Bulletin of Botanical Research ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (5): 807-815.doi: 10.7525/j.issn.1673-5102.2025.05.014
• Original Paper • Previous Articles Next Articles
Received:2025-03-01
Online:2025-09-20
Published:2025-09-28
Contact:
Peng ZHANG
E-mail:zhangpeng@nefu.edu.cn
CLC Number:
Zheng ZHANG, Peng ZHANG. Comparative Research on Growth and Physiological Characteristics of Three Poplar Varieties Grown in Western Heilongjiang[J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2025, 45(5): 807-815.
Fig.1
Radial growth rate and model of stem height and the corresponding diameter of three poplar varieties grown in west Songnen PlainA. Diameter at breast height of HQ,LF,2111Y;B. Poplar HQ;C. LF;D. 2111Y. Different lowercase letters indicated significant difference between poplar varieties at P<0.05.
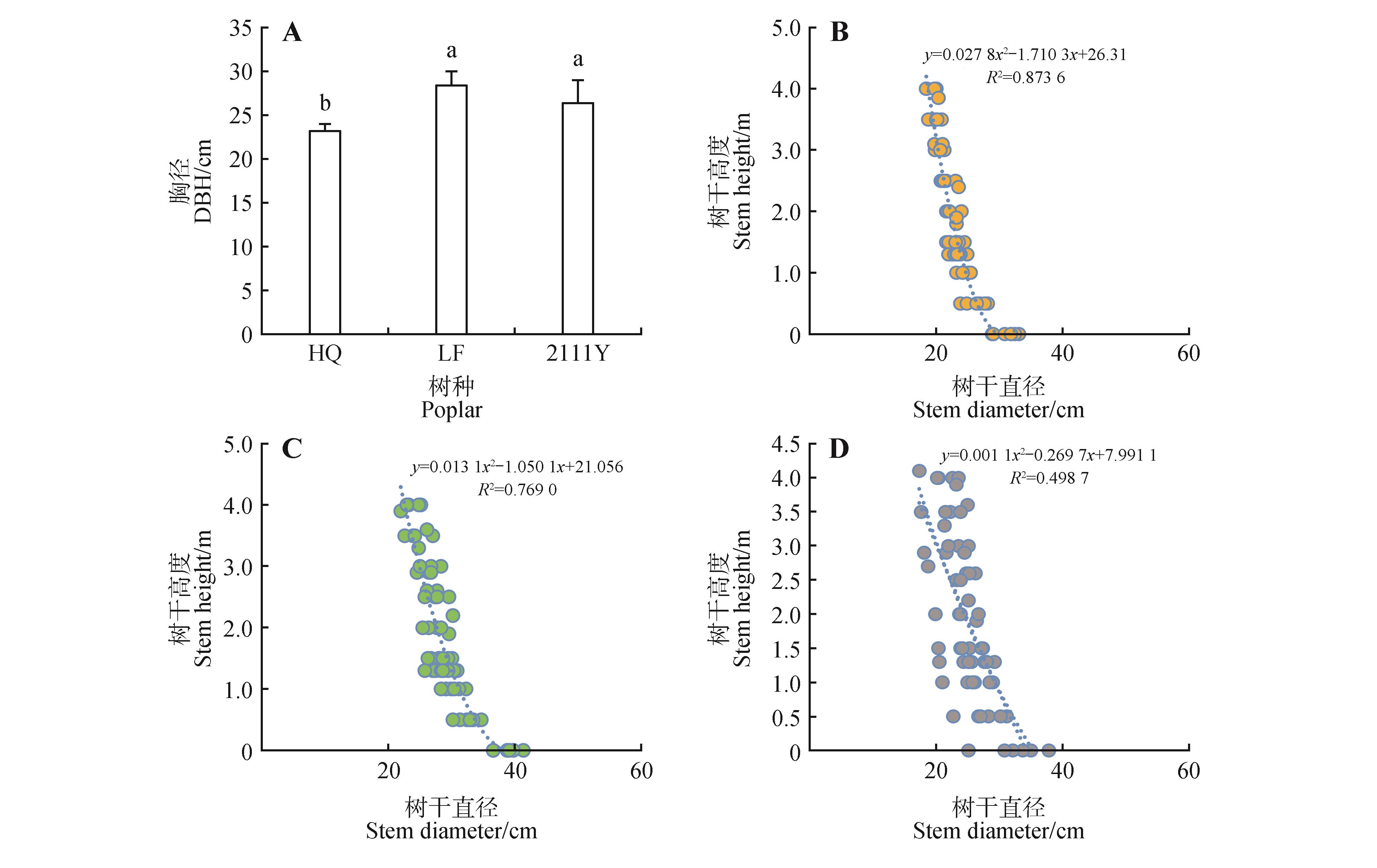
Table 1
Trade-off of branch and leaf biomass of three poplar varieties grown in west Songnen Plain
树种 Poplar | 含水率 Water content/% | 叶枝质量比 mL∶mB | 叶鲜质量与 叶面积比 mL∶AL/(g·cm-2) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
树干 Stem | 枝 Branch | 叶 Leaf | 整枝(干) Branch(Dry) | 整枝(鲜) Branch(Fresh) | 1级小枝(鲜)ClassⅠtwig (Fresh) | 2级小枝(鲜) Class Ⅱ twig (Fresh) | ||
黑青杨 HQ | 55±3a | 47±15b | 60±5a | 0.34±0.06a | 0.41±0.10a | 1.08±0.51a | 1.50±1.07a | 0.017 3±0.002 1b |
龙丰1号杨 LF | 57±1a | 52±9a | 67±7a | 0.19±0.03b | 0.30±0.09a | 0.47±0.34a | 1.33±1.40a | 0.019 1±0.003 7a |
齐林1号杨 2111Y | 58±2a | 54±12a | 64±06a | 0.20±0.09ab | 0.33±0.16a | 0.58±0.47a | 1.43±1.29a | 0.015 2±0.002 4c |
Table 2
Mass fraction and stoichiometric relationship of the elements in twigs and leaves of standard branches of three poplar varieties grown in west Songnen Plain
树种 Poplar | 3级小枝 Third-class twigs(TⅢ) | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
ω(CT)/ (g·kg-1) | ω(CL)/ (g·kg-1) | m(CL)∶ m(CT) | ω(NT)/ (g·kg-1) | ω(NL)/ (g·kg-1) | m(NL)∶ m(NT) | ω(KT)/ (g·kg-1) | ω(KL)/ (g·kg-1) | m(KL)∶ m(KT) | ω(PT)/ (g·kg-1) | ω(PL)/ (g·kg-1) | m(PL)∶ m(PT) | |
黑青杨 HQ | 464.87±3.75c | 418.01±5.53c | 0.90±0.01b | 3.12±0.07c | 19.30±0.22c | 6.19±0.12a | 6.15±0.10c | 18.83±2.47a | 3.07±0.41a | 1.04±0.54a | 2.17±0.08c | 2.52±0.91a |
龙丰1号杨 LF | 485.03±3.99a | 432.42±6.02b | 0.89±0.01b | 4.93±0.40a | 21.88±0.34a | 4.47±0.37c | 8.20±0.10a | 19.41±2.49a | 2.37±0.30b | 1.44±0.48a | 2.33±0.12b | 1.78±0.52b |
齐林1号杨 2111Y | 478.76±5.95b | 455.38±6.47a | 0.95±0.02a | 4.36±0.17b | 21.12±0.24b | 4.85±0.20b | 7.13±0.09b | 17.83±2.49a | 2.50±0.34b | 1.23±0.51a | 2.48±0.18a | 2.32±0.78a |
树种 Poplar | 4级小枝 Fourth-class twigs(TⅣ) | |||||||||||
ω(CT)/ (g·kg-1) | ω(CL)/ (g·kg-1) | m(CL)∶ m(CT) | ω(NT)/ (g·kg-1) | ω(NL)/ (g·kg-1) | m(NL)∶ m(NT) | ω(KT)/ (g·kg-1) | ω(KL)/ (g·kg-1) | m(KL)∶ m(KT) | ω(PT)/ (g·kg-1) | ω(PL)/ (g·kg-1) | m(PL)∶ m(PT) | |
黑青杨 HQ | 442.43±4.49c | 434.38±5.49c | 0.98±0.02b | 4.13±0.17c | 20.78±0.33c | 5.04±0.17a | 6.98±0.23c | 18.65±2.37b | 2.67±0.33a | 1.57±0.49a | 3.42±0.24b | 2.47±1.07a |
龙丰1号杨 LF | 471.05±10.95a | 445.68±5.90b | 0.95±0.03c | 6.99±0.13a | 22.96±0.38a | 3.29±0.07c | 9.76±0.08a | 21.30±2.58a | 2.18±0.27b | 1.79±0.26a | 3.55±0.06b | 2.02±0.27b |
| 齐林1号杨2111Y | 455.26±2.86b | 476.10±3.96a | 1.05±0.01a | 5.41±0.16b | 22.64±0.41b | 4.19±0.17b | 8.13±0.11b | 18.92±2.51b | 2.33±0.33b | 1.61±0.34a | 3.77±0.06a | 2.43±0.44a |
Table 3
Element stoichiometric relationship of twigs and leaves of three poplar varieties grown in west Songnen Plain
树种 Poplar | TⅢ | TⅣ | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| m(CT)∶m(NT) | m(CL)∶m(NL) | m(NT)∶m(PT) | m(NL)∶m(PL) | m(CT)∶m(NT) | m(CL)∶m(NL) | m(NT)∶m(PT) | m(NL)∶m(PL) | |
黑青杨 HQ | 149.05±3.46a | 21.65±0.31a | 3.39±1.54a | 8.89±0.37b | 107.39±4.06a | 20.91±0.41b | 2.93±1.22b | 6.08±0.41b |
龙丰1号杨 LF | 99.09±8.43c | 19.77±0.35b | 3.79±1.24a | 9.40±0.41a | 67.45±2.09c | 19.41±0.24c | 3.98±0.55a | 6.47±0.16a |
齐林1号杨 2111Y | 109.92±4.74b | 21.56±0.38a | 4.08±1.34a | 8.55±0.63c | 84.29±2.68b | 21.03±0.39a | 3.48±0.63a | 6.01±0.15b |
Table 4
Leaf chlorophyll and carbon metabolite levels of three poplar varieties grown in west Songnen Plain
树种 Poplar | ω/(mg·g-1) | 碳同化酶活性 Rubisco activity/ (nmol∙min-1∙g-1) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
叶绿素a Chla | 叶绿素b Chlb | 叶绿素 Chl | 可溶性糖 SS | 蔗糖 SU | 淀粉 ST | 非结构 碳水化合物 NSC | ||
黑青杨 HQ | 0.60±0.12a | 0.33±0.02a | 0.93±0.14a | 38.59±3.56a | 17.40±1.20a | 30.67±2.21a | 69.26±5.69a | 84.40±9.12a |
龙丰1号杨 LF | 0.63±0.04a | 0.30±0.02a | 0.93±0.06a | 33.58±2.08b | 18.81±1.28a | 24.07±1.89b | 57.65±1.18b | 66.45±15.24a |
齐林1号杨 2111Y | 0.73±0.07a | 0.34±0.03a | 1.07±0.09a | 31.10±0.57b | 9.05±0.45b | 24.67±1.45b | 55.77±1.90b | 77.66±35.66a |
Table 5
Comparison of leaf nitrogen metabolite level of three poplar varieties grown in west Songnen Plain
树种 Poplar | ω | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
硝态氮 | 铵态氮 | 游离氨基酸 AAs/(mg·g-1) | 可溶性蛋白 Cpr/(mg·g-1) | |
黑青杨 HQ | 302.40±41.59a | 52.64±1.20a | 0.26±0.01c | 108.30±4.57a |
龙丰1号杨 LF | 337.05±36.82a | 47.66±0.98b | 0.30±0.02b | 103.86±2.07a |
齐林1号杨 2111Y | 174.65±43.80b | 52.44±2.21a | 0.37±0.03a | 87.62±9.35b |
Table 6
Leaf hormone levels of three poplar varieties grown in west Songnen Plain
树种 Poplar | ω | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
生长素 IAA/(μg∙mg-1) | 脱落酸 ABA/(μg∙mg-1) | 水杨酸 SA/(μg∙g-1) | 赤霉素 GA/(μg∙g-1) | |
黑青杨 HQ | 0.92±0.02ab | 3.30±0.21ab | 1.59±0.07b | 0.91±0.03a |
龙丰1号杨 LF | 0.90±0.10b | 3.43±0.07a | 1.90±0.07a | 0.93±0.13a |
齐林1号杨 2111Y | 1.01±0.01a | 3.04±0.04b | 1.78±0.12a | 0.98±0.07a |
| [1] | 胡彦波,张鹏,张政,等.松嫩平原西部3种杨树生长、木材属性及形态生理学特征比较[J].生态学杂志,2024,43(10):2945-2952. |
| HU Y B, ZHANG P, ZHANG Z,et al.Comparison on growth performance,wood properties,and morpho-physiological characters among three poplar species in western Songnen Plain[J].Chinese Journal of Ecology,2024,43(10):2945-2952. | |
| [2] | 朴志勇,赵存玉,王晓娟,等.小黑杨引种及山地速生丰产栽培技术[J].东北林业大学学报,2004,32(4):9-11. |
| PIAO Z Y, ZHAO C Y, WANG X J,et al.Introduction of Populus simonii×P.nigra and its fast-growing and high-yield cultivation techniques in mountainous region[J].Journal of Northeast Forestry University,2004,32(4):9-11. | |
| [3] | 王云铭,关丽鹏,赵清峰,等.齐齐哈尔地区小黑杨生长过程研究[J].防护林科技,2008(4):33-35. |
| WANG Y M, GUANG L P, ZHAO Q F,et al.Growth process of Populus simonii×P.nigra in Qiqihar region[J].Protection Forest Science and Technology,2008(4):33-35. | |
| [4] | 李晶,王福森,李树森,等.中雄4号杨选育研究[J].防护林科技,2020(1):31-34. |
| LI J, WANG F S, LI S S,et al.Selection of Populus deltoides×Populus suaveolens [J].Protection Forest Science and Technology,2020(1):31-34. | |
| [5] | 于东阳,梅芳,王军辉,等.杨树新杂种无性系生长与材性的联合选择[J].东北林业大学学报,2014,42(2):10-16. |
| YU D Y, MEI F, WANG J H,et al.Joint selection for growth and wood properties in poplar hybrid clones[J].Journal of Northeast Forestry University,2014,42(2):10-16. | |
| [6] | 徐晶,崔莹,王福森,等.东北地区不同间伐强度青山杨人工林生长及木材性状变异[J].植物研究,2024,44(2):248-258. |
| XU J, CUI Y, WANG F S,et al.Growth and wood character variation of Populus pseudo-cathyana×Populus deltoides plantation with different thinning intensity in northeast China[J].Bulletin of Botanical Research,2024,44(2):248-258. | |
| [7] | 张宏伟,王福森.杂交新品种黑青杨的生长、抗性调查研究[J].防护林科技,2012(5):48-49. |
| ZHANG H W, WANG F S.Growth & resistance of new hybrid varieties of Populus euramericana “N3016”×Populus ussuriensis [J].Protection Forest Science and Technology,2012(5):48-49. | |
| [8] | 孙国语,马晓雨,易嘉欣,等.养分供给对黑青杨等杨树生长动态及养分分配的影响[J].植物研究,2021,41(5):690-699. |
| SUN G Y, MA X Y, YI J X,et al.Effects of nutrient supply on growth dynamics and nutrient allocation of poplars[J].Bulletin of Botanical Research,2021,41(5):690-699. | |
| [9] | 张婧,张伟溪,丁昌俊,等.五个杨树品种生长、光合生理及根尖离子流速特性比较分析[J].植物研究,2024,44(1):96-106. |
| ZHANG J, ZHANG W X, DING C J,et al.Comparative analysis of growth,photosynthetic physiology and root tip ion flow characteristics of five poplar varieties[J].Bulletin of Botanical Research,2024,44(1):96-106. | |
| [10] | 李潇,王汉时,王宏星,等.灌溉和施肥对‘新林1号’杨生长和光合生理特性的影响[J].植物研究,2025,45(1):77-87. |
| LI X, WANG H S, WANG H X,et al.Effects of irrigation and fertilization on growth and photosynthetic physiological characteristics of Populus cathayana×canadansis ‘Xinlin1’[J].Bulletin of Botanical Research,2025,45(1):77-87. | |
| [11] | 任天梦,鲍雨,苏亚勋,等.不同修枝处理对10年生三倍体毛白杨生长和光合特性的影响[J].植物研究,2023,43(6):846-856. |
| REN T M, BO Y, SU Y X,et al.Effects of different pruning treatments on growth and photosynthetic characteristics of 10-year-old triploid Populus tomentosa [J].Bulletin of Botanical Research,2023,43(6):846-856. | |
| [12] | 曹昊阳,杜阿朋,许宇星,等.尾巨桉人工林生物量分配格局的林龄效应及异速生长方程优化[J].浙江农林大学学报,2024,41(6):1124-1133. |
| CAO H Y, DU A P, XU Y X,et al.Age effect on biomass distribution pattern and optimization of allometricgrowth equation in Eucalyptus urophylla×E.grandis plantations[J].Journal of Zhejiang A&F University,2024,41(6):1124-1133. | |
| [13] | 龙嘉翼,赵宇萌,孔祥琦,等.观赏灌木小枝和叶性状在林下庇荫环境中的权衡关系[J].生态学报,2018,38(22):8022-8030. |
| LONG J Y, ZHAO Y M, KONG X Q,et al.Trade-offs between twig and leaf traits of ornamental shrubs grown in shade[J].Acta Ecologica Sinica,2018,38(22):8022-8030. | |
| [14] | 杨冬梅,毛林灿,彭国全.小枝内生物量分配关系研究:异速生长分析[J].植物研究,2011,31(4):472-477. |
| YANG D M, MAO L C, PENG G Q.Within-twig biomass allocation in evergreen and deciduous broad-leaved species:allometric scaling analyses[J].Bulletin of Botanical Research,2011,31(4):472-477. | |
| [15] | ZHAO H Z, JIANG Y, ZHANG B,et al.Hydraulic efficiency at the whole tree level stably correlated with productivity over years in 9 poplar hybrids clones[J].Forest Ecology and Management,2021,496:119382. |
| [16] | ZHAO H, HUANG X, MA B L,et al.Productive poplar genotypes exhibited temporally stable low stem embolism resistance and hydraulic resistance segmentation at the stem-leaf transition[J].Plant,Cell & Environment,2025,48:992-1004. |
| [17] | 靖磊,周延,吕偲,等.洞庭湖湿地3个林龄杨树人工林叶与土壤碳氮磷生态化学计量特征[J].生态学报,2018,38(18):6530-6538. |
| JING L, ZHOU Y, LÜ C,et al.Characterization of the soil and leaf C,N,and P stoichiometry of poplar plantations of three different stand ages in Dongting Lake wetland,China[J].Acta Ecologica Sinica,2018,38(18):6530-6538. | |
| [18] | 王亚飞,杨红青,周欧,等.水氮耦合下高密度毛白杨纸浆林树木各器官化学计量特征[J].北京林业大学学报,2023,45(12):68-79. |
| WANG Y F, YANG H Q, ZHOU O,et al.Chemical stoichiometry characteristics of various organs of trees in high-density Populus tomentosa pulp forests under water-nitrogen coupling[J].Journal of Beijing Forestry University,2023,45(12):68-79. | |
| [19] | KOERSELMAN W, MEULEMAN A F M.The vegetation N∶P ratio:a new tool to detect the nature of nutrient limitation[J].Journal of Applied Ecology,1996,33:1441-1450. |
| [20] | HU Y B, LI C M, JIANG L P,et al.Growth performance and nitrogen allocation within leaves of two poplar clones after exponential and conventional nitrogen applications[J].Plant Physiology and Biochemistry,2020,154(9):530-537. |
| [21] | HU Y B, PEUKE A D, ZHAO X Y,et al.Effects of simulated atmospheric nitrogen deposition on foliar chemistry and physiology of hybrid poplar seedlings[J].Plant Physiology and Biochemistry,2019,143:94-108. |
| [22] | BERRILL J P, O’ HARA K L.Estimating site productivity in irregular stand structures by indexing the basal area or volume increment of the dominant species[J].Canadian Journal of Forestry Research,2014,44:92-100. |
| [1] | Qize ZHAO, Xiaofei CHA, Shaojie ZHENG, Yuanyou WANG, Xinglan WEI, Qiong DONG. Response of Stoichiometric Characteristics of C, N and P and Biomass of Fraxinus malacophylla Seedlings to Rainfall Changes [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2025, 45(5): 695-706. |
| [2] | Zhuosui LI, Yilin GAO, Han LIU, Xulan SHANG. Callus Induction and Secondary Metabolites Accumulation of Diploid Cyclocarya paliurus [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2025, 45(4): 533-545. |
| [3] | Yuwei GUO, Jing LIANG, Haibing WU, Chuanjie ZHOU, Linlin SUN, Zhibao WANG, Xiaoru LI, Xiangfeng CHEN, Mulan LI. Ecosystem Carbon Storage Distribution and Influencing Factors in Different-aged Poplar Plantations in the Yellow River Floodplain in Western Shandong, China [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2025, 45(2): 241-253. |
| [4] | Zhaoxin HE, Lianfeng WU, Yongzhe WANG, Yunjie GU, Fengwei ZHAO, Xingchang WANG, Xiaochun WANG. Spatio-temporal Pattern of Aboveground Biomass in Daqing Grassland and Its Relationship with Climatic Factors [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2025, 45(1): 34-44. |
| [5] | Yang WU, Xingyong CUI, Fulin YUAN, Zhixiang ZHANG, Ce SHANG. Micromorphological Characterization of Leaf Epidermal Trichomes of Populus in China [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2024, 44(3): 341-348. |
| [6] | Yanru GAO, Junhui WANG, Wenjun MA, Fude WANG, Sanping AN, Jiacun GU. Characteristics of Fine Root Morphology and Biomass Vertical Distribution from Different Provenances and Families of Picea koraiensis [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2024, 44(3): 380-388. |
| [7] | Bingbing GUO, Mingyang LIU, Longjun DAI, Hong YANG, Lifeng WANG. Research Progress on the Mechanism of Plant Hormone Regulating Yield and Latex Flow in Hevea brasiliensis [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2024, 44(2): 161-167. |
| [8] | Juan XIA, Xudong SUN, Na WANG, Rui LI, Juan CHEN, Guoqiang GAO. Fine Root Biomass and Root Length Density of Pinus tabulaeformis and Cupressus chengiana Plantations in the Arid Valleys of the Upper Minjiang River [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2024, 44(2): 259-266. |
| [9] | Wei LIU, Ziqiang ZHU. Recent Advances on Plant Root Thermomorphogenesis [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2024, 44(1): 1-7. |
| [10] | Zhiqi CHEN, Haina ZHANG, Jiali LIU, Xianghui LU, Baocheng YANG. Effects of Nitrogen Addition on Root Growth, Biomass Allocation and Non-structural Carbohydrate Content of Cinnamomum bodinier Seedlings in Rare Earth Tailings [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2024, 44(1): 86-95. |
| [11] | Jikang XU, Yanhong HE, Tingyan LIU, Longfei HAO, Shengxi ZHANG, Zhaoyi LI. Characteristics of Rhizosphere Soil Microecological Environment of Different Ecological Restoration Vegetation in Arsenic Sandstone Areas [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2023, 43(4): 531-539. |
| [12] | Xijia JIU, Yuhui WANG, Honggang CHEN, Huizhen WANG, Cuiyun ZENG, Tao DU. Selection of Cryopreservation Conditions of Sinopodophyllum hexandrum Seeds Based on Entropy Weight TOPSIS Model [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2023, 43(3): 404-411. |
| [13] | Xueqin WAN, Yujie SHI, Jinliang HUANG, Jiaxuan MI, Yu ZHONG, Fan ZHANG, Lianghua CHEN. An Overview and Prospect on Taxonomy of the Genus Populus [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2023, 43(2): 161-168. |
| [14] | Kenian LINGHU, Shu WANG. Responses of Biomass Allocation to Population Density and Soil Water in Abutilon theophrasti at Different Growth Stages [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2023, 43(2): 272-280. |
| [15] | Kun CHEN, Gonggui FANG, Huaizhi MU, Jing JIANG. Analysis of the Promoter Sequence and Response Characteristics of the BpPIN3 gene in Betula platyphylla [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2022, 42(4): 592-601. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
