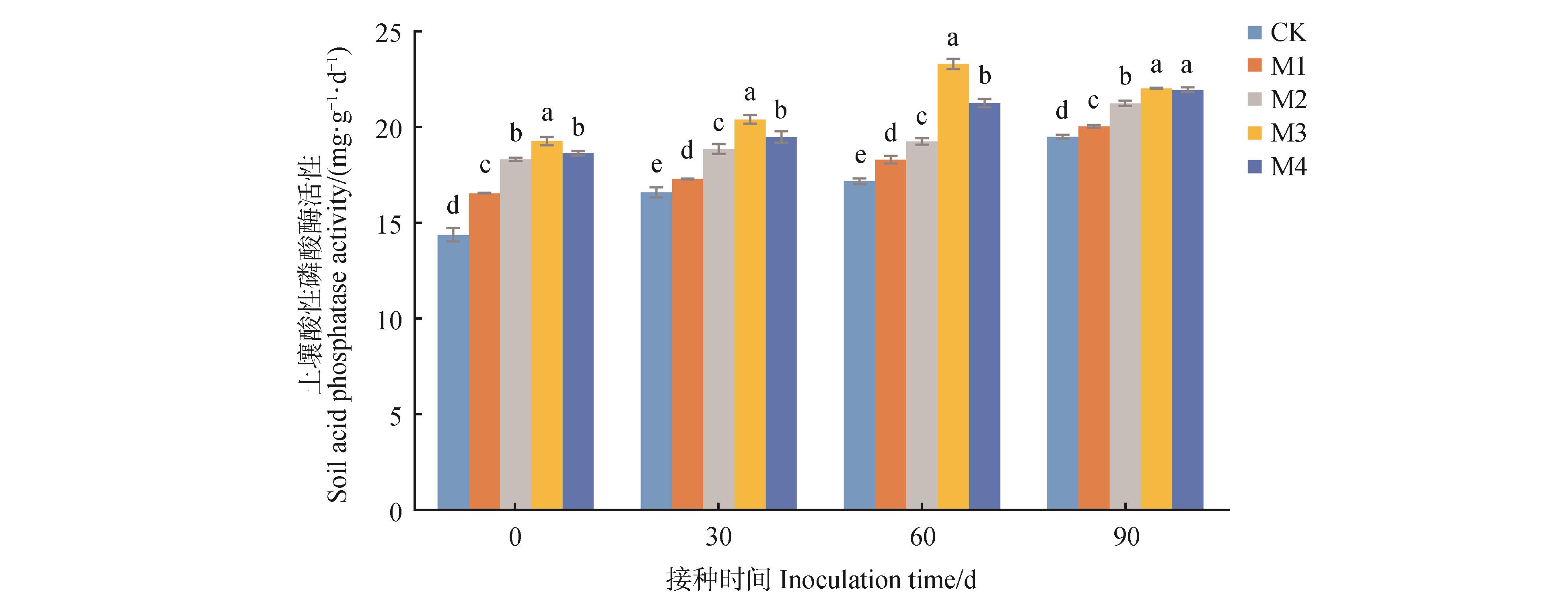
Fig.3
Acid phosphatase activity in rhizosphere soil under different inoculation treatmentsCK. Control; M1. 50 g⋅plant-1; M2. 100 g⋅plant-1; M3. 150 g⋅plant-1; M4. 200 g⋅plant-1. Different lowercase letters indicated significant differences in soil acid phosphatase activity between different treatments in the same inoculation time (P<0.05).
| 1 | 杨康,孙建茹,王妍,等.入侵植物与本地植物互作对丛枝菌根真菌AMF侵染率的影响[J].菌物学报,2019, 38(11):1938-1947. |
| YANG K, SUN J R, WANG Y,et al.Effects of invasive plants interacting with native plants on colonization of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi[J].Mycosystema,2019,38(11):1938-1947. | |
| 2 | TOJU H, SATO H, YAMAMOTO S,et al.Structural diversity across arbuscular mycorrhizal,ectomycorrhizal,and endophytic plant-fungus networks[J].BMC Plant Biology,2018,18(1):292. |
| 3 | GENRE A, LANFRANCO L, PEROTTO S,et al.Unique and common traits in mycorrhizal symbioses[J].Nature Reviews Microbiology,2020,18(11):649-660. |
| 4 | 林宇岚,王琳,楼玫娟,等.AM真菌与有机磷配施对油茶光合特性的影响[J].江西农业大学学报,2021,43(1):136-143. |
| LIN Y L, WANG L, LOU M J,et al.Effects of AM fungi combined with organic phosphorus on photosynthetic characteristics of Camellia oleifera [J].Acta Agriculturae Universitis Jiangxiensis,2021,43(1):136-143. | |
| 5 | 卫玲玲.丛枝菌根真菌和生物炭对不同盐碱地紫花苜蓿生长和土壤化学性质的影响[D].南京:南京农业大学,2020. |
| WEI L L.Effects of biochar and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi on alfalfa growth and soil chemical properties in different saline and alkaline land[D].Nanjing:Nanjing Agricultural University,2020. | |
| 6 | 苗志加,孟祥源,李书缘,等.丛枝菌根真菌修复重金属污染土壤及增强植物耐性研究进展[J].农业环境科学学报,2023,42(2):252-262. |
| MIAO Z J, MENG X Y, LI S Y,et al.Research progress on arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi(AMF) in remediation of heavy metal contaminated soil and enhancement of plant tolerance[J].Journal of Agro-Environment Science,2023,42(2):252-262. | |
| 7 | LIU G M, ZHANG X C, WANG X P,et al.Soil enzymes as indicators of saline soil fertility under various soil amendments[J].Agriculture,Ecosystems & Environment,2017,237:274-279. |
| 8 | 刘晴,徐阳,张妍,等.抚育间伐对辽东山区红松人工林土壤酶活性的影响[J].森林工程,2021,37(3):67-71. |
| LIU Q, XU Y, ZHANG Y,et al.Effects of thinning on soil enzyme activities of Pinus koraiensis plantation in Liaodong mountain area[J].Forest Engineering,2021,37(3):67-71. | |
| 9 | SINSABAUGH R L, FOLLSTAD SHAH J J.Ecoenzymatic stoichiometry and ecological theory[J].Annual Review of Ecology,Evolution,and Systematics,2012,43(1):313-343. |
| 10 | 王瑾,毕银丽,张延旭,等.接种丛枝菌根对矿区扰动土壤微生物群落及酶活性的影响[J].南方农业学报,2014,45(8):1417-1423. |
| WANG J, BI Y L, ZHANG Y X,et al.Effects of arbuscular mycorrhiza on soil microorganisms and enzyme activities in disturbed coal mine areas[J].Journal of Southern Agriculture,2014,45(8):1417-1423. | |
| 11 | 黄绍华,张扬,游欣,等.根系分泌物提高土壤磷有效性研究概述[J].林业科学研究,2024,37(4):193-203. |
| HUANG S H, ZHANG Y, YOU X,et al.Root exudates improving soil phosphorus availability:a review[J].Forest Research,2024,37(4):193-203. | |
| 12 | 张晓兵,李喜梅,向儒江,等.外生菌根菌对红松苗木生长的影响[J].林业科技,2009,34(3):30-32. |
| ZHANG X B, LI X M, XIANG R J,et al.Effect of ectomycorrhizal fungi on the growth of Pinus koraiensis [J].Forestry Science & Technology,2009,34(3):30-32. | |
| 13 | 冯乐,宋福强.外生菌根真菌与丝状真菌混合对红松凋落物降解效能的影响[J].生态科学,2011,30(3):315-320. |
| FENG L, SONG F Q.The impacts of combination of ectomycorrhizal fungi with filamentous fungi on decomposition of Korean-pine litterfall[J].Ecological Science,2011,30(3):315-320. | |
| 14 | 王淑清,徐丽华.东北主要用材树种外生菌根真菌资源调查研究[J].辽宁林业科技,2002(3):17-20. |
| WANG S Q, XU L H.Investigation of ectomycorrhizal fungal resources of major timber species in Northeast China[J].Liaoning Forestry Science and Technology,2002(3):17-20. | |
| 15 | 刘远开.红松外生菌根真菌与凋落物分解相关性研 究[D].哈尔滨:黑龙江大学,2010. |
| LIU Y K.Study on the correlation between ectomycorrhizal fungi and litter decomposition in Pinus koraiensis [D].Harbin:Heilongjiang University,2010. | |
| 16 | 庞丽杰,王文革,宋福强.3株外生菌根真菌对红松苗木的接种效应[J].防护林科技,2015(11):41-43. |
| PANG L J, WANG W G, SONG F Q.Inoculation effects of three ectomycorrhizal fungi on Pinus koraiensis seedlings[J].Protection Forest Science and Technology, 2015(11):41-43. | |
| 17 | 潘艳艳,潘丽铭,孙艳华,等.紫丁香蘑研究进展及前景展望[J].吉林林业科技,2024,53(3):40-43. |
| PAN Y Y, PAN L M, SUN Y H,et al.Research progress of Lepista nuda and its application prospect[J].Journal of Jilin Forestry Science and Technology,2024,53(3):40-43. | |
| 18 | 弓明饮,陈应龙,仲崇禄.菌根研究及应用[M].北京:中国林业出版社,1997. |
| GONG M Y, CHEN Y L, ZHONG C L.Mycorrhizal research and application[M].Beijing:China Forestry Publishing House,1997. | |
| 19 | 潘名好,朱庆征,巩闪闪,等.华北石质山区不同土地利用方式对土壤生物理化性质的影响[J].中国水土保持科学(中英文),2021,19(4):24-33. |
| PAN M H, ZHU Q Z, GONG S S,et al.Effects of different land-use types on soil biological and physicochemical properties[J].Science of Soil and Water Conservation,2021,19(4):24-33. | |
| 20 | 关松荫.土壤酶及其研究法[M].北京:农业出版社,1986:115-131. |
| GUAN S Y.Soil enzymes and research methods[M].Beijing:Agricultural Press,1986:115-131. | |
| 21 | GENG Y Q, WANG D M, YANG W B.Effects of different inundation periods on soil enzyme activity in riparian zones in Lijiang[J].Catena,2017,149:19-27. |
| 22 | 刘润进,陈应龙.菌根学[M].北京:科学出版社,2007:302-308. |
| LIU R J, CHEN Y L.Mycorrhizology[M].Beijing:Science Press,2007:302-308. | |
| 23 | 李婷婷.矿区复垦土壤沃土微生物菌剂的制备及应用研究[D].太原:山西农业大学,2021. |
| LI T T.Study on preparation and application of microbial agents in reclaimed soil of mining areas[D].Taiyuan:Shanxi Agricultural University,2021. | |
| 24 | ZOU Y N, SRIVASTAVA A K, NI Q D,et al.Disruption of mycorrhizal extraradical mycelium and changes in leaf water status and soil aggregate stability in rootbox-grown trifoliate orange[J].Frontiers in Microbiology,2015,6:203. |
| 25 | OLIVEIRA R S, FRANCO A R, CASTRO P M L.Combined use of Pinus pinaster plus and inoculation with selected ectomycorrhizal fungi as an ecotechnology to improve plant performance[J].Ecological Engineering,2012,43(7):95-103. |
| 26 | SANCHEZ-ZABALA J, MAJADA J, MARTÍN-RODRIGUES N,et al.Physiological aspects underlying the improved outplanting performance of Pinus pinaster Ait.seedlings associated with ectomycorrhizal inoculation[J].Mycorrhiza,2013,23:627-640. |
| 27 | 赵敏.红花尔基樟子松林下外生菌根真菌资源调查及优良菌树组合的筛选[D].呼和浩特:内蒙古农业大学,2017. |
| ZHAO M.Resources investigation of ectomycorrhizal fungal in Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica and selection of the optimum combination of ECM fungi with P.sylvestris var.mongolica in Honghuaerji,Da Hinggan Mountains[D].Hohhot:Inner Mongolia Agricultural University,2017. | |
| 28 | 毕银丽,孙江涛, ZHAKYPBEK Y,等.不同施磷水平下接种菌根玉米营养状况及光谱特征分析[J].煤炭学报,2016,41(5):1227-1235. |
| BI Y L, SUN J T, ZHAKYPBEK Y,et al.Hyperspectral characterization and nutrition condition of maize inoculated with arbuscular mycorrhiza in different phosphorus levels[J].Journal of China Coal Society,2016,41(5):1227-1235. | |
| 29 | 王幼珊,张淑彬,张美庆.中国丛枝菌根真菌资源与种质资源[M].北京:中国农业出版社,2012:40. |
| WANG Y S, ZHANG S B, ZHANG M Q.Resources and germplasm resources of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi in China[M].Beijing:China Agricultural Press,2012:40. | |
| 30 | 刘欢.不同丛枝菌根真菌对四种植物生长特性影响[D].兰州:甘肃农业大学,2016. |
| LIU H.Effect of various arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi on plant growth characteristics[D].Lanzhou:Gansu Agricultural University,2016. | |
| 31 | 李晴,段文艳,李鑫,等.丛枝菌根真菌对元宝枫生长及其根系形态的影响[J].西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版),2024,52(1):79-86. |
| LI Q, DUAN W Y, LI X,et al.Effect of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi on growth and root morphology of Acer truncatum [J].Journal of Northwest A&F University (Natural Science Edition),2024,52(1):79-86. | |
| 32 | 王艺,丁贵杰.外生菌根对马尾松幼苗生长的影响[J].中南林业科技大学学报,2011,31(4):74-78. |
| WANG Y, DING G J.Effects of exogenous mycorrhiza on growth of Pinus massoniana seedlings[J].Journal of Central South University of Forestry & Technology,2011, 31(4):74-78. | |
| 33 | KING J S, THOMAS R B, STRAIN B R.Morphology and tissue quality of seedling root systems of Pinus taeda and Pinus ponderosa as affected by varying CO2,temperature,and nitrogen[J].Plant and Soil,1997,195(1):107-119. |
| 34 | 李少朋,毕银丽,陈昢圳,等.外源钙与丛枝菌根真菌协同对玉米生长的影响与土壤改良效应[J].农业工程学报,2013,29(1):109-116. |
| LI S P, BI Y L, CHEN P Z,et al.Effects of AMF cooperating with exogenous calcium on maize growth and soil improvement[J].Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering,2013,29(1):109-116. | |
| 35 | 张晓曦,胡嘉伟,刘凯旋,等.黄土丘陵区刺槐人工林林龄增加土壤微环境变化对凋落物分解的影响[J].生态学报,2024,44(7):2931-2945. |
| ZHANG X X, HU J W, LIU K X,et al.Effects of the alterations in soil micro-environment with increasing stand age of Robinia pseudocacia plantation on the litter decomposition in the Loess Hilly Region[J].Acta Ecologica Sinica,2024,44(7):2931-2945. | |
| 36 | 张辉,李维炯,倪永珍,等.生物有机无机复合肥效应的初步研究[J].农业环境保护,2002,21(4):352-356. |
| ZHANG H, LI W J, NI Y Z,et al.Preliminary studies on efficiency of biological-organic-inorganic compound fertilizer[J].Agro-Environmental Protection,2002,21(4),352-356. | |
| 37 | 孙文.典型城乡生境外生菌根真菌多样性及2种EMFs对柳树耐盐性的作用研究[D].济南:济南大学,2022. |
| SUN W.Diversity of ectomycorrhizal fungi in typical urban and rural habitats and the role of two EMFs in the salt tolerance of willows[D].Jinan:University of Jinan,2022. | |
| 38 | SUBHASHINI D V.Effect of NPK fertilizers and co-inoculation with phosphate-solubilizing arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus and potassium-mobilizing bacteria on growth,yield,nutrient acquisition,and quality of tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum L.)[J].Communications in Soil Science & Plant Analysis,2016,47(3):328-337. |
| 39 | 闫妮,桑毅振,王明钦,等.生物炭和丛枝菌根真菌对番茄幼苗生长及土壤性质的影响[J].农业开发与装备,2023(12):137-140. |
| YAN N, SANG Y Z, WANG M Q,et al.Effects of biochar and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi on tomato seedling growth and soil properties[J].Agricultural Development & Equipments,2023(12):137-140. | |
| 40 | 解媛媛,谷洁,高华,等.微生物菌剂酶制剂化肥不同配比对秸秆还田后土壤酶活性的影响[J].水土保持研究,2010,17(2):233-238. |
| XIE Y Y, GU J, GAO H,et al.Dynamic changes of soil enzyme activities in microorganism inoculants,enzymes and chemical fertilizers in different proportions after straw returning soil[J].Research of Soil and Water Conservation,2010,17(2):233-238. | |
| 41 | 罗晓蔓,丁贵杰,翟帅帅,等.褐环乳牛肝菌对马尾松幼苗根际土壤微环境的影响[J].中南林业科技大学学报,2016,36(10):60-64. |
| LUO X M, DING G J, ZHAI S S,et al.Effects of Suillus luteus on soil microenvironment in rhizosphere of Pinus massoniana [J].Journal of Central South University of Forestry & Technology,2016,36(10):60-64. | |
| 42 | 李敏,赵熙州,王好运,等.干旱胁迫及外生菌根菌对马尾松幼苗根系形态及分泌物的影响[J].林业科学,2022,58(7):63-72. |
| LI M, ZHAO X Z, WANG H Y,et al.Effects of drought stress and ectomycorrhizal fungi on the root morphology and exudates of Pinus massoniana seedlings[J].Scientia Silvae Sinicae,2022,58(7):63-72. | |
| 43 | 李艳,吴强盛.菌根真菌对不同基因型柑橘根际有效磷含量和磷酸酶活性的影响[J].江苏农业科学,2014,42(6):186-188. |
| LI Y, WU Q S.Effects of mycorrhizal fungi on rhizosphere available phosphorus content and phosphatase activity of different genotypes of citrus[J].Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences,2014,42(6):186-188. | |
| 44 | 苏友波,林春,张福锁,等.不同AM菌根菌分泌的磷酸酶对根际土壤有机磷的影响[J].土壤,2003,35(4):334-338. |
| SU Y B, LIN C, ZHANG F S,et al.Effects of arbuscular mycorrhiza fungi on phosphatase activities and soil organic phosphate content in clover rhizosphere [J].Soils,2003,35(4):334-338. | |
| 45 | YIN D C, DENG X, CHET I,et al.Physiological responses of Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica seedlings to the interaction between Suillus luteus and Trichoderma virens [J].Current Microbiology,2014,69:334-342. |
| 46 | 刘玉槐,魏晓梦,魏亮,等.水稻根际和非根际土磷酸酶活性对碳、磷添加的响应[J].中国农业科学,2018,51(9):1653-1663. |
| LIU Y H, WEI X M, WEI L,et al.Responses of extracellular enzymes to carbon and phosphorus additions in rice rhizosphere and bulk soil[J].Scientia Agricultura Sinica,2018,51(9):1653-1663. | |
| 47 | MEEDS J A, KRANABETTER J M, ZIGG I,et al.Phosphorus deficiencies invoke optimal allocation of exoenzymes by ectomycorrhizas[J].The ISME Journal,2021,15(5):1478-1489. |
| 48 | CHENG X Q, KANG F F, HAN H R,et al.Effect of thinning on partitioned soil respiration in a young Pinus tabulaeformis plantation during growing season[J].Agricultural and Forest Meteorology,2015,214-215:473-482. |
| 49 | 谷文超,张杰,周浓,等.不同丛枝菌根真菌组合与接种时期对滇重楼幼苗根际土壤理化性质与微生物数量的影响[J].中国实验方剂学杂志,2020,26(22):116-130. |
| GU W C, ZHANG J, ZHOU N,et al.Effect of different arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi combinations and inoculation periods on rhizosphere soil physicochemical properties and microbial quantity of Paris polyphylla var.yunnanensis seedlings[J].Chinese Journal of Experimental Traditional Medical Formulae,2020,26(22):116-130. | |
| 50 | 贾冰冰.AM真菌提高牧草在重金属污染盐碱化土壤中耐受性的作用机制[D].呼和浩特:内蒙古大学,2021. |
| JIA B B.The mechanism of AM fungi improving tolerance of grasses in heavy metal contaminated saline soil[D].Hohhot:Inner Mongolia University,2021. | |
| 51 | 尹大川,邓勋,宋小双,等.Cd胁迫下外生菌根菌对樟子松生理指标和根际土壤酶的影响[J].生态学杂志,2017,36(11):3072-3078. |
| YIN D C, DENG X, SONG X S,et al.Effects of ectomycorrhizal fungi on physiological indexes of Pinus sylvestris var.mongolica seedlings and soil enzyme activities under cadmium stress[J].Chinese Journal of Ecology,2017,36(11):3072-3078. | |
| 52 | 陈朝.长白山阔叶红松林细根及菌根真菌菌丝对氮、水交互的响应[D].沈阳:沈阳农业大学,2019. |
| Chen C.Effects of nitrogen-water interaction on fine roots and mycorrhizal fungal mycelium in a mixed Pinus koraiensis forest in Changbai Mountains,Northeastern China[D].Shenyang:Shenyang Agricultural University,2019. | |
| 53 | 李宽莹,王泽林,徐兴有,等.不同施肥处理对日光温室内土壤微生物数量与酶活性的影响[J].西北林学院学报,2019,34 (2):56-61. |
| LI K Y, WANG Z L, XU X Y,et al.Effects of fertilization pattern on soil microorganism quantity and soil enzyme activity under the greenhouse grape-cultivating system[J].Journal of Northwest Forestry University,2019,34(2):56-61. | |
| 54 | 徐小冲,王新杰,卢妮妮,等.不同林龄杉木人工林根际土添加对其幼苗菌根侵染及生长的影响[J].北京林业大学学报,2020,42(12):74-82. |
| XU X C, WANG X J, LU N N,et al.Effects of rhizosphere soil addition of different aged Chinese fir plantation on the mycorrhizal colonization and growth of its seedlings[J].Journal of Beijing Forestry University,2020,42(12):74-82. | |
| 55 | 李健平.菌根化红松幼苗对干旱胁迫的响应研究[D].长春:吉林农业大学,2023. |
| LI J P.Study on the response of mycorrhizal Pinus koraiensis seedlings to drought stress[D].Changchun:Jilin Agricultural University,2023. |
| [1] | Wenhui GUO, Yue WANG, Lin WU, Jianfei YANG, Ling YANG, Peng ZHANG, Haibo WU, Hailong SHEN. Effects of Exogenous Flavonoids on Embryogenic Callus Proliferation and Somatic Embryogenesis of Korean Pine [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2025, 45(1): 130-138. |
| [2] | Yitong LUAN, Niansen LI, Lujing QIAO, Cunyong JU, Tijiu CAI, Peili SUN. Niches, Interspecific Associations and Community Stability of Dominant Tree Species of Piceakoraiensis-Abies nephrolepis-Pinus koraiensis Forest [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2024, 44(5): 753-762. |
| [3] | Xuelai WANG, Xiaoting LIU, Liran WANG, Shitong LI, Taijin ZHANG, Jiafeng ZHANG, Jinghua XU, Guanzheng QU, Xiyang ZHAO. Coupling Evaluation of Growth and Wood Properties of Pinus koraiensis Half-sib Families [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2024, 44(4): 554-564. |
| [4] | Lijuan LUO, Qingxiao YIN, Wei SUN, Xi ZAN, Qingmao SHI, Jing ZHANG, Yamei CHEN, Xiao XU. Soil Enzyme Activities and Stoichiometric Characteristics of Different Plant Communities under Natural Fagus Forest in Micang Mountain Nature Reserve, Sichuan [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2024, 44(3): 470-480. |
| [5] | Fazhi FANG, Huiying GUI, Zhaojia LI, Xiaofeng ZHANG. Physiological Adaptation of Six Mangrove Seedlings to Different Salinity [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2023, 43(6): 881-889. |
| [6] | Jikang XU, Yanhong HE, Tingyan LIU, Longfei HAO, Shengxi ZHANG, Zhaoyi LI. Characteristics of Rhizosphere Soil Microecological Environment of Different Ecological Restoration Vegetation in Arsenic Sandstone Areas [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2023, 43(4): 531-539. |
| [7] | Yuhui REN, Shuai NIE, Chunxue PENG, Ling YANG, Hailong SHEN. Effects of Hormone Combinations, Carbon Source Type and Proliferation Cycle on Embryogenic Callus Proliferation of Pinus koraiensis [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2022, 42(4): 704-712. |
| [8] | Zhi-Gang WEI, De-An XIA, Rui-Qi Wang, Yang ZHANG, Ying-Ying Liu, Ruo-Lin LI, Chuan-Ping YANG. Provenance Test of Pinus koraiensis in Different Types of Natural Secondary Forests in Xiaoxing’an Mountains [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2021, 41(5): 807-815. |
| [9] | Fang WANG, Zhi-Min LU, Jun WANG, Shi-Kai ZHANG, Yu-Xi LI, Shao-Chen LI, Jian-Qiu ZHANG, Yu-Chun YANG. Photosynthetic and Stomatal Characteristics of Pinus koraiensis and P.sibirica under Low Temperature Stress [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2021, 41(2): 205-212. |
| [10] | ZHAO Chun-Jian, LI Yu-Zheng, GUAN Jia-Jing, SU Wei-Ran, TIAN Yao, WANG Ting-Ting, LI Shen, LI Chun-Ying. Effect of Interplanting Taxus cuspidata with Ficus carica on Growth of Two Plants and Activities of Soil Enzymes [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2020, 40(5): 679-685. |
| [11] | LI Xiang, FAN Zuo-Yi, WANG Jing-Yuan, WANG Qi, LI Xi-Peng, WANG De-Qiu, KONG Ling-Yuan, CAO Sen-Lin, MENG Qing-Gang, ZHAO Xi-Yang. Codon Usage Bias of Chalcone Synthase Gene CHS in Pinus koraiensis [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2020, 40(3): 447-457. |
| [12] | ZHOU Xue-Yan, GAO Hai-Yan, LI Zhao-Min, ZHAO Yin-Kun, GE Li-Li, HOU Qing-Wen, DING Wen-Ya, ZHAO Xi-Yang. Evaluating Parents of Pinus koraiensis Seeds Orchard with Growth and Fruiting [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2020, 40(3): 376-385. |
| [13] | LIU Ting-Yan, HAO Long-Fei, WANG Qing-Cheng, BAI Shu-Lan. Effects of Different Planting Densities on Cultivating Quality of Padus maackii Seedlings [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2019, 39(6): 863-868. |
| [14] | MA Peng-Yu, ZHANG Hong-Guang, ZAN Peng, GU Wei-Ping, WEN Lu-Ning, ZHANG Zi-Jia, WENG Hai-Long, SUN Tao, MAO Zi-Jun. Effects of Long-term Nitrogen Addition on Soil Enzymes in Larix gmelinii Plantation in Northeast China [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2019, 39(4): 598-603. |
| [15] | ZHANG Qin-Hui, WANG Hong-Wu, JIANG Guo-Yun, SHEN Guang, WANG Lian-Kui, LI Yan-Long, WANG Lei, WANG Li-Xiang, LI Yue-Ji, LI Rui, ZHAO Xi-Yang. Variation Analysis and Selection of Pinus koraiensis Half-sib Families [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2019, 39(4): 557-567. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||