Bulletin of Botanical Research ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (5): 731-744.doi: 10.7525/j.issn.1673-5102.2025.05.008
• Original Paper • Previous Articles Next Articles
Siyao WU, Xinyu WANG, Ziteng SUN, Zhimin ZHENG( )
)
Received:2025-02-19
Online:2025-09-20
Published:2025-09-28
Contact:
Zhimin ZHENG
E-mail:zmzheng@nefu.edu.cn
CLC Number:
Siyao WU, Xinyu WANG, Ziteng SUN, Zhimin ZHENG. Bioinformatics Analysis of the BpDMPs Gene Family in Betula platyphylla and Exploration of the Function of BpDMP7 gene[J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2025, 45(5): 731-744.
Table 1
Analysis of the physicochemical properties of the proteins encoded by BpDMPs gene family in birch
基因名称 Gene name | 基因ID Gene ID | 所在染色体 Chromosome | 基因位置 Gene location | 氨基酸数目 Number of amino acids | 分子质量 Molecular mass/Da | 等电点 Isoelectric point | 总平均亲水性 Total average hydrophilicity | 亚细胞定位 Subcellular location |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BpDMP1 | BPChr08G17023 | 8 | 38650991-38651641 | 216 | 23 342.28 | 6.50 | 0.292 | CP |
| BpDMP2 | BPChr07G18894 | 7 | 22585554-22586180 | 208 | 22 727.21 | 5.61 | 0.279 | CM |
| BpDMP3 | BPChr11G17728 | 11 | 3219693-3220379 | 228 | 24 285.32 | 9.18 | 0.347 | CM |
| BpDMP4 | BPChr11G13419 | 11 | 25274063-25274683 | 206 | 22 923.87 | 9.03 | 0.264 | CP,Mito,Nucleus |
| BpDMP5 | BPChr08G05126 | 8 | 10638147-10638761 | 204 | 21 735.80 | 8.54 | 0.093 | CM,CW |
| BpDMP6 | BPChr01G23597 | 1 | 6378106-6378753 | 215 | 24 248.03 | 8.15 | 0.191 | CM |
| BpDMP7 | BPChr06G30721 | 6 | 19021326-19021925 | 199 | 21 589.71 | 5.84 | 0.232 | CM |
| BpDMP8 | BPChr08G05134 | 8 | 10612115-10612687 | 190 | 20 441.58 | 8.66 | 0.357 | CM |
| BpDMP9 | BPChr12G26817 | 12 | 3237953-3238363 | 156 | 17 233.41 | 9.13 | 0.160 | CP |
| BpDMP10 | BPChr06G30778 | 6 | 19025688-19026779 | 363 | 39 524.96 | 5.56 | -0.182 | CM |
| BpDMP11 | BPChr10G03440 | 10 | 10633218-10633790 | 190 | 20 246.45 | 8.79 | 0.297 | CM |
| BpDMP12 | BPChr10G03567 | 10 | 10667452-10668458 | 198 | 21 427.86 | 9.08 | 0.360 | CM |
| BpDMP13 | BPChr10G03436 | 10 | 10671858-10672481 | 207 | 22 453.96 | 6.25 | 0.561 | CM |
| BpDMP14 | BPChr10G03476 | 10 | 10661594-10661917 | 107 | 11 381.06 | 9.64 | -0.040 | CM |
Table 2
Gene editing plant information statistics
载体名称 Vector name | 外植体数量 Number of explants | 阳性植株数量 Number of positive plants | 转化效率 Transformation efficiency/% | 基因编辑数量 (Indel或有意义突变) Number of gene edits (Indel or significant mutation) | 基因编辑效率 (Indel或有意义突变) Gene editing efficiency (Indel or significant mutation)/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 合计 | 175 | 131 | 74.06 | 4 | 3.05 |
| pSC1-CRISPR-BpU6-2-sgRNA1 | 76 | 56 | 73.68 | 2 | 3.57 |
| pSC1-CRISPR-BpU6-2-sgRNA2 | 66 | 52 | 78.79 | 2 | 3.85 |
| pSC1-CRISPR-BpU6-2-sgRNA3 | 33 | 23 | 69.70 | — | — |

Fig.1
Bioinformatics analysis of the BpDMPs gene family in birchBp. Birch; Sl. Tomato; St. Potato; Bn. Edible rape; Mt. Medicago truncatula; Gh. Cotton; Nt. Tobacco; Gm. Soybean; Cs. Cucumber; Cl. Watermelon; Zm. Corn; At. Arabidopsis; Pp. Black cottonwood. The red box represented the conservative area. A. DMP phylogenetic trees of birch, tomato, potato,edible rape, Medicago truncatula, cotton, tobacco, soybean, cucumber, watermelon, corn, Arabidopsis and black cottonwood; B. Conservative domain analysis of BpDMPs gene family in birch; C. Conservative motif (left) and gene structure (right) analysis of the BpDMPs gene family in birch; D. Analysis of cis-acting elements in the promoter of the BpDMPs gene in birch.
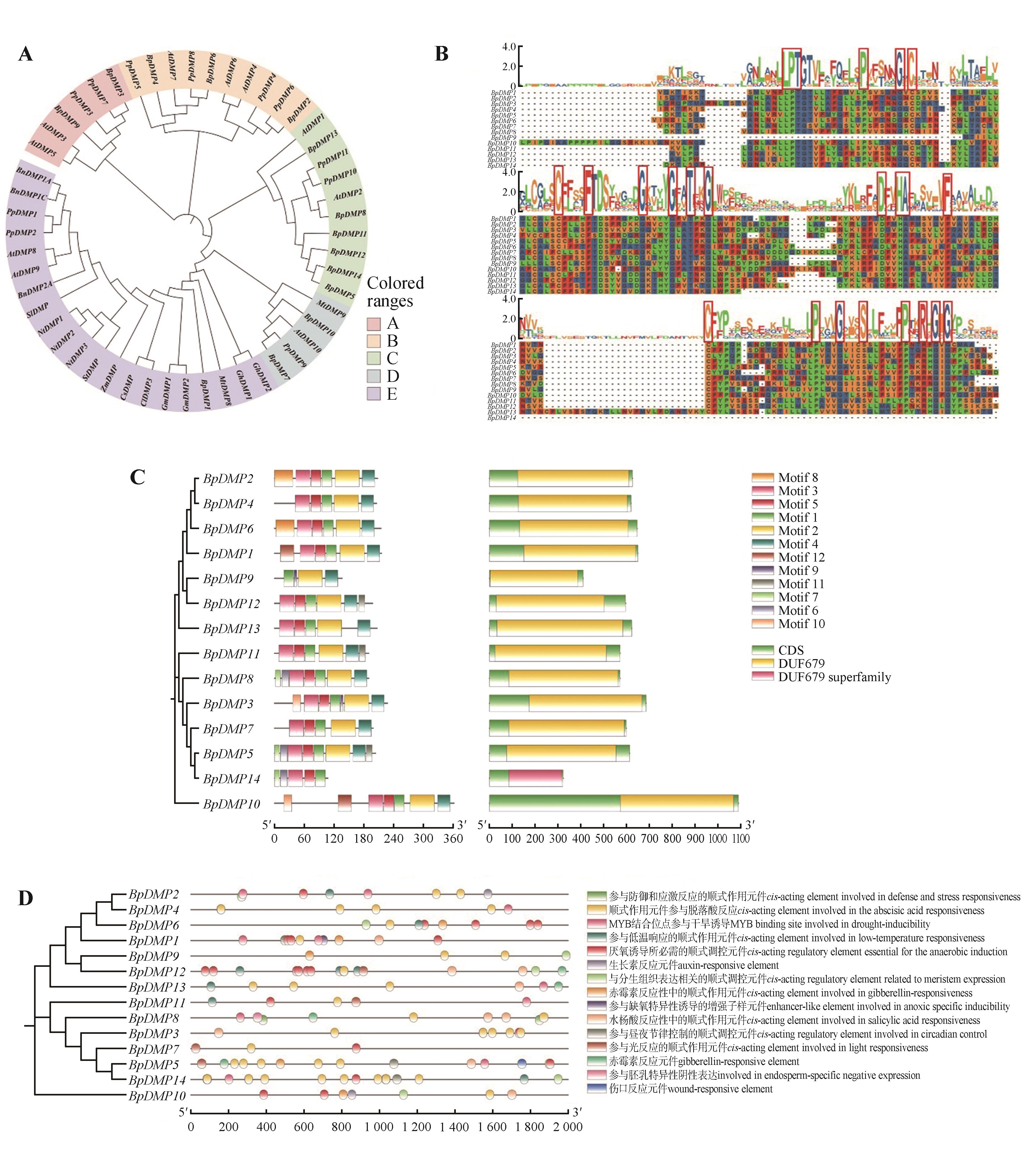
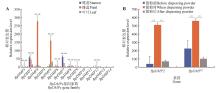
Fig.2
Analysis of tissue expression of BpDMPs gene family in birchA. Relative expression level of BpDMPs gene family in different tissues; B. Expression pattern of BpDMP2, BpDMP7 gene in stamens of birch. The significance of Fig.2A was obtained by Student’s t-test for each gene of the stamens, pistils, and leaves; the significance of Fig.2B was obtained by Student’s t-test for each gene before dispersing powder, dispersing powder and after dispersing powder (***. P<0.001).
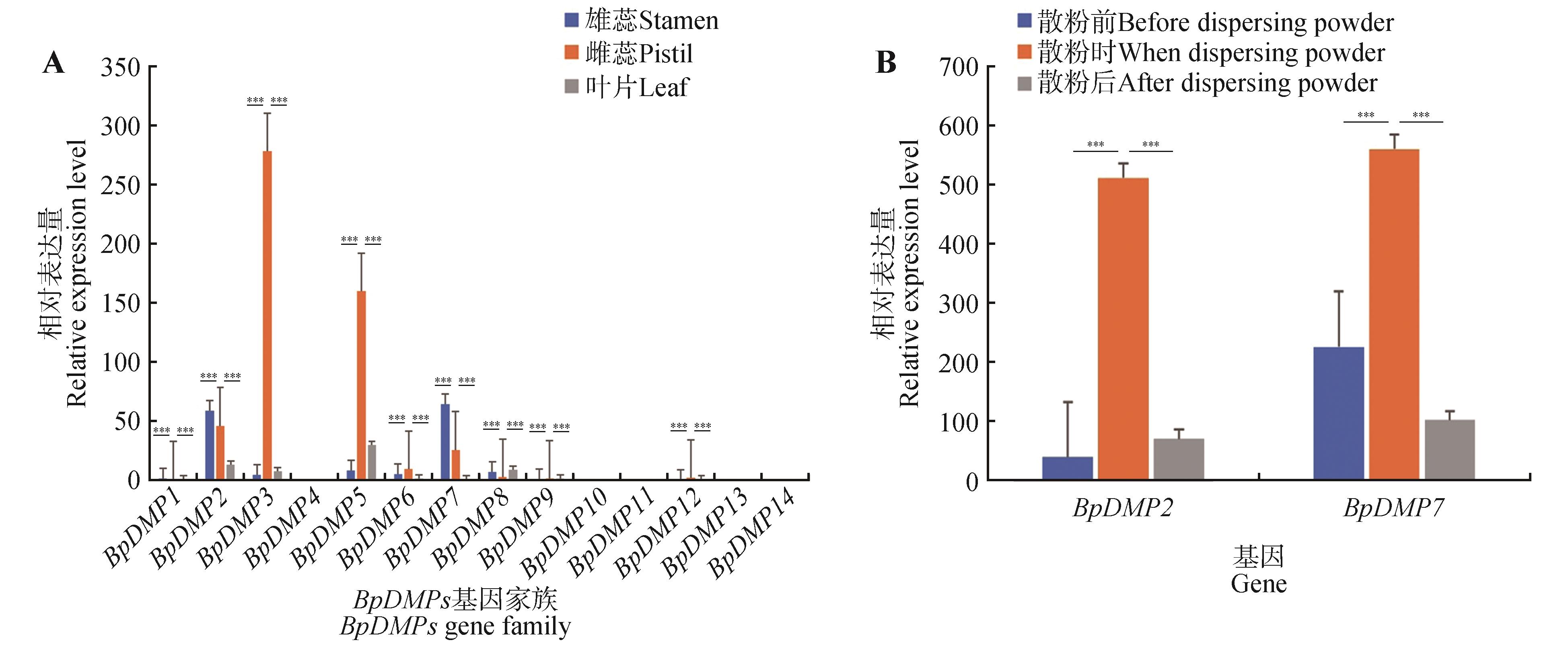
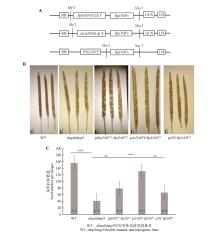
Fig.3
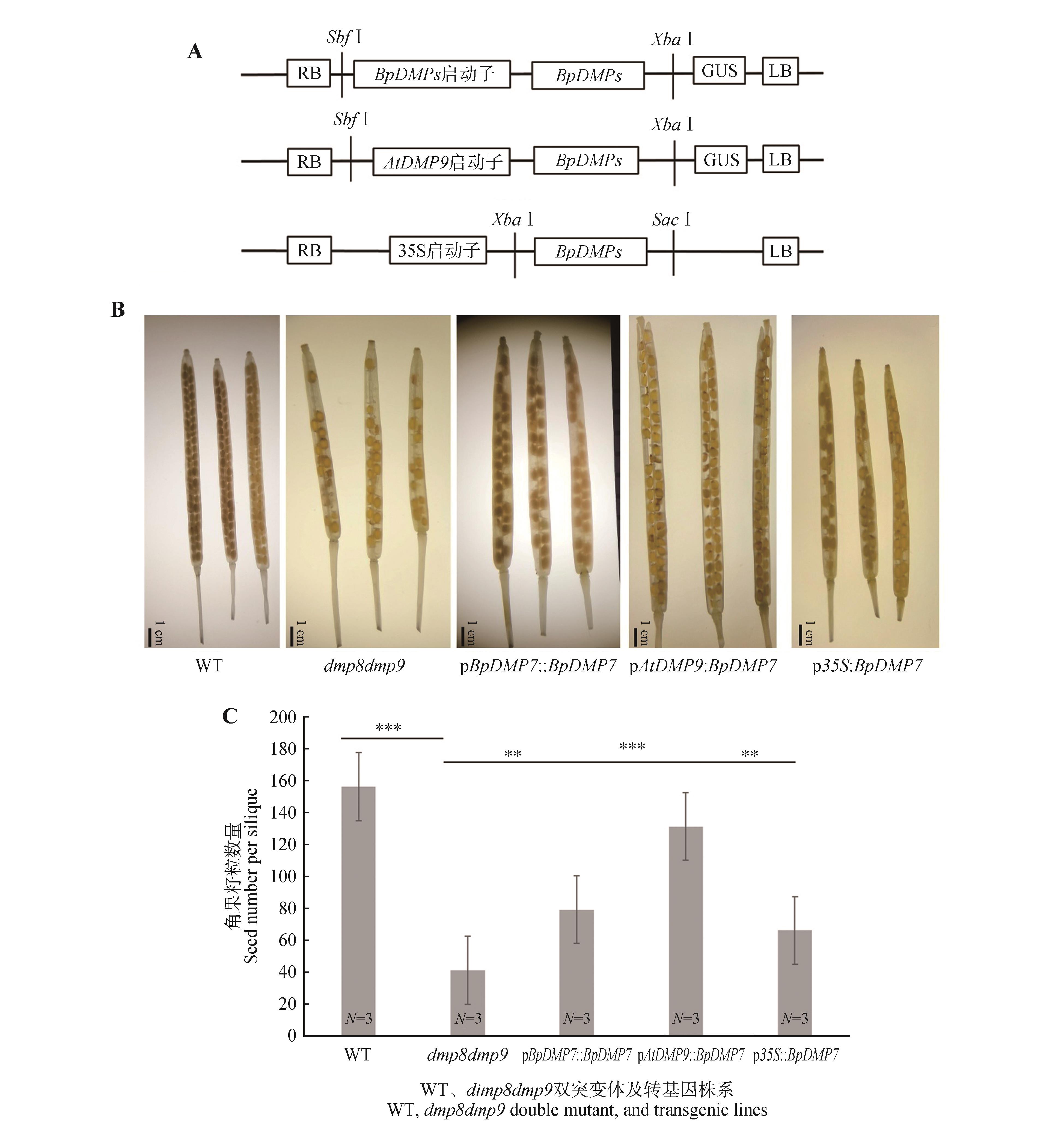
BpDMP7 genes complement dmp8dmp9 phenotypes in ArabidopsisA. The BpDMP7 gene complementation constructs; B. Images of siliques from the dmp8dmp9 mutant and the different BpDMP7 genes complementation lines in the dmp8dmp9 background; C. Quantification of seed number per silique in the dmp8dmp9 mutant and the BpDMP7 genes corresponding complementation lines. WT represented the wild-type strain, dmp8dmp9 represented the double mutant of ArabidopsisDMP gene, pBpDMP7::BpDMP7, pAtDMP9::BpDMP7, p35s::BpDMP7 represented the three complementation lines, respectively. The error line represented the standard error of three biological replicates. The significance was obtained through Student’s t-test between WT and dmp8dmp9, between dmp8dmp9 and pBpDMP7::BpDMP7, between dmp8dmp9 and pAtDMP9::BpDMP7, and between dmp8dmp9 and p35s::BpDMP7, respectively (**.P<0.01, **.P<0.001). N represented the number of biological replicates.
| [1] | CHANG M T, COE E H. Doubled haploids[M]//KRIZ A L,LARKINS B A.Molecular genetic approaches to maize improvement.Heidelberg: Springer Berlin Heidelberg,2009:127-142. |
| [2] | KALINOWSKA K, CHAMAS S, UNKEL K,et al.State-of-the-art and novel developments of in vivo haploid technologies[J].Theoretical and Applied Genetics,2019,132:593-605. |
| [3] | DWIVEDI S L, BRITT A B, TRIPATHI L,et al.Haploids:constraints and opportunities in plant breeding[J].Biotechnology Advances,2015,33(6):812-829. |
| [4] | GUHA S, MAHESHWARI S C. In vitro production of embryos from anthers of Datura [J].Nature,1964,204:497. |
| [5] | DAVEY M R.Advances in haploid production in higher plants[J].Annals of Botany,2009,104(7):10. |
| [6] | MALUSZYNSKI M, KASHA K J, FORSTER B P,et al.Doubled haploid production in crop plants:a manual[M].New York:Springer Dordrecht,2003:309-335. |
| [7] | BAJAJ Y P S. In vitro production of haploids and their use in cell genetics and plant breeding[M]//BAJAJ Y P S.Haploids in crop improvement I:from fundamentals to quantum computing.New York:Springer Berlin Heidelberg,1990:3-30. |
| [8] | MOHAN JAIN S, SOPORY S K, VEILLEUX R E. In vitro haploid production in higher plants[M].Dordrecht:Springer Dordrecht,1996. |
| [9] | JACQUIER N M A, GILLES L M, PYOTT D E,et al.Puzzling out plant reproduction by haploid induction for innovations in plant breeding[J].Nature Plants,2020,6:610-619. |
| [10] | 王敬驹,朱至清,孙敬三.杨树花粉植株的诱导[J].植物学报,1975(1):56-59. |
| WANG J J, ZHU Z Q, SUN J S.The induction of Populus pollen-plants[J].Journal of Integrative Plant Biology,1975(1):56-59. | |
| [11] | DEUTSCH F, KUMLEHN J, ZIEGENHAGEN B,et al.Stable haploid poplar callus lines from immature pollen culture[J].Physiologia Plantarum,2004,120(4):613-622. |
| [12] | LI Y, LI H, CHEN Z,et al.Haploid plants from anther cultures of poplar(Populus×beijingensis)[J].Plant Cell,Tissue and Organ Culture,2013,114:39-48. |
| [13] | YANG J L, LI K, LI C Y,et al. In vitro anther culture and Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of the AP1 gene from Salix integra Linn.in haploid poplar(Populus simonii×P.nigra)[J].Journal of Forestry Research,2017,29:321-330. |
| [14] | LIU B, WANG S, TAO X Y,et al.Molecular karyotyping on Populus simonii × P.nigra and the derived doubled haploid[J].International Journal of Molecular Sciences,2021,22(21):11424. |
| [15] | GHARYAL P K, RASHID A, MAHESHWARI S C.Production of haploid plantlets in anther cultures of Albizzia lebbeck L.[J].Plant Cell Reports,1983,2:308-309. |
| [16] | SERAN T H, HIRIMBUREGAMA K, SHANMUGARAJAH V.Regeneration of plantlets from cultured anthers of tea (Camellia sinenesis (L.) O.Kuntze)[J].Journal of Tropical Agricultural Research,1998,10:271-281. |
| [17] | SRIVASTAVA P, CHATURVEDI R.Increased production of azadirachtin from an improved method of androgenic cultures of a medicinal tree Azadirachta indica A.Juss[J].Plant Signaling & Behavior,2011,6(7):974-981. |
| [18] | PINTOS B, MANZANERA J A, GÓMEZ-GARAY A.Production of doubled haploid embryos from cork oak anther cultures by antimitotic agents and temperature stress[J].Methods in Molecular Biology,2021,2289:199-219. |
| [19] | AROCKIASAMY S, PATIL M, YEPURI V,et al.Anther culture in Jatropha curcas L.:a tree species[J].Methods in Molecular Biology,2021,2289:221-233. |
| [20] | MISHRA V K, BAJPAI R, CHATURVEDI R.Androgenic haploid plant development via embryogenesis with simultaneous determination of bioactive metabolites in Cambod tea (Camellia assamica ssp.lasiocalyx)[J].Plant Cell,Tissue and Organ Culture,2022,148:515-531. |
| [21] | CARDEMIL L, JORDAN M.Light and electron microscopic stuay of in vitro cultured female gametophyte of Araucaria araucaria (Mol.) Koch[J].Zeitschrift für Pflanzenphysiologie,1982,107(4):329-338. |
| [22] | LI Y L, HUANG S W, ZHANG J Y,et al.A protocol of homozygous haploid callus induction from endosperm of Taxus chinensis Rehd.var.mairei [J].SpringerPlus,2016,5:659. |
| [23] | WINTON L L, EINSPAHR D W.The use of heat-treated pollen for aspen haploid production[J].Forest Science,1968,14(4):406-407. |
| [24] | LI Y, WEI H R, YANG J,et al.High-quality de novo assembly of the Eucommia ulmoides haploid genome provides new insights into evolution and rubber biosynthesis[J].Horticulture Research,2020,7:183. |
| [25] | HOOGHVORST I, NOGUÉS S.Opportunities and challenges in doubled haploids and haploid inducer-mediated genome-editing systems in cucurbits[J].Agronomy,2020,10(9):1441. |
| [26] | HOOGHVORST I, NOGUÉS S.Chromosome doubling methods in doubled haploid and haploid inducer-mediated genome-editing systems in major crops[J].Plant Cell Reports,2021,40:255-270. |
| [27] | Jr E H COE.A line of maize with high haploid frequency[J].The American Naturalist,1959,93:381-382. |
| [28] | BARRET P, BRINKMANN M, BECKERT M.A major locus expressed in the male gametophyte with incomplete penetrance is responsible for in situ gynogenesis in maize[J].Theoretical and Applied Genetics,2008,117:581-594. |
| [29] | PRIGGE V, XU X W, LI L,et al.New insights into the genetics of in vivo induction of maternal haploids,the backbone of doubled haploid technology in maize[J].Genetics,2012,190(2):781-793. |
| [30] | LIU C X, LI W, ZHONG Y,et al.Fine mapping of qhir8 affecting in vivo haploid induction in maize[J].Theoretical and Applied Genetics,2015,128:2507-2515. |
| [31] | DONG X, XU X, MIAO J,et al.Fine mapping of qhir1 influencing in vivo haploid induction in maize[J].Theoretical and Applied Genetics,2013,126:1713-1720. |
| [32] | KELLIHER T, STARR D, RICHBOURG L,et al. MATRILINEAL,a sperm-specific phospholipase,triggers maize haploid induction[J].Nature,2017,542:105-109. |
| [33] | LIU C X, LI X, MENG D X,et al.A 4-bp insertion at ZmPLA1 encoding a putative phospholipase a generates haploid induction in maize[J].Molecular Plant,2017,10(3):520-522. |
| [34] | JANG J H, SEO H S, WIDIEZ T,et al.Loss-of-function of gynoecium-expressed phospholipase pPLAIIγ triggers maternal haploid induction in Arabidopsis [J].New Phytologist,2023,238(5):1813-1824. |
| [35] | ZHONG Y, LIU C X, QI X L,et al.Mutation of ZmDMP enhances haploid induction in maize[J].Nature Plants,2019,5:575-580. |
| [36] | YAO L, ZHANG Y, LIU C X,et al. OsMATL mutation induces haploid seed formation in indica rice[J].Nature Plants,2018,4:530-533. |
| [37] | LIU C X, ZHONG Y, QI X L,et al.Extension of the in vivo haploid induction system from diploid maize to hexaploid wheat[J].Plant Biotechnology Journal,2020,18(2):316-318. |
| [38] | LIU H Y, WANG K, JIA Z M,et al.Efficient induction of haploid plants in wheat by editing of TaMTL using an optimized Agrobacterium-mediated CRISPR system[J].Journal of Experimental Botany,2020,71(4):1337-1349. |
| [39] | CYPRYS P, LINDEMEIER M, SPRUNCK S.Gamete fusion is facilitated by two sperm cell-expressed DUF679 membrane proteins[J].Nature Plants,2019,5:253-257. |
| [40] | KASARAS A, KUNZE R.Expression,localisation and phylogeny of a novel family of plant-specific membrane proteins[J].Plant Biology,2010,12(s1):140-152. |
| [41] | ZHONG Y, CHEN B J, LI M R,et al.A DMP-triggered in vivo maternal haploid induction system in the dicotyledonous Arabidopsis [J].Nature Plants,2020,6:466-472. |
| [42] | ZHONG Y, CHEN B J, WANG D,et al. In vivo maternal haploid induction in tomato[J].Plant Biotechnology Journal,2022,20:250-252. |
| [43] | WANG N, XIA X Z, JIANG T,et al. In planta haploid induction by genome editing of DMP in the model legume Medicago truncatula [J].Plant Biotechnology Journal,2022,20(1):22-24. |
| [44] | CHEN X E, LI Y X, AI G L,et al.Creation of a watermelon haploid inducer line via ClDMP3-mediated single fertilization of the central cell[J].Horticulture Research,2023,10(6):uhad081. |
| [45] | YIN S, LI S, SUN L,et al.Mutating the maternal haploid inducer gene CsDMP in cucumber produces haploids in planta [J].Plant Physiology,2024,194(3):1282-1285. |
| [46] | ZHONG Y, WANG Y W, CHEN B J,et al.Establishment of a DMP based maternal haploid induction system for polyploid Brassica napus and Nicotiana tabacum [J].Journal of Integrative Plant Biology,2022,64(6):1281-1294. |
| [47] | LONG L, FENG Y M, SHANG S Z,et al. In vivo maternal haploid induction system in cotton[J].Plant Physiology,2024,194(3):1286-1289. |
| [48] | ZHANG J Z, YIN J, LUO J Y,et al.Construction of homozygous diploid potato through maternal haploid induction[J].aBIOTECH,2022,3:163-168. |
| [49] | CHEN S, WANG Y C, YU L L,et al.Genome sequence and evolution of Betula platyphylla [J].Horticulture Research,2021,8:37. |
| [50] | LIU Z Y, WANG P L, ZHANG T Q,et al.Comprehensive analysis of BpHSP genes and their expression under heat stresses in Betula platyphylla [J].Environmental and Experimental Botany,2018,152:167-176. |
| [51] | SONG Q X, LI Q T, LIU Y F,et al.Soybean GmbZIP123 gene enhances lipid content in the seeds of transgenic Arabidopsis plants[J].Journal of Experimental Botany,2013,64(14):4329-4341. |
| [52] | CHENG D W, LIU Y Y, WANG Y,et al.Establishment of high-efficiency genome editing in white birch (Betula platyphylla Suk.)[J].Plant Biotechnology Journal,2024,22:7-9. |
| [53] | TAKAHASHI T, MORI T, UEDA K,et al.The male gamete membrane protein DMP9/DAU2 is required for double fertilization in flowering plants[J].Development,2018,145(23):dev170076. |
| [54] | KOSKI V, ROUSI M.A review of the promises and constraints of breeding silver birch (Betula pendula Roth) in Finland[J].Forestry:An International Journal of Forest Research,2005,78(2):187-198. |
| [55] | KELLIHER T, STARR D, SU X J,et al.One-step genome editing of elite crop germplasm during haploid induction[J].Nature Biotechnology,2019,37:287-292. |
| [56] | WANG B B, ZHU L, ZHAO B B,et al.Development of a haploid-inducer mediated genome editing system for accelerating maize breeding[J].Molecular Plant,2019,12(4):597-602. |
| [57] | WANG C, LIU Q, SHEN Y,et al.Clonal seeds from hybrid rice by simultaneous genome engineering of meiosis and fertilization genes[J].Nature Biotechnology,2019,37:283-286. |
| [58] | MARIMUTHU M P A, JOLIVET S, RAVI M,et al.Synthetic clonal reproduction through seeds[J].Science,2011,331(6019):876. |
| [59] | GENG W L, LI Y Y, SUN D Q,et al.Prediction of the potential geographical distribution of Betula platyphylla Suk.in China under climate change scenarios[J].PLoS One,2022,17(3):e0262540. |
| [60] | 陈柄华,张杰,刘桂丰,等.白桦半同胞家系纸浆材优良家系选择及选择方法评价[J].植物研究,2023,43(5):690-699. |
| CHEN B H, ZHANG J, LIU G F,et al.Selection of excellent families and evaluation of selection method for pulpwood half-siblin families of Betula platyphylla [J].Bulletin of Botanical Research,2023,43(5):690-699. | |
| [61] | 孙子腾,王新宇,侯丽丽,等.白桦BpGRFs基因鉴定与功能初步分析[J].植物研究,2025,45(2):191-201. |
| SUN Z T, WANG X Y, HOU L L,et al. Identification and prelimina functional analysis of the BpGRFs gene in Betula platyphylla [J].Bulletin of Botanical Research,2025,45(2):191-201. |
| [1] | Ziteng SUN, Xinyu WANG, Lili HOU, Yueying LIU, Zhimin ZHENG. Identification and Preliminary Functional Analysis of the BpGRFs Gene in Betula Platyphylla [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2025, 45(2): 191-201. |
| [2] | Xinyi YU, Huiyue JI, Pingping LU, Jiayu ZHOU, Hai LIAO. The Bioinformatic Analysis on the Plant Isopentenyl Pyrophosphate Isomerase [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2024, 44(5): 774-782. |
| [3] | Shanshan WANG, Rui WANG, Erqin FAN, Pengyue FU, Guanzheng QU, Nan WANG. Bioinformatics Analysis of CbuDELLAs Gene Family and Functional Analysis of CbuGRAS9 [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2024, 44(1): 139-151. |
| [4] | Zhanmin ZHENG, Yubing SHANG, Guangbo ZHOU, Di XIAO, Yi LIU, Xiangling YOU. Genetic Transformation and Function Analysis of PsnHB13 and PsnHB15 of Populus simonii × Populus nigra [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2023, 43(3): 340-350. |
| [5] | Shixian LIAO, Yuting WANG, Liben DONG, Yongmei GU, Fenglin JIA, Tingbo JIANG, Boru ZHOU. Function Analysis of the Transcription Factor PsnbZIP1 of Populus simonii×P. nigra in Response to Salt Stress [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2023, 43(2): 288-299. |
| [6] | Senyao LIU, Fenglin JIA, Qing GUO, Gaofeng FAN, Boru ZHOU, Tingbo JIANG. Response Analysis of Transcription Factor PsnbHLH162 Gene in Populus simonii × P. nigra under Salt Stress and Low Temperature Stress [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2023, 43(2): 300-310. |
| [7] | Anying HUANG, Dean XIA, Yang ZHANG, Dongchen NA, Qing YAN, Zhigang WEI. Cloning and Drought Tolerance Expression Analysis of PtrWRKY51 Gene in Populus trichocarpa [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2022, 42(6): 1005-1013. |
| [8] | Huafeng CHEN, Longjun DAI, Mingyang LIU, Bingbing GUO, Hong YANG, Lifeng WANG. Stress Tolerance Functional Analysis of the High Expression Heat Shock Protein HbHSP90.4 Gene from the Latex of Hevea brasiliensis [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2022, 42(6): 1023-1032. |
| [9] | Denggao LI, Rui LIN, Qinghui MU, Na ZHOU, Yanru ZHANG, Wei BAI. Identification and Analysis of the Potato StCRKs Gene Family and Expression Patterns in Response to Stress Signals [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2022, 42(6): 1033-1043. |
| [10] | Mingyang LIU, Huaxing XIAO, Lifeng WANG, Xiaoxu LIANG, Yu ZHANG, Meng WANG. Cloning and Functional Analysis of Heat Shock Protein HbHSP90.8-1 from Hevea brasiliensis Müll. Arg. [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2022, 42(5): 811-820. |
| [11] | He CHENG, Shuanghui TIAN, Yang ZHANG, Cong LIU, De’an XIA, Zhigang WEI. Genome-wide Identification and Expression Analysis of nsLTP Gene Family in Populus trichocarpa [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2022, 42(3): 412-423. |
| [12] | Qian Sun, Yuhang Wu, Yaxuan Zhang, Jingdan Cao, Jingjing Shi, Chao Wang. Bioinformatic Analysis and Expression Pattern of LTP Family Genes in Populus davidiana × P. alba var. pyramidalis [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2022, 42(2): 211-223. |
| [13] | Yuning Yang, Hao Dong, Shiwei Dong, Nairui Wang, Yue Song, Hanguo Zhang, Shujuan Li. Cloning and Expression Analysis of Transcription Factor LobHLH34 from Larix olgensis [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2022, 42(1): 112-120. |
| [14] | Shuang Ma, Boya Wang, Ying Cao, Shanglian Hu, Zhimin Gao. Identification and Expression Analysis of Expansin Genes in Moso Bamboo (Phyllostachys edulis) [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2022, 42(1): 29-38. |
| [15] | Jiaming Zhao, Erqin Fan, Yi Liu, Zhi Wang, Junhui Wang, Guanzheng Qu. Cloning and Bioinformatics Analysis of CbuATX1,CbuATX1-like and CbuATX2 Genes from Catalpa bungei [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2022, 42(1): 47-61. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||