Bulletin of Botanical Research ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (4): 603-613.doi: 10.7525/j.issn.1673-5102.2025.04.012
• Original Paper • Previous Articles Next Articles
Minwei CHAI1,2, Yifan WU1,2, Ruili LI1,2, Lin ZHOU1,2, Xiaoxue SHEN1,2( )
)
Received:2025-01-06
Online:2025-07-20
Published:2025-07-25
Contact:
Xiaoxue SHEN
E-mail:shenxxy@pku.edu.cn
CLC Number:
Minwei CHAI, Yifan WU, Ruili LI, Lin ZHOU, Xiaoxue SHEN. The Influence of Cadmium, Microplastics, and Their Combination on the Growth and Photosynthetic Characteristics of Kandelia obovata[J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2025, 45(4): 603-613.
Table 1
The experimental setup with combined cadmium and microplastics stresses
处理组 Treatment group | 处理方式 Treatment method |
|---|---|
| Cd0N-MPs | 不添加MPs和Cd |
| Cd0PE-L | 830 μm PE(5%) |
| Cd0PE-S | 13 μm PE(5%) |
| Cd0PVC-L | 830 μm PVC(5%) |
| Cd0PVC-S | 13 μm PVC(5%) |
| Cd5N-MPs | Cd(5 mg·kg-1) |
| Cd5PE-L | Cd(5 mg·kg-1)+830 μm PE(5%) |
| Cd5PE-S | Cd(5 mg·kg-1)+13 μm PE(5%) |
| Cd5PVC-L | Cd(5 mg·kg-1)+830 μm PVC(5%) |
| Cd5PVC-S | Cd(5 mg·kg-1)+13 μm PVC(5%) |
| Cd50N-MPs | Cd(50 mg·kg-1) |
| Cd50PE-L | Cd(50 mg·kg-1)+830 μm PE(5%) |
| Cd50PE-S | Cd(50 mg·kg-1)+13 μm PE(5%) |
| Cd50PVC-L | Cd(50 mg·kg-1)+830 μm PVC(5%) |
| Cd50PVC-S | Cd(50 mg·kg-1)+13 μm PVC(5%) |
Fig.2
Root(A),stem(B),leaf(C),total biomass(D) and root-to-shoot ratio(E)of Kandelia obovata exposed to combined cadmium and microplastics stressesN-MPs. No MPs added; PE-L. Large particle of PE; PE-S. Small particle of PE; PVC-L. Large particle of PVC; PVC-S. Small particle of PVC. Mean±SD. In the same cadmium treatment, different lowercase letters indicated significant differences among microplastics treatments(P<0.05).
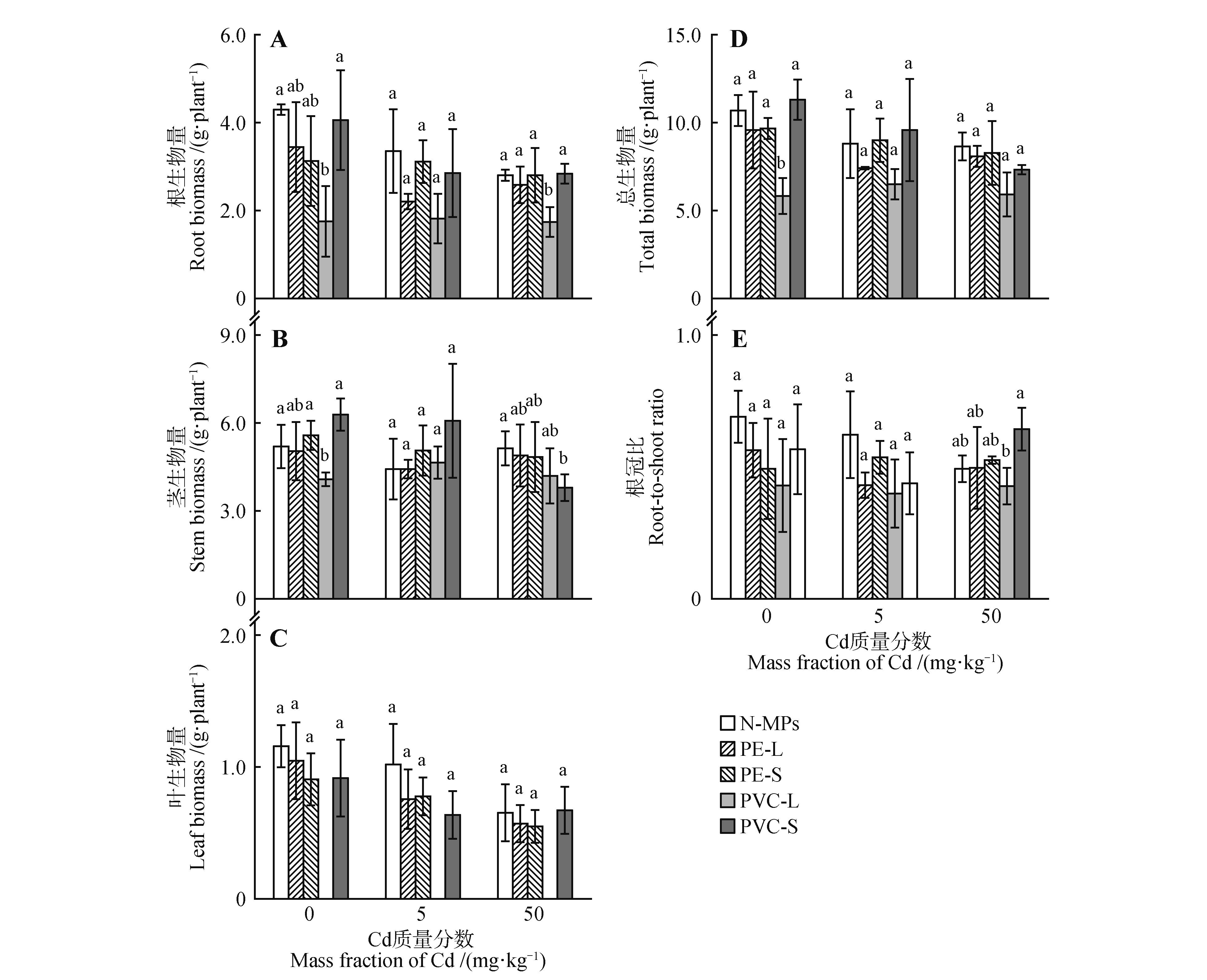
Table 2
Two-way ANOVA of effects of Cd,MPs,and their interactions on plant growth of Kandelia obovata
指标 Indicators | 变异来源 Sources | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PE | Cd | PE×Cd | PVC | Cd | PVC×Cd | |
| 根生物量 Root biomass | 0.75 | 1.52 | 1.17 | 17.02** | 1.22 | 1.32 |
| 茎生物量 Stem biomass | 3.10 | 2.07 | 0.02 | 1.34 | 16.55*** | 0.11 |
| 叶生物量 Leaf biomass | 0.26 | 6.72* | 0.27 | — | — | — |
| 总生物量 Total biomass | 0.72 | 2.22 | 0.59 | 22.62*** | 2.75 | 2.88 |
| 根冠比 Root-shoot ratio | 0.30 | 2.27 | 0.77 | 2.72 | 8.68** | 4.47* |
| 叶Na含量 Leaf Na content | 22.77** | 17.60** | 0.40 | — | — | — |
| 叶K含量 Leaf K content | 3.12 | 1.23 | 3.36 | — | — | — |
| 叶Ca含量 Leaf Ca content | 0.10 | 13.16** | 1.56 | — | — | — |
| 叶Mg含量 Leaf Mg content | 0.05 | 19.05** | 7.28* | — | — | — |
| 叶叶绿素a含量 Leaf chlorophyll a content | 1.21 | 5.43* | 4.15* | — | — | — |
| 叶叶绿素b含量 Leaf chlorophyll b content | 1.65 | 4.56* | 3.21 | — | — | — |
| 叶类胡萝卜素含量 Leaf carotenoids content | 0.30 | 8.33** | 2.22 | — | — | — |
| 叶总叶绿素含量 Leaf total chlorophyll content | 1.48 | 4.99* | 3.94* | — | — | — |
| 叶净光合速率 Leaf Pn | 8.23** | 64.70*** | 0.55 | — | — | — |
| 叶气孔导度 Leaf Gs | 12.43*** | 23.57*** | 41.79*** | — | — | — |
| 叶蒸腾速率 Leaf Tr | 0.34 | 34.97*** | 44.10*** | — | — | — |
| 叶水分利用效率 Leaf EWU | 0.56 | 132.51*** | 103.47*** | — | — | — |
| 叶最大光化学量子产量 Leaf Fv/Fm | 0.18 | 10.65** | 3.11 | — | — | — |
| 叶实际光化学量子产量 Leaf Y(Ⅱ) | 0.08 | 79.17*** | 5.18* | — | — | — |
| 叶电子传递速率 Leaf ETR | 0.08 | 79.17*** | 5.18* | — | — | — |
| 叶光化学淬灭系数 Leaf qP | 0.43 | 33.04*** | 1.25 | — | — | — |
| 叶非光化学淬灭系数 Leaf NPQ | 0.62 | 15.15*** | 1.51 | — | — | — |
| 叶PSⅡ调节性能量耗散的量子产量 Leaf Y(NPQ) | 0.73 | 29.24*** | 2.46 | — | — | — |
| 叶PSⅡ非调节性能量耗散的量子产量 Leaf Y(NO) | 0.72 | 0.92 | 0.81 | — | — | — |
| 光化学耗散的相对份额 Leaf P | 0.08 | 79.17*** | 5.18* | — | — | — |
| 非光化学耗散的相对份额 Leaf Ex | 0.68 | 15.75*** | 0.64 | — | — | — |
| 天线热耗散份额Leaf D | 2.01 | 73.90*** | 6.02* | — | — | — |
Table 3
The nutrient element in Kandelia obovata leaves exposed to combined cadmium and microplastics stresses
组别 Group | 元素质量分数 Element mass fraction/(mg·g-1) | Na∶K | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Na | K | Ca | Mg | ||
| Cd0N-MPs | 10.60±2.46a | 24.30±1.01a | 11.24±1.45a | 7.63±0.73a | 0.44±0.12a |
| Cd0PE-L | 6.01±0.90a | 17.99±2.14b | 12.05±1.63a | 7.04±0.82a | 0.34±0.07a |
| Cd0PE-S | 7.82±1.53a | 12.05±1.17c | 9.27±0.36a | 5.87±0.45a | 0.61±0.09a |
| Cd0PVC-L | — | — | — | — | — |
| Cd0PVC-S | 7.00±1.87a | 13.57±2.71c | 9.43±0.41a | 6.18±1.11a | 0.51±0.07a |
| Cd5N-MPs | 11.08±3.76a | 16.82±1.03b | 9.54±2.04a | 6.41±1.39a | 0.66±0.21a |
| Cd5PE-L | 11.72±1.51a | 22.23±1.54a | 10.79±3.17a | 6.94±1.29a | 0.53±0.05a |
| Cd5PE-S | 7.23±2.19a | 22.35±4.20ab | 11.90±0.52a | 8.10±0.35a | 0.34±0.16a |
| Cd5PVC-L | — | — | — | — | — |
| Cd5PVC-S | 7.84±0.30a | 19.25±±1.07ab | 9.18±1.53a | 6.45±0.49a | 0.41±0.02a |
| Cd50N-MPs | 8.58±1.93b | 23.28±1.34a | 10.28±0.98a | 6.56±0.66a | 0.37±0.08a |
| Cd50PE-L | 14.69±1.55a | 23.57±1.70a | 7.94±2.62ab | 6.28±0.27a | 0.63±0.09a |
| Cd50PE-S | 11.24±1.10ab | 16.90±5.20b | 6.05±0.45b | 5.31±0.28b | 0.70±0.19a |
| Cd50PVC-L | — | — | — | — | — |
| Cd50PVC-S | 8.63±2.51b | 11.96±1.14b | 10.21±1.40a | 7.14±0.50a | 0.70±0.25a |
Fig.3
Leaf chlorophyll a(A),chlorophyll b(B),carotenoid(C),total chlorophyll(D),net photosynthetic rate Pn(E),stomatal conductance Gs(F), transpiration rate Tr(G) and water use efficiency EWU(H) of Kandelia obovata exposed to combined cadmium and microplastics stressesN-MPs. No MPs added; PE-L. Large particle of PE; PE-S. Small particle of PE; PVC-L. Large particle of PVC; PVC-S. Small particle of PVC. Mean±SD. In the same cadmium treatment, different lowercase letters indicated significant differences among microplastics treatments(P<0.05).
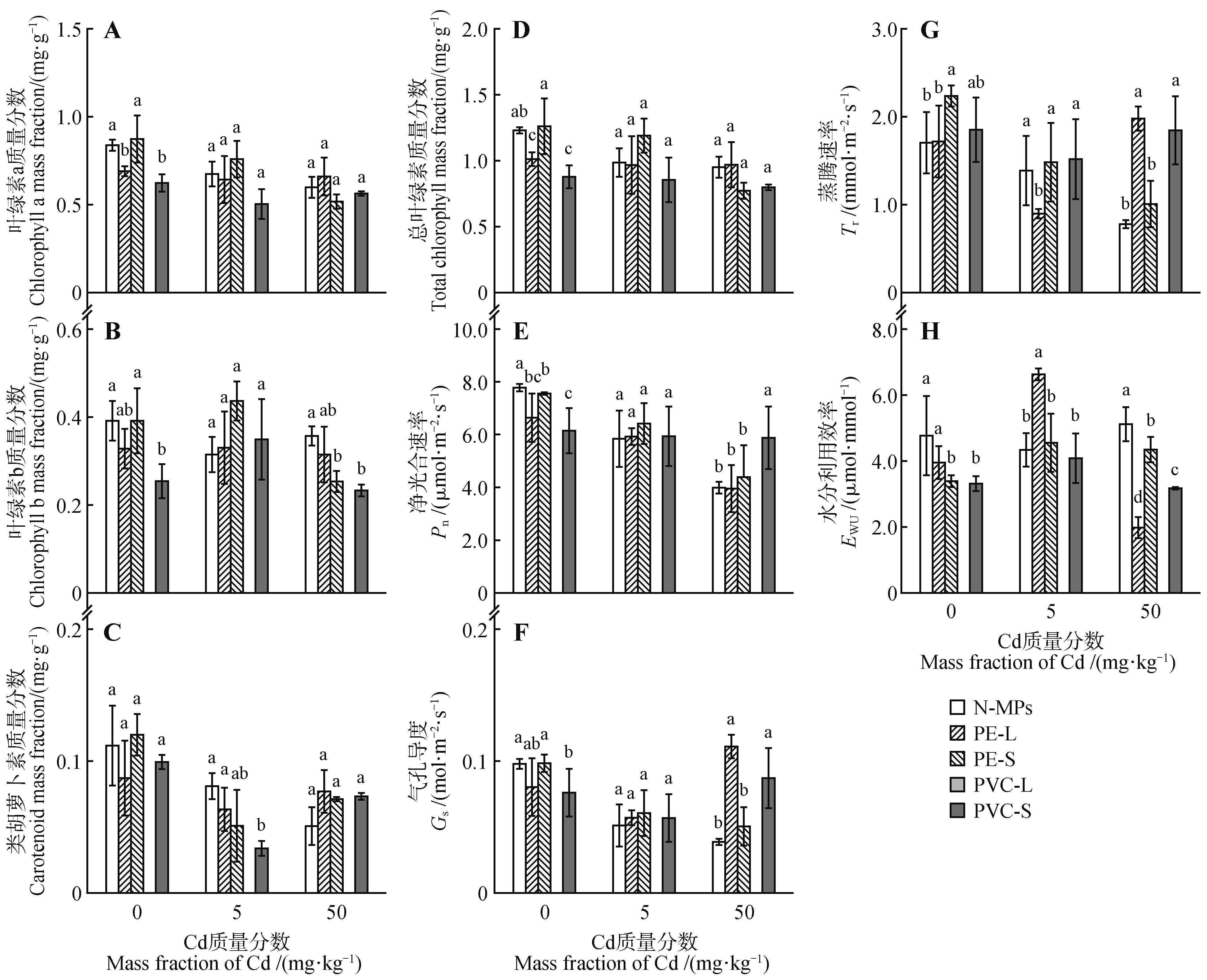
Table 4
Characteristics of leaf fluorescence parameters of Kandelia obovata exposed to combined cadmium and microplastics stresses
组别 Group | 最大光化学量 子产量Fv/Fm | 实际光化学量 子产量Y(Ⅱ) | 电子传递 速率ETR | 光化学淬 灭系数qP | 非光化学 淬灭系数NPQ | PSⅡ调节性能量 耗散的量子产量 Y(NPQ) | PSⅡ非调节性能量耗散的量子产量Y(NPQ) | 光化学耗散的 相对份额P | 非光化学耗散 的相对份额Ex | 天线热耗 散份额D |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cd0N-MPs | 0.813±0.037a | 0.67±0.02a | 38.75±1.20a | 0.911±0.029a | 0.20±0.04a | 0.06±0.01a | 0.27±0.01a | 0.67±0.02a | 0.066±0.021c | 0.260±0.008b |
| Cd0PE-L | 0.811±0.011a | 0.64±0.03ab | 36.66±1.42ab | 0.880±0.035ab | 0.26±0.13a | 0.07±0.03a | 0.29±0.01a | 0.64±0.03ab | 0.087±0.025bc | 0.276±0.001ab |
| Cd0PE-S | 0.813±0.009a | 0.60±0.02bc | 34.74±0.95bc | 0.854±0.008bc | 0.37±0.10a | 0.11±0.03a | 0.29±0.01a | 0.60±0.02bc | 0.103±0.009ab | 0.293±0.025a |
| Cd0PVC-L | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| Cd0PVC-S | 0.811±0.002a | 0.59±0.02c | 33.63±1.25c | 0.816±0.028c | 0.30±0.05a | 0.10±0.01a | 0.32±0.02a | 0.59±0.02c | 0.132±0.020a | 0.283±0.004ab |
| Cd5N-MPs | 0.807±0.006ab | 0.56±0.02a | 31.99±1.15a | 0.814±0.024a | 0.42±0.04a | 0.13±0.01a | 0.31±0.02a | 0.56±0.02a | 0.127±0.016a | 0.317±0.005a |
| Cd5PE-L | 0.799±0.006b | 0.57±0.01a | 32.80±0.58a | 0.838±0.011a | 0.42±0.04a | 0.13±0.01a | 0.30±0.01a | 0.57±0.01a | 0.110±0.007a | 0.320±0.003a |
| Cd5PE-S | 0.809±0.003a | 0.62±0.04a | 35.44±2.29a | 0.855±0.044a | 0.27±0.09a | 0.08±0.03a | 0.30±0.01a | 0.62±0.04a | 0.104±0.031a | 0.280±0.018b |
| Cd5PVC-L | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| Cd5PVC-S | 0.804±0.009ab | 0.58±0.02a | 33.02±0.90a | 0.836±0.017a | 0.39±0.07a | 0.12±0.02a | 0.31±0.02a | 0.57±0.02a | 0.113±0.009a | 0.310±0.021a |
| Cd50N-MPs | 0.782±0.005ab | 0.44±0.02c | 25.40±1.31c | 0.763±0.029ab | 1.08±0.13a | 0.29±0.01a | 0.27±0.02a | 0.44±0.02c | 0.137±0.016bc | 0.422±0.012a |
| Cd50PE-L | 0.795±0.003ab | 0.48±0.01b | 27.34±0.53b | 0.768±0.004b | 0.80±0.07a | 0.23±0.01b | 0.29±0.01a | 0.48±0.01b | 0.143±0.004ab | 0.381±0.012b |
| Cd50PE-S | 0.777±0.019b | 0.47±0.01b | 27.13±0.67b | 0.755±0.009b | 0.67±0.29ab | 0.21±0.06bc | 0.32±0.06a | 0.47±0.01b | 0.153±0.006a | 0.376±0.012b |
| Cd50PVC-L | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| Cd50PVC-S | 0.804±0.003a | 0.56±0.02a | 31.92±1.24a | 0.825±0.009a | 0.47±0.05b | 0.14±0.01c | 0.30±0.02a | 0.56±0.02a | 0.118±0.003c | 0.327±0.020c |
| [1] | SHI C, YU L Y, CHAI M W,et al.The distribution and risk of mercury in Shenzhen mangroves,representative urban mangroves affected by human activities in China[J].Marine Pollution Bulletin,2020,151:110866. |
| [2] | RAHMAN S U, HAN J C, ZHOU Y,et al.Adaptation and remediation strategies of mangroves against heavy metal contamination in global coastal ecosystems:a review[J].Journal of Cleaner Production,2024,441:140868. |
| [3] | CHEN Z L, LEE S Y.Contribution of microplastics to carbon storage in coastal wetland sediments[J].Environmental Science & Technology Letters,2021,8(12):1045-1050. |
| [4] | RICO A, REDONDO-HASSELERHARM P E, SCHELL T,et al.Microplastic burial potential and ecological risks in mangrove forests of the Amazon River delta[J].Science of the Total Environment,2024,957:177666. |
| [5] | GUO J J, HUANG X P, XIANG L,et al.Source,migration and toxicology of microplastics in soil[J].Environment International,2020,137:105263. |
| [6] | 刘加强,崔陆,周子振,等.土壤中微塑料:类型、载体效应、迁移行为和潜在风险综述[J].生态学报,2024,44(9):3586-3599. |
| LIU J Q, CUI L, ZHOU Z Z,et al.Microplastics in soils:a review of types,carrier effects,migration behavior,and potential risks[J].Acta Ecologica Sinica,2024,44(9):3586-3599. | |
| [7] | MAI L, HE H, BAO L J,et al.Plastics are an insignificant carrier of riverine organic pollutants to the coastal oceans[J].Environmental Science & Technology,2020,54(24):15852-15860. |
| [8] | DENG J, GUO P Y, ZHANG X Y,et al.Microplastics and accumulated heavy metals in restored mangrove wetland surface sediments at Jinjiang Estuary(Fujian,China)[J].Marine Pollution Bulletin,2020,159:111482. |
| [9] | 刘倡君,罗专溪,闫钰,等.九龙江口红树林湿地表层沉积物中微塑料赋存特征与重金属的关系[J].环境科学,2022,43(1):239-246. |
| LIU C J, LUO Z X, YAN Y,et al.Occurrence characteristics of microplastics in mangrove sediments in the Jiulong River estuary and the association with heavy metals[J].Environmental Science,2022,43(1):239-246. | |
| [10] | 吴萍,张杏锋,高波,等.微塑料对超富集植物少花龙葵Cd累积的影响[J].环境科学与技术,2022,45(1):174-181. |
| WU P, ZHANG X F, GAO B,et al.Effects of polyethylene on Cd accumulation of hyperaccumulator Solanum photeinocarpum [J].Environmental Science & Technology,2022,45(1):174-181. | |
| [11] | WANG F Y, ZHANG X Q, ZHANG S Q,et al.Effects of co-contamination of microplastics and Cd on plant growth and Cd accumulation[J].Toxics,2020,8(2):36. |
| [12] | ZHANG Z Q, LI Y, QIU T Y,et al.Microplastics addition reduced the toxicity and uptake of cadmium to Brassica chinensis L[J].Science of the Total Environment,2022,852:158353. |
| [13] | 王泽正,杨亮,李婕,等.微塑料和镉及其复合对水稻种子萌发的影响[J].农业环境科学学报,2021,40(1):44-53. |
| WANG Z Z, YANG L, LI J,et al.Single and combined effects of microplastics and cadmium on the germination characteristics of rice seeds[J].Journal of Agro-Environment Science,2021,40(1):44-53. | |
| [14] | 刘沙沙,杨越,吴静华.微(纳)米塑料介导下多环芳烃的毒性效应研究进展[J].肇庆学院学报,2022,43(2):61-65. |
| LIU S S, YANG Y, WU J H.Toxic effects of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons mediated by micro (nano) plastics[J].Journal of Zhaoqing University,2022,43(2):61-65. | |
| [15] | WANG B B, WANG P H, ZHAO S B,et al.Combined effects of microplastics and cadmium on the soil-plant system:phytotoxicity,Cd accumulation and microbial activity[J].Environmental Pollution,2023,333:121960. |
| [16] | CAO Y X, ZHAO M J, Ma X Y,et al.A critical review on the interactions of microplastics with heavy metals:mechanism and their combined effect on organisms and humans[J].Science of the Total Environment,2021,788:147620. |
| [17] | HUANG F Y, CHEN L, YANG X,et al.Unveiling the impacts of microplastics on cadmium transfer in the soil-plant-human system:a review[J].Journal of Hazardous Materials,2024,477:135221. |
| [18] | 李荣玉,邱国玉,沈小雪,等.镉胁迫下铵态氮对红树植物秋茄(Kandelia obovata)生理生态特征的影响[J].植物研究,2018,38(5):653-660. |
| LI R Y, QIU G Y, SHEN X X,et al.Effects of ammonium nitrogen on physiological and ecological characteristics of Kandelia obovata under cadmium stress[J].Bulletin of Botanical Research,2018,38(5):653-660. | |
| [19] | CHAI M W, LI R L, LI B,et al.Responses of mangrove (Kandelia obovata) growth,photosynthesis,and rhizosphere soil properties to microplastic pollution[J].Marine Pollution Bulletin,2023,189:114827. |
| [20] | NACARIO P B,ALFAFARA P A M, CENIZA N A M,et al.Uptake,growth,and oxidative stress responses of Rhizophora mucronata (Poir.in Lam.) propagules exposed to high-density polyethylene microplastics[J].Marine Pollution Bulletin,2025,212:117569. |
| [21] | DAI M Y, LU H L, LIU W W,et al.Phosphorus mediation of cadmium stress in two mangrove seedlings Avicennia marina and Kandelia obovata differing in cadmium accumulation[J].Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety,2017,139:272-279. |
| [22] | CHAI M W, LI R L, DING H,et al.Occurrence and contamination of heavy metals in urban mangroves:a case study in Shenzhen,China[J].Chemosphere,2019,219:165-173. |
| [23] | FULLER S, GAUTAM A.A procedure for measuring microplastics using pressurized fluid extraction[J].Environmental Science & Technology,2016,50(11):5774-5780. |
| [24] | FEI Y F, HUANG S Y, ZHANG H B,et al.Response of soil enzyme activities and bacterial communities to the accumulation of microplastics in an acid cropped soil[J].Science of the Total Environment,2020,707:135634. |
| [25] | 郝再彬,苍晶,徐仲.植物生理实验[M].哈尔滨:哈尔滨工业大学出版社,2004. |
| HAO Z B, CANG J, XU Z.Plant physiological experiment[M].Harbin:Harbin Industrial University Press,2004. | |
| [26] | GENTY B, BRIANTAIS J M, BAKER N R.The relationship between the quantum yield of photosynthetic electron transport and quenching of chlorophyll fluorescence[J].Biochimica et Biophysica Acta(BBA)-General Subjects,1989,990(1):87-92. |
| [27] | 张守仁.叶绿素荧光动力学参数的意义及讨论[J].植物学通报,1999,16(4):444-448. |
| ZHANG S R.A discussion on chlorophyll fluorescence kinetics parameters and their significance[J].Chinese Bulletin of Botany,1999,16(4):444-448 | |
| [28] | KLUGHAMMER C, SCHREIBER U.Saturation pulse method for assessment of energy conversion in PSⅠ[J].PAM Application Notes,2008,1:11-14. |
| [29] | DEMMIG-ADAMS B, ADAMS W W, BARKER D H,et al.Using chlorophyll fluorescence to assess the fraction of absorbed light allocated to thermal dissipation of excess excitation[J].Physiologia Plantarum,1996,98(2):253-264. |
| [30] | 杨杰,李连祯,周倩,等.土壤环境中微塑料污染:来源、过程及风险[J].土壤学报,2021,58(2):281-298. |
| YANG J, LI L Z, ZHOU Q,et al.Microplastics contamination of soil environment:sources,processes and risks[J].Acta Pedologica Sinica,2021,58(2):281-298. | |
| [31] | WANG F Y, ZHANG X Q, ZHANG S Q,et al.Interactions of microplastics and cadmium on plant growth and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal communities in an agricultural soil[J].Chemosphere,2020,254:126791. |
| [32] | 陈欣,郭薇,李济之,等.土壤微塑料影响植物生长的因素与机制研究进展[J].农业环境科学学报,2024,43(3):488-495. |
| CHEN X, GUO W, LI J Z,et al.Research progress on the influencing factors and mechanisms of soil microplastics on plant growth[J].Journal of Agro-Environment Science,2024,43(3):488-495. | |
| [33] | URBINA M A, CORREA F, ABURTO F,et al.Adsorption of polyethylene microbeads and physiological effects on hydroponic maize[J].Science of the Total Environment,2020,741:140216. |
| [34] | QI Y L, YANG X M, PELAEZ A M,et al.Macro- and micro- plastics in soil-plant system:effects of plastic mulch film residues on wheat (Triticum aestivum) growth[J].Science of the Total Environment,2018,645:1048-1056. |
| [35] | JIANG X F, CHEN H, LIAO Y C,et al.Ecotoxicity and genotoxicity of polystyrene microplastics on higher plant Vicia faba [J].Environmental Pollution,2019,250:831-838. |
| [36] | DE SOUZA MACHADO A A, LAU C W, KLOAS W,et al.Microplastics can change soil properties and affect plant performance[J].Environmental Science & Technology,2019,53(10):6044-6052. |
| [37] | JAMES R A, MUNNS R, VON CAEMMERER S,et al.Photosynthetic capacity is related to the cellular and subcellular partitioning of Na+,K+ and Cl- in salt-affected barley and durum wheat[J].Plant,Cell & Environment,2006,29(12):2185-2197. |
| [38] | GOGORCENA Y, LARBI A, ANDALUZ S,et al.Effects of cadmium on cork oak(Quercus suber L.) plants grown in hydroponics[J].Tree Physiology,2011,31(12):1401-1412. |
| [39] | 李贞霞,李庆飞,李瑞静,等.黄瓜幼苗对微塑料和镉污染的生理响应[J].农业环境科学学报,2020,39(5):973-981. |
| LI Z X, LI Q F, LI R J,et al.Physiological response of cucumber seedlings to microplastics and cadmium[J].Journal of Agro-Environment Science,2020,39(5):973-981. | |
| [40] | WANG J L, LIU W T, WANG X,et al.Assessing stress responses in potherb mustard (Brassica juncea var. multiceps) exposed to a synergy of microplastics and cadmium:insights from physiology,oxidative damage,and metabolomics[J].Science of the Total Environment,2024,907:167920. |
| [41] | ZOUARI M, AHMED C BEN, ZORRIG W,et al.Exogenous proline mediates alleviation of cadmium stress by promoting photosynthetic activity,water status and antioxidative enzymes activities of young date palm (Phoenix dactylifera L.)[J].Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety,2016,128:100-108. |
| [42] | YAN Z Z, TAM N F Y.Effects of lead stress on anti-oxidative enzymes and stress-related hormones in seedlings of Excoecaria agallocha Linn[J].Plant and Soil,2013,367(1/2):327-338. |
| [43] | BENAVIDES M P, GALLEGO S M, TOMARO M L.Cadmium toxicity in plants[J].Brazilian Journal of Plant Physiology,2005,17(1):21-34. |
| [1] | Huibo ZHAO, Zhiqiang ZHAO, Chunguang BAO, Qi WEN, Ruxin LI, Fenglan HUANG. Proteomic Screening and RcBSK7 Resistance of Ricinus communis under Cadmium(Cd) Stress [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2023, 43(1): 36-50. |
| [2] | Shubing BAI, Xiaoyi XING, Wenyu GUAN, Li DONG. Effects of Shouyun Iron Mine Abandoned Soil on the Growth of Two Sedum Species [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2022, 42(4): 677-687. |
| [3] | Chun-Xue PENG, Xue-Mei CUI, Hai-Long SHEN. Callus Induction and Somatic Embryogenesis and Physiological State Analysis from Mature Zygotic Embryo Explant of Syringa reticulata var. mandshurica [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2021, 41(4): 557-563. |
| [4] | REN Jia-Bo, WEN Zhi-Bin. Effect of different NaCl contents on Seed Germination and Seeding Growth of Chenopodium glaucum L. [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2019, 39(5): 716-721. |
| [5] | LI Rong-Yu, QIU Guo-Yu, SHEN Xiao-Xue, CHAI Min-Wei. Effects of Ammonium Nitrogen on Physiological and Ecological Characteristics of Kandelia obovata under Cadmium Stress [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2018, 38(5): 653-660. |
| [6] | YANG Ling, LIU Hong-Nan, ZHANG Dong-Yan, WEI Cheng, SHEN Hai-Long. Effect of Plant Growth Regulators and Osmoticums on Somatic Embryogenesis of Fraxinus mandshurica Rupr. [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2017, 37(5): 682-689. |
| [7] | LIU Da-Li;MAO Zi-Jun;AN Zhi-Gang*;MA Long-Biao;LU Zhen-Qiang. Enhanced Heavy Metal Tolerance and Accumulation of E.coli by Overexpressed AtGCS from Arabidopsis thaliana [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2013, 33(3): 325-329. |
| [8] | FU Lan;ZHANG Zhao-Hui;*. Bryophyte Diversity and Their Monitoring for Heavy Metal Pollution from Xinlu Carlin Gold Deposit in Guizhou Province [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2012, 32(5): 636-640. |
| [9] | WANG Ai-Xia;FANG Yan-Ming*. Tissue Distribution of 6 Kinds of Transport Heavy Metal Pollutants in Platanus hispanica Leaves and Annual Branches [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2011, 31(4): 478-488. |
| [10] | XIE Fei;ZHANG Zhao-Hui;*. Accumulation Characteristic of Heavy Metals Between Gametophytes and Sporophytes of Moss Funaria hygrometrica [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2011, 31(1): 117-120. |
| [11] | SHEN Jia;JI Gui-Qin;XU Wen;ZHOU Xing-Long;SHI Fu-Chen*. Biosorption and Bioaccumulation of Heavy Metals Copper,Lead and Zinc by a Submerged Aquatic Plant Potamogeton crispus L. at Low Temperature [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2009, 29(5): 585-591. |
| [12] | WANG Ai-Xia;ZHANG Min;HUANG Li-Bin;FANG Yan-Ming*;GAO Cai-Yun. Accumulation Capacity of Nanjing 14 Virescence Tree Species to Heavy Metal Pollutants of the Atmosphere [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2009, 29(3): 368-374. |
| [13] | WANG Wen-Yun;ZHANG Zhao-Hui*. Mensuration and Analysis of Heavy Metals in Eupatorium adenophorum from Shui Yindong Gold Deposit in Guizhou [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2008, 28(6): 760-763. |
| [14] | ZHANG Yi-Xian;LI Xiao-Ke. Effects of Cd,Pb and Their Combined Pollution on Physiological Indexes in Leaf of the Hordeum vulgare Seedling [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2008, 28(1): 43-46. |
| [15] | XU Hui;ZHANG Jie*. Effects of Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungi on Plant Growth [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2007, 27(5): 636-640. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||