Bulletin of Botanical Research ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (4): 614-626.doi: 10.7525/j.issn.1673-5102.2025.04.013
• Original Paper • Previous Articles Next Articles
Ying WANG1,2, Maojin ZHAO1, Xiuming LIU1, Yixuan WU1, Jiahao ZHU1, Chengzhong WANG1( )
)
Received:2024-08-25
Online:2025-07-20
Published:2025-07-25
Contact:
Chengzhong WANG
E-mail:754409736@qq.com
CLC Number:
Ying WANG, Maojin ZHAO, Xiuming LIU, Yixuan WU, Jiahao ZHU, Chengzhong WANG. Tolerance and Enrichment Characteristics of Agapanthus praecox ssp. orientalis ‘Big Blue’ under Cadmium Stress[J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2025, 45(4): 614-626.
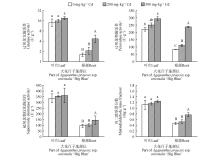
Fig.2
Effects of heavy metal cadmium stress on antioxidant enzyme activity and malondialdehyde mass fraction of Agapanthus praecox ssp. orientalis ‘Big Blue’Different capital or lowercase letters in case represented significant differences in root or leaf parameter between treatments (P<0.05), respectively.
Table 1
Effects of heavy metal cadmium stress on photosynthetic pigment mass fraction of Agapanthus praecox ssp. orientalis‘Big Blue’
镉质量分数 Cadmium mass fraction/ (mg·kg-1) | 叶绿素a Chla/(mg·g-1) | 叶绿素b Chlb/(mg·g-1) | 叶绿素a+b Chla+b/(mg·g-1) | 叶绿素a/b Chla/b | 类胡萝卜素 Carotenoid/(mg·g-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0.89±0.02a | 0.36±0.01a | 2.51±0.03a | 2.46±0.01a | 0.21±0.01a |
| 200 | 0.88±0.02a | 0.35±0.01a | 2.47±0.02a | 2.45±0.05a | 0.20±0.01a |
| 500 | 0.66±0.01b | 0.30±0.01b | 0.96±0.01b | 2.22±0.03b | 0.17±0.01b |
Table 2
Effects of heavy metal cadmium on the chlorophyll fluorescence parameters of Agapanthus praecox ssp. orientalis‘Big Blue’
镉质量分数 Cadmium mass fraction/ (mg·kg-1) | 最大光化学效率 Fv/Fm | PSⅡ潜在活性 Fv/Fo | 实际光化学效率 ΦPSⅡ | 光化学淬灭系数 qP | 非光化学淬灭系数 NPQ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0.83±0.01a | 4.38±0.01a | 0.36±0.01a | 0.63±0.01a | 0.60±0.01a |
| 200 | 0.81±0.01a | 4.21±0.30a | 0.34±0.03a | 0.58±0.01a | 0.62±0.01a |
| 500 | 0.69±0.02b | 3.66±0.01b | 0.29±0.01b | 0.42±0.01b | 0.43±0.01b |
Table 3
Effects of cadmium stress on the heavy metal enrichment characteristics of Agapanthus praecox ssp. orientalis ‘Big Blue’
镉质量分数 Cd mass fraction/ (mg·kg-1) | 叶片镉质量分数 Leaf Cd mass fraction/ (mg·kg-1) | 根部镉质量分数 Root Cd mass fraction/ (mg·kg-1) | 叶片富集系数 Leaf enrichment coefficient | 根部富集系数 Root enrichment coefficient | 转运系数 Transport coefficient |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | — | — | — | — | — |
| 200 | 172.45±1.05b | 164.93±1.58b | 0.86±0.01a | 0.82±0.01a | 1.05±0.01b |
| 500 | 422.37±1.12a | 318.03±1.39a | 0.84±0.01a | 0.64±0.01b | 1.33±0.01a |
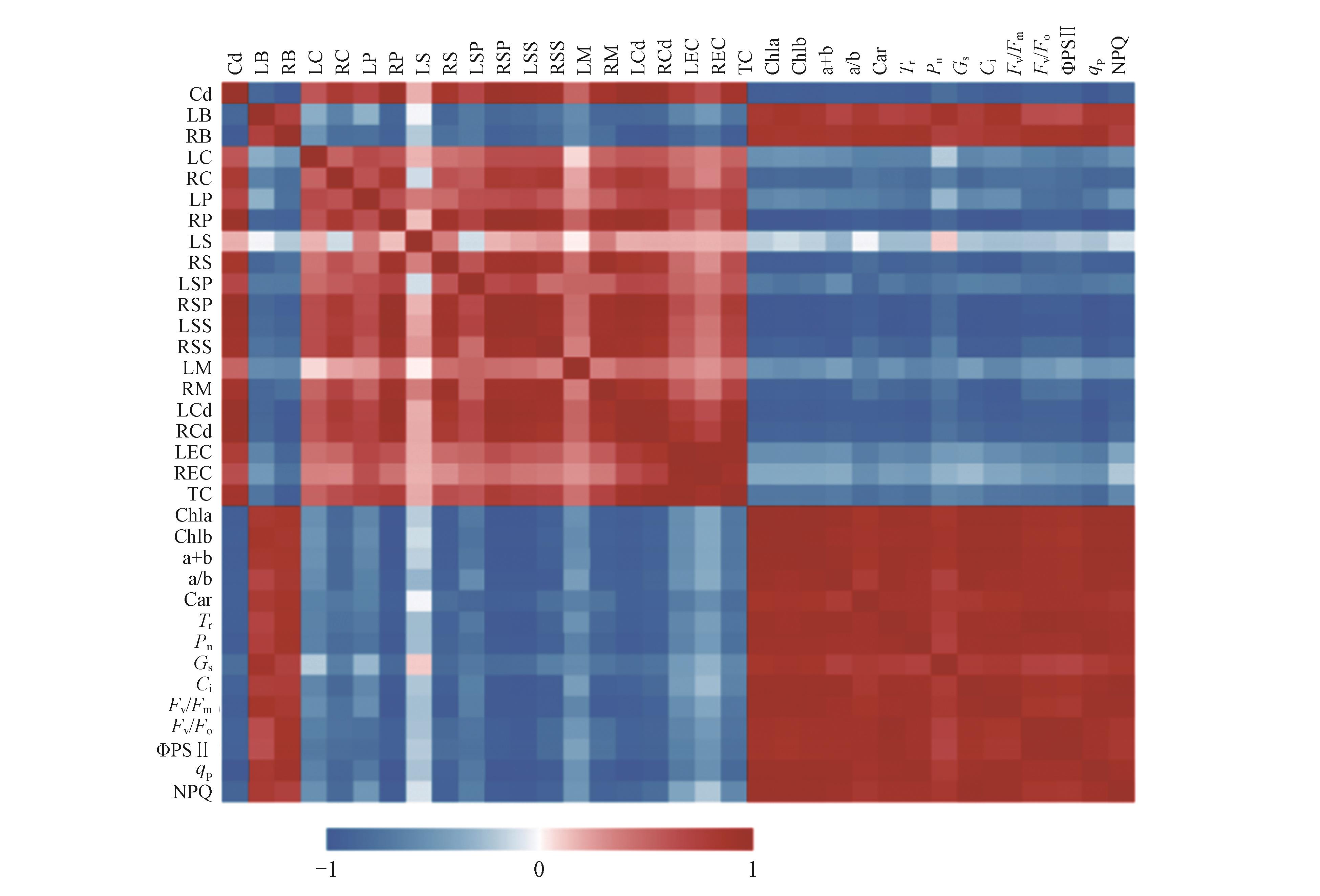
Fig.5
Correlation analysis between various indices of Agapanthus praecox ssp. orientalis ‘Big Blue’ under Cd treatmentsCd. Cd mass fraction;LB. Leaf biomass;RB. Root biomass; LC. Leaf CAT;RC. Root CAT;LP. Leaf POD;RP. Root POD;LS. Leaf SOD; RS. Root SOD; LSP. Leaf soluble protein; RSP. Root soluble protein;LSS. Leaf soluble sugar; RSS. Root soluble sugar;LM. Leaf malondialdehyde; RM. Root malondialdehyde; LCd. Leaf Cd mass fraction;RCd. Root Cd mass fraction;LEC. Leaf enrichment coefficients; REC. Root enrichment coefficients; TC. Transport coefficients;Chla. Chlorophyll a; Chlb. Chlorophyll b; a+b. Chlorophyll a+b;a/b. Chlorophyll a/b;Car. Carotenoid;Tr. Transpiration rate;Pn. Photosynthetic rate;Gs. Stomatal conductance;Ci. Intercellular CO2 mole fraction;Fv/Fm. PSⅡ maximum photochemistry efficiency;Fv/Fo. PSⅡ potential activity;ΦPSⅡ. PSⅡ actual photochemical quantum efficiency;qP Chemical quenching coefficient;NPQ Non-photochemical quenching coefficient.
| [1] | 纪文贵,王珂,蒙建波,等.中国土壤重金属污染状况及其风险评价[J].农业研究与应用,2020,33(5):22-28. |
| JI W G, WANG K, MENG J B,et al.Distribution characteristics and risk assessment of soil heavy metal pollution in China[J].Agricultural Research and Application,2020,33(5):22-28. | |
| [2] | 罗昱.螯合剂及有机酸强化凤尾鸡冠花修复Pb、Cd污染土壤研究[D].昆明:昆明理工大学,2021. |
| LUO Y.Study on remediation of Pb and Cd contaminated soil by chelating agents and organic acids[D].Kunming:Kunming University of Science and Technology,2021. | |
| [3] | ZHANG Y, ZHOU J, GAO F J,et al.Comprehensive ecological risk assessment for heavy metal pollutions in three phases in rivers[J].Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China,2015,25(10):3436-3441. |
| [4] | SHI Y K, MU X M, LI K R,et al.Soil characterization and differential patterns of heavy metal accumulation in woody plants grown in coal gangue wastelands in Shaanxi,China[J].Environmental Science and Pollution Research,2016,23(13):13489-13497. |
| [5] | 赵慧博,赵志强,包春光,等.镉(Cd)胁迫下蓖麻蛋白质组学筛查及RcBSK7抗性功能研究[J].植物研究,2023,43(1):36-50. |
| ZHAO H B, ZHAO Z Q, BAO C G,et al.Proteomic screening and RcBSK7 resistance of Ricinus communis under cadmium(Cd) stress[J].Bulletin of Botanical Research,2023,43(1):36-50. | |
| [6] | 慈敦伟,姜东,戴廷波,等.镉毒害对小麦幼苗光合及叶绿素荧光特性的影响[J].麦类作物学报,2005,25(5):88-91. |
| CI D W, JIANG D, DAI T B,et al.Effect of Cd toxicity on photosynthesis and chlorophyll fluorescence of wheat seedling[J].Journal of Triticeae Crops,2005,25(5):88-91. | |
| [7] | 王春瑶,雷晓锦,刘中原.逆境胁迫下山新杨PdbHMGs基因表达模式分析[J].植物研究,2023,43(6):932-942. |
| WANG C Y, LEI X J, LIU Z Y.Expression pattern analysis of PdbHMGs genes in Populus davidiana×P.bolleana under abiotic stress[J].Bulletin of Botanical Research,2023,43(6):932-942. | |
| [8] | 李源恒,赵春莉,郭宏亮,等.镉胁迫对黄秋英生理及富集特性的影响[J].山东农业科学,2024,56(1):81-90. |
| LI Y H, ZHAO C L, GUO H L,et al.Effects of cadmium stress on physiological and enrichment characteristics of Cosmos sulphureus [J].Shandong Agricultural Science,2024,56(1):81-90. | |
| [9] | 自海云,李琬婷,程小毛,等.镉胁迫对洋常春藤叶绿素荧光特性的影响[J].西南林业大学学报,2018,38(5):7-12. |
| ZI H Y, LI W T, CHENG X M,et al.Effects of cadmium stress on chlorophyll fluorescence characteristics of Hedera helix [J].Journal of Southwest Forestry University,2018,38(5):7-12. | |
| [10] | 张涵洋,李爱,张卫华,等.镉胁迫对西瓜幼苗生长及其叶片解剖结构和生理特性的影响[J].西北植物学报,2023,43(3):401-409. |
| ZHANG H Y, LI A, ZHANG W H,et al.Effects of cadmium stress on the growth,leaf anatomical structure and physiological characteristics of Citrullus lanatus seedlings[J].Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica,2023,43(3):401-409. | |
| [11] | 徐小逊,董袁媛,邓玉兰,等.镉胁迫对豨莶生长及光合作用相关参数的影响[J].农业环境科学学报,2016,35(9):1672-1679. |
| XU X X, DONG Y Y, DENG Y L,et al.Effects of cadmium stress on growth and photosynthetic parameters of Sigesbeckia orientalis L.[J].Journal of Agro-Environment Science,2016,35(9):1672-1679. | |
| [12] | 李继光,李廷强,朱恩,等.氮对超积累植物东南景天生长和镉积累的影响[J].水土保持学报,2007,21(1):54-58. |
| LI J G, LI T Q, ZHU E,et al.Effects of nitrogen fertilizer on growth and cadmium accumulation in hyperaccumulator of Sedum alfredii Hance[J].Journal of Soil and Water Conservation,2007,21(1):54-58. | |
| [13] | 杨荣孑.镉胁迫对超积累植物龙葵(Solanum nigrum L.)生理生化的影响及不同氮形态的调节作用[D].雅安:四川农业大学,2014. |
| YANG R J.Effects of physiological and biochemical in hyperaccumulator Solanum nigrum L.under cadium stress and the regulation of different nitrogen forms[D].Ya'an:Sichuan Agricultural University,2014. | |
| [14] | 孙颖,王阿香,刘颖竹,等.大花百子莲的开花物候与生殖特性[J].西北植物学报,2013,33(12):2423-2431. |
| SUN Y, WANG A X, LIU Y Z,et al.Flowering phonolology and reproductive features of Agapanthus praecox ssp.orientalis ‘Big Blue’[J].Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica,2013,33(12):2423-2431. | |
| [15] | 刘涛,陈海荣,汪成忠,等.干旱和盐胁迫下百子莲的抗逆生理研究[J].浙江农业学报,2022,34(12):2669-2681. |
| LIU T, CHEN H R, WANG C Z,et al.Physiology of stress resistance of Agapanthus praecox under drought and salt stress[J].Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis,2022,34(12):2669-2681. | |
| [16] | 李治慧.4种宿根花卉的耐旱性及园林应用研究[D].福州:福建农林大学,2015. |
| LI Z H.Study on the drought tolerance and the landscape application of four perennial flower [D].Fuzhou:Fujian Agriculture and Forestry University,2015. | |
| [17] | 汪成忠,王磊,成海钟.4个百子莲品种的抗寒性鉴定[J].贵州农业科学,2015,43(5):58-60. |
| WANG C Z, WANG L, CHENG H Z.Cold resistance identification of four Agapanthus varieties[J].Guizhou Agricultural Sciences,2015,43(5):58-60. | |
| [18] | 许春娇,卓丽环.温度调控使百子莲花期提前[J].园林,2013(3):74-75. |
| XU C J, ZHUO L H.The temperature control makes the flowering period of the Agapanthus praecox earlier[J].Garden,2013(3):74-75. | |
| [19] | YANG X E, LONG X X, YE H B,et al.Cadmium tolerance and hyperaccumulation in a new Zn-hyperaccumulating plant species (Sedum alfredii Hance)[J].Plant and Soil,2004,259:181-189. |
| [20] | 邹琦.植物生理学实验指导[M].北京:中国农业出版社,2000:110-174. |
| ZOU Q.Plant physiology experiment guide[M].Beijing:China Agricultural Press,2000:110-174. | |
| [21] | 沈伟其.测定水稻叶片叶绿素含量的混合液提取法[J].植物生理学通讯,1988(3):62-64. |
| SHEN W Q.Extraction of mixed solution for determination of chlorophyll content in rice leaf blade[J].Plant Physiology Communications,1988(3):62-64. | |
| [22] | 张宪政.作物生理研究法[M].北京:农业出版社,1992:142. |
| ZHANG X Z.Methods of crop physiology research[M].Beijing:Agricultural Press,1992:142. | |
| [23] | WAN G L, NAJEEB U, JILANI G,et al.Calcium invigorates the cadmium-stressed Brassica napus L.plants by strengthening their photosynthetic system[J].Environmental Science and Pollution Research,2011,18(9):1478-1486. |
| [24] | 贾中民,程华,魏虹,等.三峡库区岸生植物秋华柳对镉胁迫的光合响应[J].林业科学,2012,48(6):152-158. |
| JIA Z M, CHENG H, WEI H,et al.Photosynthetic responses of the riparian Salix variegata to cadmium stress in Three Gorges Reservoir Region[J].Scientia Silvae Sinicae,2012,48(6):152-158. | |
| [25] | 郭晖,金振锐,周君丽,等.铅、镉单一及复合污染对3种观赏植物生长的影响及其积累特性研究[J].西北林学院学报,2022,37(3):64-71. |
| GUO H, JIN Z R, ZHOU J L,et al.Growth and accumulation characteristics of three ornamental plants under single and combined pollution of Pb and Cd[J].Journal of Northwest Forestry University,2022,37(3):64-71. | |
| [26] | LIU X Q, PENG K J, WANG A G,et al.Cadmium accumulation and distribution populations of Phytolacca americana L.and the role of transpiration[J].Chemosphere,2010,78(9):1136-1141. |
| [27] | 徐佩贤,费凌,陈旭兵,等.四种冷季型草坪植物对镉的耐受性与积累特性[J].草业学报,2014,23(6):176-188. |
| XU P X, FEI L, CHEN X B,et al.Cadmium tolerance and accumulation in four cool-season turfgrasses[J].Acta Prataculturae Sinica,2014,23(6):176-188. | |
| [28] | 陈露.镉胁迫对不同品种桑树种子萌发及幼苗生长的影响[D].贵阳:贵州大学,2019. |
| CHEN L.Effects of cadmium stress on seed germination and seedling growth of different mulberry varieties[D].Guiyang:Guizhou University,2019. | |
| [29] | 顾翠花,王懿祥,白尚斌,等.四种园林植物对土壤镉污染的耐受性[J].生态学报,2015,35(8):2536-2544. |
| GU C H, Wang Y X, BAI S B,et al.Tolerance and accumulation of four ornamental species seedlings to soil cadmium contamination[J].Acta Ecologica Sinica,2015,35(8):2536-2544. | |
| [30] | 鲁艳,李新荣,何明珠,等.Ni和Cu胁迫对骆驼蓬抗氧化酶活性的影响[J].草业学报,2012,21(3):147-155. |
| LU Y, LI X R, HE M Z,et al.Effects of Ni and Cu on antioxidative enzymes in Peganum harmala [J].Acta Prataculturae Sinica,2012,21(3):147-155. | |
| [31] | 查应琴,潘凤,关萍.镉胁迫对鸡冠花种子萌发及幼苗生理生化特性的影响[J].西北植物学报,2020,40(11):1900-1908. |
| ZHA Y Q, PAN F, GUAN P.Seed germination and seedling physiological and biochemical characteristics of Celosia cristata L.under cadmium stress[J].Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica,2020,40(11):1900-1908. | |
| [32] | WEI S H, ZHOU Q X, WANG X,et al.A newly-discovered Cd-hyper accumulator Solatium nigrum L.[J].Chinese Science Bulletin,2005,50(1):33-38. |
| [33] | 周健民,沈仁芳.土壤学大辞典[M].北京:科学出版社,2013. |
| ZHOU J M, SHEN R F.Dictionary of soil science[M].Beijing:Science Press,2013. | |
| [34] | BAKER A J M, BROOKS R R.Terrestrial higher plants which hyperaccumulate metallic elements-a review of their distribution,ecology and phytochemistry[J].Biorecovery,1989,1(2):81-126. |
| [35] | 康育鑫,廖水兰,兰婕,等.镉胁迫对不同叶用莴苣品种生长及生理特性的影响[J].江苏农业科学,2021,49(7):149-154. |
| KANG Y X, LIAO S L, LAN J,et al.Effects of cadmium stress on the growth and physiological characteristics of different types of leaf lettuce[J].Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences,2021,49(7):149-154. | |
| [36] | 何俊瑜,任艳芳,王阳阳,等.不同耐性水稻幼苗根系对镉胁迫的形态及生理响应[J].生态学报,2011,31(2):522-528. |
| HE J Y, REN Y F, WANG Y Y,et al.Root morphological and physiological response of rice seedlings with different tolerance to cadmium stress[J].Acta Ecologica Sinica,2011,31(2):522-528. | |
| [37] | 贾莲,张冬,张吉斯,等.镉胁迫对忍冬抗氧化酶活性及内源激素含量的影响[J].地球与环境,2024,52(1):21-28. |
| JIA L, ZHANG D, ZHANG J S,et al.Effect of cadmium stress on antioxidant enzyme activity and endogenous hormones content in Lonicera japonica Thunb[J].Earth and Environment,2024,52(1):21-28. | |
| [38] | 田小霞,毛培春,郭强,等.镉胁迫对马蔺根系形态及部分生理指标的影响[J].西北植物学报,2019,39(6):1105-1113. |
| TIAN X X, MAO P C, GUO Q,et al.Effect of cadmium on root morphology and partial physiological indexes of Iris lactea var.chinensis [J].Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica,2019,39(6):1105-1113. | |
| [39] | DAI H P, WEI S H, TWARDOWSKA I. et al.Hyperaccumulating potential of Bidens pilosa L. for Cd and elucidation of its translocation behavior based on cell membrane permeability[J].Environmental Science and Pollution Research,2017,24:23161-23167. |
| [40] | WEI S H, BAI J Y, YANG C J,et al.Compound amino acids added in media improved Solanum nigrum L. phytoremediating CD-PAHS contaminated soil[J].International Journal of Phytoremediation,2016,18(4):358-363. |
| [41] | 杨叶萍,简敏菲,余厚平,等.镉胁迫对苎麻(Boehmeria nivea)根系及叶片抗氧化系统的影响[J].生态毒理学报,2016,11(4):184-193. |
| YANG Y P, JIANG M F, YU H P,et al.Influence on the antioxidant system in roots and leaves of Boehmeria nivea under different cadmium stress [J].Asian Journal of Ecotoxicology,2016,11(4):184-193. | |
| [42] | 杨海燕,施国新,徐勤松,等.Cd2+胁迫对竹叶眼子菜的毒理学效应分析[J].应用与环境生物学报,2008,14(3):366-370. |
| YANG H Y, SHI G X, XU Q S,et al.Phytotoxicity of Cd2+ on leaf cells of Potamogeton malaianus [J].Chinese Journal of Applied and Environmental Biology,2008,14(3):366-370. | |
| [43] | 马鑫颖,宋晨,孟妍君,等.外源褪黑素对镉胁迫下棉花种子萌发、抗氧化酶活性及渗透调节物质含量的影响[J].棉花学报,2023,35(4):313-324. |
| MA X Y, SONG C, MENG Y J,et al.Effects of exogenous melatonin on germination,antioxidant enzymes activity,and osmotic adjustment substance content of cotton seed under cadmium stress[J].Cotton Science,2023,35(4):313-324. | |
| [44] | 张阿芳,张庆,代惠萍,等.镉胁迫对银灰杨根和叶片渗透调节物质的影响[J].西北林学院学报,2018,33(2):83-87. |
| ZHANG A F, ZHANG Q, DAI H P,et al.Effects of cadmium stress on the osmotic adjustment substance of Populus canecens in leaves and roots[J].Journal of Northwest Forestry University,2018,33(2):83-87. | |
| [45] | DINAKAR N, NAGAJYOTHI P C, SURESH S,et al.Cadmium induced changes on proline,antioxidant enzymes,nitrate and nitrite reductases in Arachis hypogaea L.[J].Journal of Environmental Biology,2009,30(2):289-294. |
| [46] | KHAN M R, NAZIR F, ASGHER M,et al.Selenium and sulfur influence ethylene formation and alleviate cadmium-induced oxidative stress by improving proline and glutathione production in wheat[J].Journal of Plant Physiology,2015,173:9-18. |
| [47] | HAYAT S, HAYAT Q, ALYEMENI M N,et al.Proline enhances antioxidative enzyme activity,photosynthesis and yield of Cicer arietinum L. exposed to cadmium stress[J].Acta Botanica Croatica,2013,72(2):323-335. |
| [48] | CUTRARO J, GOLDSTEIN N.Cleaning up contaminants with plants[J].BioCycle:Journal of Composting & Recycling,2005,46:3-32. |
| [49] | 苏明洁,廖源林,叶充,等.镉胁迫下苦楝(Melia azedarach L.)幼苗的生长及生理响应[J].农业环境科学学报,2016,35(11):2086-2093. |
| SU M J, LIAO Y L, YE C,et al.The growth and physiological responses of Melia azedarach L. seedlings to cadmium stress[J].Journal of Agro-Environment Science,2016,35(11):2086-2093. | |
| [50] | 铁得祥,胡红玲,喻秀艳,等.桢楠幼树光合特性对镉胁迫的响应[J].生态学报,2020,40(11):3738-3746. |
| TIE D X, HU H L, YU X Y,et al.Responses of photosynthetic characteristics and chlorophyll fluorescence parameters of Phoebe zhennan saplings to cadmium stress[J].Acta Ecologica Sinica,2020,40(11):3738-3746. | |
| [51] | POZO A D, PÉREZ P, MORCUENDE R,et al.Acclimatory responses of stomatal conductance and photosynthesis to elevated CO2 and temperature in wheat crops grown at varying levels of N supply in a Mediterranean environment[J].Plant Science,2005,169(5):908-916. |
| [52] | 赵弘益,管珏镧,张雪媛,等.土壤镉胁迫对檫木光合特性的影响[J].植物研究,2021,41(4):506-513. |
| ZHAO H Y, GUAN J L, ZHANG X Y,et al.Photosynthetic characteristics of Sassafras tzumu under cadmium stress in soil[J].Bulletin of Botanical Research,2021,41(4):506-513. | |
| [53] | 张磊,于燕玲,张磊.外源镉胁迫对玉米幼苗光合特性的影响[J].华北农学报,2008,23(1):101-104. |
| ZHANG L, YU Y L, ZHANG L.Influence of added cadmium stress on photosynthetic characteristics of maize in seedling stage[J].Acta Agriculturae Boreali-Sinica,2008,23 (1):101-104. | |
| [54] | 苏玲,章永松,林咸永,等.维管植物的镉毒和耐性机制[J].植物营养与肥料学报,2000,6 (1):106 -112. |
| SU L, ZHANG Y S, LIN X Y,et al.Cadmium toxicity and tolerance in vascular plants[J].Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers,2000,6 (1):106-112. | |
| [55] | 刘会超,刘孟刚,姚连芳,等.镉胁迫对银条生物量及光合特性的影响[J].华北农学报,2010,25(4):162-165. |
| LIU H C, LIU M G, YAO L F,et al.Effects of cadmium stress on biomass and photosynthetic characteristics of Stachys floridana [J].Acta Agriculturae Boreali-Sinica,2010,25(4):162-165. | |
| [56] | 简敏菲,杨叶萍,余厚平,等.不同浓度Cd2+胁迫对苎麻叶绿素及其光合荧光特性的影响[J].植物生理学报,2015,51 (8):1331-1338. |
| JIAN M F, YANG Y P, YU H P,et al.Influences of different cadmium concentration stress on chlorophyll and its photosynthetic fluorescence characteristics of Ramie (Boehmeria nivea)[J].Plant Physiology Journal,2015,51(8):1331-1338. |
| [1] | Baojie TONG, Dongying DAN, Jiawei LI. Research Progress on Heat Tolerance and Regulatory Strategies of Plant Leaves [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2025, 45(2): 171-180. |
| [2] | Jianan GUO, Yipeng ZHAO, Yuanzhi YANG, Qingjie GUAN. Roles of Superoxide Dismutase in Plant Response to Drought, Salinity and Cold Stress [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2024, 44(4): 481-490. |
| [3] | Hongzheng WANG, Shaolian YU, Yuehua MA, Lingyun REN, Hongwei NI. Analysis of the Alleviating Mechanism of Selenium on Cadmium Stress in Astragalus membranaceus [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2024, 44(4): 565-575. |
| [4] | Yajie LIU, Lizhe AN. Nitric Oxide Mediates Brassinosteroids-induced Chilling Tolerance in Chorispora bungeana Suspension Cultured Cells [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2024, 44(1): 118-131. |
| [5] | Luhua ZHOU, Junyi FANG, Zimo XIONG, Weifeng WU, Jiarui LIU, Qiao LU, Hongqing LING, Danyu KONG. Evaluation on Waterlogging Tolerance of Different Tomato Germplasm [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2023, 43(5): 657-666. |
| [6] | Jingzhe WANG, Chaokui NIU, Xinyuan LIANG, Chenjing SHEN, Jing YIN. Regulation of Salicylic Acid on Tolerance to Saline Alkali Stress at Seedling Stages of Betula platyphylla [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2023, 43(3): 379-387. |
| [7] | Anying HUANG, Dean XIA, Yang ZHANG, Dongchen NA, Qing YAN, Zhigang WEI. Cloning and Drought Tolerance Expression Analysis of PtrWRKY51 Gene in Populus trichocarpa [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2022, 42(6): 1005-1013. |
| [8] | Xin’ai ZHONG, Shiqi MENG, Wanting Zhou, Qi YAO, Qiong ZHANG, Wang XING, Dali LIU. Identification of Glutathione S-transferase Gene Family in Sugar Beet and the Response to Cadmium Stress [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2022, 42(5): 790-801. |
| [9] | Bing GAO, Pengfei GAO, Weifang FAN, Zhenghong FENG, Jianhui WU. Effects of Cadmium Stress on the Root Structure and Physiology of Symbiont of Potentilla sericea and Arbuscular Mycorrhizal fungi [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2022, 42(4): 647-656. |
| [10] | Hong-Yi ZHAO, Jue-Lan GUAN, Xue-Yuan ZHANG, Qing LIANG, Jian ZHANG, Hong-Ling HU. Photosynthetic Characteristics of Sassafras tzumu under Cadmium Stress in Soil [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2021, 41(4): 506-513. |
| [11] | He-Xian JIN, Xu-Yue SHEN, Rong-Rong CHEN, Zhen WU, Ya-Mei SHEN, Dong-Mei ZHANG. Effects of NaCl Stress on Morphological and Physiological Characteristics of Magnolia denudata Desr. [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2021, 41(4): 596-603. |
| [12] | Dong QIU, Jing ZHANG, Nan WU, Ye TAO. Effects of Micro-habitats on Water Retention and Loss of a Drought-tolerant Saxicolous Moss Grimmia pilifera [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2021, 41(2): 180-190. |
| [13] | SONG Zi-Wen, LIU Huan-Zhen, MA Xiao-Yu, SUN Guo-Yu, YI Jia-Xin, ZHANG Chun-Hua, YOU Yuan-Xiang, WANG De-Qiu, LI Kai-Long. Effects of Cadmium Stress on Growth,Physiology and Biochemistry of Different Ploidy of Populus ussuriensis [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2020, 40(5): 728-734. |
| [14] | GUAN Tao, LIU Chao, LI Kai-Long, XIA De-An, MA Xu-Jun. Function of Populus trichocarpa HDA902 Gene in Response to Cold Stress [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2020, 40(2): 251-256. |
| [15] | LI Zi-Yi, HE Zi-Hang, LU Hui-Jun, WANG Yu-Cheng, JI Xiao-Yu. Study on Salt Tolerance of AtUNE12 Gene in Arabidopsis thaliana [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2020, 40(2): 257-265. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||