Bulletin of Botanical Research ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (2): 217-227.doi: 10.7525/j.issn.1673-5102.2025.02.008
• Original Paper • Previous Articles
Yao TONG1,2, Danrong ZOU3( ), Yuqi HUANG2, Huijuan TAO3, Yazhong JIN1(
), Yuqi HUANG2, Huijuan TAO3, Yazhong JIN1( ), Xueqing GENG2(
), Xueqing GENG2( )
)
Received:2024-11-20
Online:2025-03-20
Published:2025-04-07
Contact:
Danrong ZOU, Yazhong JIN, Xueqing GENG
E-mail:65669132@qq.com;jyz_hsp@126.com;xqgeng@sjtu.edu.cn
CLC Number:
Yao TONG, Danrong ZOU, Yuqi HUANG, Huijuan TAO, Yazhong JIN, Xueqing GENG. Differences in Flavor Quality of Huangdu Tomato (Solanum lycopersicum) under Different Soil Conditions[J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2025, 45(2): 217-227.
Table 1
qRT-PCR primers
基因 Gene | 引物序列(5′→3′) Primer sequences(5′→3′) |
|---|---|
| LeFRK2 | F: CGACGATGAGTTCGGTCACA R: CAAGATTCAACTCAGCGGGC |
| LePFK | F: GGTGAAGCTAATGGGTCGCT R: GCCCCTTCGGCTATCACAAT |
| LeME | F: ATCTCGGTTGCCAGGGAATG R: TTCCTTCCCGGTGACTCTCT |
| LeHXK3 | F: TTGGGCAAGATGTGGTTGGA R: TATTGTACCGACCTCCCGCT |
| LeSS | F: CCCAGATGAACCGAGTGAGG R: GGCAGACCACAAGTCATTGC |
| LeLYCB | F: CGACGTGATCATTATCGGAGC R: GTGGTGAAGGGTCAACACAACA |
| LeLYCE | F: GCCACAGGTTATTCAGTCGTCA R: CCAGTCCAAATAGGAAAAACGAT |
| LePSY | F: GGGCGGCCATTTGACAT R: AATGGCTGAATATCAACTGGAAAGT |
| LeUBI | F: TCGTAAGGAGTGCCCTAATGCTGA R: CAATCGCCTCCAGCCTTGTTGTAA |
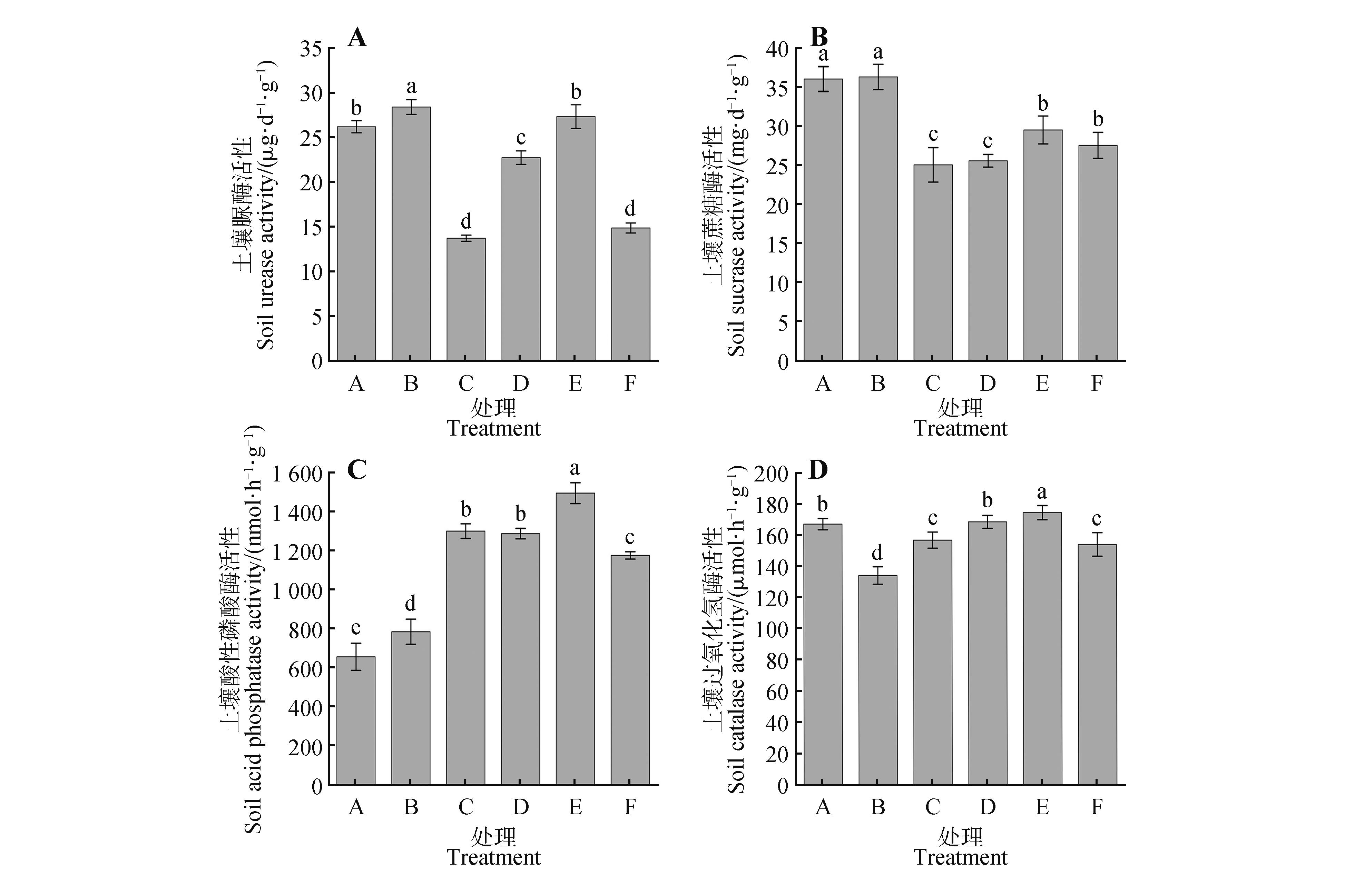
Fig.1
Soil enzyme activity in different planting greenhousesA. farmer 1 shed; B. farmer 2 shed; C. B085 shed; D. B091 shed; E. B072 shed; F. B077 shed; different lowercase letters in the figure indicated significant differences between different treatments (P<0.05); values were mean ± standard deviation. The same as below.
| 1 | 陶惠娟,陈钰.嘉定区黄渡番茄品牌发展历史、现状及建议[J].上海农业科技,2023(3):16-17. |
| TAO H J, CHEN Y.Development history,current situation and suggestions of Huangdu tomato brand in Jiading District[J].Shanghai Agricultural Science and Technology,2023(3):16-17. | |
| 2 | 张宁宁,欧阳小雪,张孟娟,等.土壤理化性质与卫青萝卜品质相关性研究[J].中国土壤与肥料,2024(6):134-141. |
| ZHANG N N, OUYANG X X, ZHANG M J,et al.Study on the correlation between soil physicochemical properties and the quality of Weiqing radish[J].Soil and Fertilizer Sciences in China,2024(6):134-141. | |
| 3 | 苏兰茜,濮秋婕,白亭玉,等.土壤质地对菠萝蜜根际微生物碳源利用、线虫群落及果实糖分的影响[J].中国农业科学,2024,57(2):349-362. |
| SU L X, PU Q J, BAI T Y,et al.Effects of soil texture on rhizosphere microbial carbon source utilization,nematode community and fruit sugar of jackfruit[J].Scientia Agricultura Sinica,2024,57(2):349-362. | |
| 4 | BASTIDA F, ZSOLNAY A, HERNÁNDEZ T,et al.Past,present and future of soil quality indices:a biological perspective[J].Geoderma,2008,147(3/4):159-171. |
| 5 | 林玥,郝嘉琪,王维钰,等.不同耕作措施对黄土高原区域大豆根际土壤微生物量、酶活性和养分的影响[J].西北农业学报,2019,28(4):620-630. |
| LIN Y, HAO J Q, WANG W Y,et al.Effects of different tillage measures on soil microbial biomass,enzyme activities and nutrients in rhizosphere soil of the Loess Plateau[J].Acta Agriculturae Boreali-occidentalis Sinica,2019,28(4):620-630. | |
| 6 | GOMOLA C E, MCKAY J K, WALLENSTEIN M D,et al.Within-species trade-offs in plant-stimulated soil enzyme activity and growth,flowering,and seed size[J].Ecology and Evolution,2018,8(23):11717-11724. |
| 7 | 罗义菊,蓝增全,陶燕蓝,等.古老茶园茶叶生化品质与土壤环境因子的综合评价[J].江苏农业科学,2023, 51(17):204-211. |
| LUO Y J, LAN Z Q, TAO Y L,et al.Comprehensive evaluation of tea biochemical quality and soil environmental factors in ancient tea gardens[J].Jiangsu Agricultural Science,2023,51(17):204-211. | |
| 8 | 司玉坤.不同土壤类型下氮磷肥类型对小麦生长发育的影响[D].郑州:河南农业大学,2019. |
| SI Y K.Effects of nitrogen and phosphorus fertilizer types on growth and development of wheat under different soil types[D].Zhengzhou:Henan Agricultural University,2019. | |
| 9 | 杨梅,胡晓婷,徐卫红.不同类型土壤与辣椒风味品质的相关性研究[J].西南大学学报(自然科学版),2024,46(1):2-16. |
| YANG M, HU X T, XU W H.Study on correlation between different types of soil and flavor quality of pepper[J].Journal of Southwest University (Natural Science Edition),2024,46(1):2-16. | |
| 10 | 侯永侠,车畅,温璇,等.草莓果实品质及其与土壤养分的相关性分析[J].沈阳农业大学学报,2024,55(2):153-162. |
| HOU Y X, CHE C, WEN X,et al.Analysis on fruit quality of strawberry and its correlation with soil nutrient[J].Journal of Shenyang Agricultural University,2024,55(2):153-162. | |
| 11 | 曹永庆,任华东,王开良,等.不同类型土壤栽培香榧种仁品质综合评价和分析[J].果树学报,2022,39(5):836-845. |
| CAO Y Q, REN H D, WANG K L,et al.Comprehensive evaluation and analysis of kernel quality of Torreya grandis ‘Merrillii’ from different soil types[J].Journal of Fruit Science,2022,39(5):836-845. | |
| 12 | 许泽华,黄小晶,牛锐敏,等.贺兰山东麓赤霞珠葡萄产区土壤和葡萄及葡萄酒品质差异化分析[J].黑龙江农业科学,2023(4):65-70. |
| XU Z H, HUANG X J, NIU R M,et al.Quality difference of soil,grape and wine in the Cabernet Sauvignon grape producing areas at the eastern foot of Helan Mountain[J].Heilongjiang Agricultural Science,2023(4):65-70. | |
| 13 | 唐都,高疆生,徐崇志,等.土壤养分因子对灰枣果实风味品质的相关分析[J].新疆农业科学,2014,51(1):66-71. |
| TANG D, GAO J S, XU C Z,et al.Correlation analysis between soil factors and fruit quality of Ziziphus jujuba Mill.cv.Huizao[J].Xinjiang Agricultural Science,2014,51(1):66-71. | |
| 14 | 赵景景.不同土壤有机质水平对苹果叶片光合、果实糖酸代谢及品质的影响[D].杨凌:西北农林科技大学,2018. |
| ZHAO J J.Effects of different levels of soil organic matter on photosynthesis of leaves,sugar and organic acid metabolism as well as quality in apple fruit[D].Yangling:Northwest A&F University,2018. | |
| 15 | 李合生.植物生理生化实验原理和技术[M].北京:高等教育出版社,2000. |
| LI H S.Principles and techniques of plant physiological biochemical experiment[M].Beijing:Higher Education Press,2000:123,184,195,248. | |
| 16 | 李贞霞,沈欢欢,高苗苗,等.番茄红素在不同溶剂中的分光光度法分析[J].光谱学与光谱分析,2019, 39(4):1114-1117. |
| LI Z X, SHEN H H, GAO M M,et al.Analysis of lycopene in different solvents by spectrophotometry[J].Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis,2019,39(4):1114-1117. | |
| 17 | 关松荫.土壤酶及其研究法[M].北京:农业出版社,1986. |
| GUAN S Y.Soil enzymes and their research methods[M].Beijing:Agriculture Press,1986. | |
| 18 | 宋以玲,于建,陈士更,等.化肥减量配施生物有机肥对油菜生长及土壤微生物和酶活性影响[J].水土保持学报,2018,32(1):352-360. |
| SONG Y L, YU J, CHEN S G,et al.Effects of reduced chemical fertilizer with application of bio-organic fertilizer on rape growth,microorganism and enzymes activities in soil[J].Journal of Soil and Water Conservation,2018,32(1):352-360. | |
| 19 | 孔涛,马瑜,刘民,等.生物有机肥对土壤养分和土壤微生物的影响[J].干旱区研究,2016,33(4):884-891. |
| KONG T, MA Y, LIU M,et al.Effect of applying biological organic fertilizer on soil nutrients and soil microbes[J].Arid Zone Research,2016,33(4):884-891. | |
| 20 | LIVAK K J, SCHMITTGEN T D.Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2-ΔΔ C T method[J].Methods,2001,25(4):402-408. |
| 21 | 李欣,陈小华,顾海蓉,等.典型农田土壤酶活性分布特征及影响因素分析[J].生态环境学报,2021,30(8):1634-1641. |
| LI X, CHEN X H, GU H R,et al.Distribution characteristics and influencing factors of enzyme activities in typical farmland soils[J].Ecology and Environment,2021,30(8):1634-1641. | |
| 22 | 姚槐应,黄昌勇.土壤微生物生态学及其实验技术[M].北京:科学出版社,2006. |
| YAO H Y, HUANG C Y.Soil microbial ecology and experimental techniques[M].Beijing:Science Press,2006. | |
| 23 | 熊湖,郑顺林,张德银,等.轮作与连作对马铃薯生长及土壤酶活性的影响[J].福建农业学报,2022,37(1):25-32. |
| XIONG H, ZHENG S L, ZHANG D Y,et al.Potato growth and soil enzyme activities as affected by rotation or continuous cropping cultivation[J].Fujian Journal of Agricultural Sciences,2022,37(1):25-32. | |
| 24 | ZHANG C J, KANG W J, ZHANG C M,et al.Evaluation of the effects of different rotation patterns on soil fertility based on principal component-cluster analysis[J].Journal of Soil and Water Conservation,2020,34(1):292-300. |
| 25 | ZHANG G L.Effects of straw and living grass mulching on soil nutrients,soil microbial quantities and soil enzyme activities in a peach orchard[J].Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology,2011,35(12):1236-1244. |
| 26 | 李茜,徐瑞蔓,陈迪,等.不同栽培年限人参根际土壤细菌群落与土壤理化性质和酶活性的相关性[J].植物营养与肥料学报,2022,28(2):313-324. |
| LI Q, XU R M, CHEN D,et al.Correlation of bacterial community with soil physicochemical properties and enzyme activities in rhizosphere soil under different cultivation years of ginseng (Panax ginseng C.A.Mey.)[J].Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer,2022,28(2):313-324. | |
| 27 | 吴金平,周洁,矫振彪,等.不同施肥方式对甘蓝生长、产量、品质及土壤酶活性的影响[J].中国瓜菜,2023,36(9):75-79. |
| WU J P, ZHOU J, JIAO Z B,et al.Effects of different fertilization methods on soil enzyme activity and growth,yield,quality of cabbage[J].Chinese Cucurbits and Vegetables,2023,36(9):75-79. | |
| 28 | 钟冰,陈远喜.施氮量对柑橘产量·品质·经济效益的影响[J].安徽农业科学,2016,44(36):74-76. |
| ZHONG B, CHEN Y X.Effects of nitrogen application on yield,quality and economic performance of citrus fruits[J].Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences,2016,44(36):74-76. | |
| 29 | 段文学,张海燕,解备涛,等.化肥和生物有机肥配施对鲜食型甘薯块根产量、品质及土壤肥力的影响[J].植物营养与肥料学报,2021,27(11):1971-1980. |
| DUAN W X, ZHANG H Y, XIE B T,et al.Effects of chemical and bio-organic fertilizers on tuber yield,quality,and soil fertility of edible sweetpotato[J].Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer,2021,27(11):1971-1980. | |
| 30 | 高柱,陈璐,张小丽,等.‘红阳’猕猴桃果园土壤养分与果实品质关系的多元分析及优化方案[J].江西农业大学学报,2022,44(2):358-367. |
| GAO Z, CHEN L, ZHANG X L,et al.Multivariate analysis and optimization of relationship between soil nutrients and fruit quality in Hongyang kiwifruit orchard[J].Acta Agriculturae Universitis Jiangxiensis,2022,44(2):358-367. | |
| 31 | 孙玲玲,刘鹏琰,王玉玲,等.江苏省绿色食品梨特征营养品质挖掘与保持技术研究[J].江苏农业科学,2024,52(12):141-149. |
| SUN L L, LIU P Y, WANG Y L,et al.Study on excavation and maintenance technology of characteristic nutritional quality of green food pear in Jiangsu Province[J].Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences,2024,52(12):141-149. | |
| 32 | 王同林,叶红霞,郑积荣,等.番茄果实中主要风味物质研究进展[J].浙江农业学报,2020,32(8):1513-1522. |
| WANG T L, YE H X, ZHENG J R,et al.Research progress of main flavor compounds in tomato fruits[J].Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis,2020,32(8):1513-1522. | |
| 33 | JIANG H Y, LI W, HE B J,et al.Sucrose metabolism in grape (Vitis vinifera L.) branches under low temperature during overwintering covered with soil[J].Plant Growth Regulation,2014,72(3):229-238. |
| 34 | 苏静.苹果果糖激酶基因MdFRK2调控果糖及纤维素含量的机制解析[D].杨凌:西北农林科技大学,2022. |
| SU J.Study on mechanism of apple fructokinase MdFRK2 in regulating sugar and cellulose content[D].Yangling:Northwest A&F University,2022. | |
| 35 | 秦伟,崔新仪,陈波浪,等.不同氮磷钾配比施肥对新疆红富士苹果糖分积累相关酶活性的影响[J].新疆农业大学学报,2013,36(6):431-436. |
| QIN W, CUI X Y, CHEN B L,et al.Effects of different fertilization ratio of N,P and K on related enzyme activities of sugar accumulation in Xinjiang Red Fuji apple[J].Journal of Xinjiang Agricultural University,2013,36(6):431-436. | |
| 36 | 田志娇.不同土壤养分和微生物群落结构对芦柑果实品质的影响[D].福州:福建农林大学,2024. |
| TIAN Z J.The effects of different soil nutrients and microbial community structures on the quality of ponkan fruit[D].Fuzhou:Fujian Agriculture and Forestry University,2024. | |
| 37 | DAI N, SCHAFFER A, PETREIKOV M,et al.Potato (Solanum tuberosum L.) fructokinase expressed in yeast exhibits inhibition by fructose of both in vitro enzyme activity and rate of cell proliferation[J].Plant Science,1997,128(2):191-197. |
| 38 | 李文娟,何萍,金继运.钾素对玉米茎腐病抗性反应中糖类物质代谢的影响[J].植物营养与肥料学报,2011,17(1):55-61. |
| LI W J, HE P, JIN J Y.Effect of potassium on sugar metabolism in resistant response to corn stalk rot[J].Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers,2011,17(1):55-61. | |
| 39 | 沈衡,王琳,李骞,等.番茄风味和功能性成分研究进展[J].园艺学报,2024,51(2):423-438. |
| SHEN H, WANG L, LI Q,et al.Research progress on flavor and functional components of tomato[J].Acta Horticulturae Sinica,2024,51(2):423-438 | |
| 40 | BANG H, KIM S, LESKOVAR D,et al.Development of a codominant CAPS marker for allelic selection between canary yellow and red watermelon based on SNP in lycopene β-cyclase (LCYB) gene[J].Molecular Breeding,2007,20(1):63-72. |
| 41 | 马荣雪,周永海,程登虎,等.不同外源物质对西瓜番茄红素含量及其关键酶基因表达的影响[J].西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版),2021,49(12):80-88. |
| MA R X, ZHOU Y H, CHENG D H,et al.Effect of different exogenous substances on watermelon lycopene content and gene expression of key enzymes[J].Journal of Northwest A&F University (Natural Science Edition),2021,49(12):80-88. | |
| 42 | 陈选阳,张招娟.甘薯生长期间块根β-胡萝卜素合成基因的表达分析[J].热带作物学报,2011,32(10):1838-1842. |
| CHEN X Y, ZHANG Z J.Study on the relationship between accumulation of β-carotene and expression of genes for β-carotene biosynthesis in the storage roots of sweet potato [Ipomoea batatas L.(Lam)][J].Chinese Journal of Tropical Crops,2011,32(10):1838-1842. | |
| 43 | 王慧,欧承刚,庄飞云,等.胡萝卜中类胡萝卜素积累与主要合成基因转录水平相关性分析[J].园艺学报,2014,41(12):2513-2520. |
| WANG H, OU C G, ZHUANG F Y,et al.Relationship of carotenoid accumulation and transcript of main genes in carotenoid biosynthesis in carrot[J].Acta Horticulturae Sinica,2014,41(12):2513-2520. | |
| 44 | YAN J B, KANDIANIS C B, HARJES C E,et al.Rare genetic variation at Zea mays crtRB1 increases β-carotene in maize grain[J].Nature Genetics,2010,42(4):322-327. |
| [1] | Lijuan LUO, Qingxiao YIN, Wei SUN, Xi ZAN, Qingmao SHI, Jing ZHANG, Yamei CHEN, Xiao XU. Soil Enzyme Activities and Stoichiometric Characteristics of Different Plant Communities under Natural Fagus Forest in Micang Mountain Nature Reserve, Sichuan [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2024, 44(3): 470-480. |
| [2] | Luhua ZHOU, Junyi FANG, Zimo XIONG, Weifeng WU, Jiarui LIU, Qiao LU, Hongqing LING, Danyu KONG. Evaluation on Waterlogging Tolerance of Different Tomato Germplasm [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2023, 43(5): 657-666. |
| [3] | Jikang XU, Yanhong HE, Tingyan LIU, Longfei HAO, Shengxi ZHANG, Zhaoyi LI. Characteristics of Rhizosphere Soil Microecological Environment of Different Ecological Restoration Vegetation in Arsenic Sandstone Areas [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2023, 43(4): 531-539. |
| [4] | Ting-Yan LIU, Long-Fei HAO, Xu-Fu WANG, Hai-Xia YAN, Shu-Lan BAI. Effects of Nitrogen Deposition and Ectomycorrhizal Fungi on Root Architecture and Rhizosphere Soil Enzyme Activities of Larix olgensis Seedlings [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2021, 41(1): 145-151. |
| [5] | ZHAO Chun-Jian, LI Yu-Zheng, GUAN Jia-Jing, SU Wei-Ran, TIAN Yao, WANG Ting-Ting, LI Shen, LI Chun-Ying. Effect of Interplanting Taxus cuspidata with Ficus carica on Growth of Two Plants and Activities of Soil Enzymes [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2020, 40(5): 679-685. |
| [6] | MA Peng-Yu, ZHANG Hong-Guang, ZAN Peng, GU Wei-Ping, WEN Lu-Ning, ZHANG Zi-Jia, WENG Hai-Long, SUN Tao, MAO Zi-Jun. Effects of Long-term Nitrogen Addition on Soil Enzymes in Larix gmelinii Plantation in Northeast China [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2019, 39(4): 598-603. |
| [7] | WANG Xiao-Ping, XIAO Xiao, TANG Tian-Wen, LI Yun-Xiang, XIAO Juan. Seasonal Changes of the Input of Root Exudates and Its Driving Characteristics of Rhizosphere Microbe in a Cercidiphyllum japonicum Sieb. Plantation [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2018, 38(1): 47-55. |
| [8] | SONG Fang-Yuan1;SU Hong-Yan2*;CHENG Xian-Hao2;ZHU Lu-Ying2;WANG Lei1. Characterization and Expression Analysis of TNAC Genes of Tomato [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2015, 35(6): 898-903. |
| [9] | LIU Xia;HU Zong-Li;ZHANG Yan-Jie;ZHU Ming-Ku;YIN Wen-Cheng;CHEN Guo-Ping*. Cloning,Bioinformatics and Expression Analysis of SlMYBL Gene in Tomato [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2014, 34(5): 664-670. |
| [10] | CAO Ying;TANG Xiao-Feng;LIU Yong-Sheng. Cloning, Expression Pattern and Bioinformation Analyses of COBRA Gene in Tomato(Solanum lycopersicum) [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2012, 32(3): 304-310. |
| [11] | LONG Jiao-Yue;HU Zong-Li;CHEN Xu-Qing;YAN Bo;CHEN Guo-Ping*. Molecular Cloning and Characterization of LeEBF1 and LeEBF2 from Tomato [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2008, 28(6): 710-715. |
| [12] | HE Xiu-Xia;YU Yuan-Hua;GUO Hong-Yu;ZHANG Shu-Hua. A Effective Preparation Method for DNA from Gene Silencing Plant Induced by Virus [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2008, 28(6): 726-729. |
| [13] | LIU Chao;FENG Yu-Long*;TIAN Yao-Hua. Effects of Eupatorium adenophorum Sprengel invasion on Soil Enzyme Activities and Physical and Chemical Factors [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2007, 27(6): 729-735. |
| [14] | SHANG Sang;TIAN Li-Bo;HUANG Mian-Jia;CAI Jie. Effect of Simulated Acid Rain on Seed Germination of Three Solanaceous Vegetables [J]. , 2007, 27(4): 494-499. |
| [15] | LIU Hui-Min;ZHU Yue-Lin*;CHEN Lei. In Virto Comparision of Ca(NO3)2 Tolerance of Different Tomato Cultivars and Rootstock Selfed Lines at Seedling Stage [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2007, 27(2): 175-181. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||