Bulletin of Botanical Research ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (5): 769-782.doi: 10.7525/j.issn.1673-5102.2025.05.011
• Original Paper • Previous Articles Next Articles
Wenbiao DUAN, Zhizhen WANG, Jiayi GAO, Lixin CHEN, Yanrui FU( )
)
Received:2024-11-22
Online:2025-09-20
Published:2025-09-28
Contact:
Yanrui FU
E-mail:fuyanrui@nefu.edu.cn
CLC Number:
Wenbiao DUAN, Zhizhen WANG, Jiayi GAO, Lixin CHEN, Yanrui FU. Carbon Density and C, N, P Stoichiometric Characteristics of Forest Litter in Different Succession Stages in the Xiaoxing'an Mountains[J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2025, 45(5): 769-782.
Table 1
Basic information of forest community plots in different succession stages
森林群落 Forest community | 林分类型 Forest type | 坡位 Slope position | 坡向 Slope direction | 坡度 Slope degree/(°) | 海拔 Elevation /m | 郁闭度 Crown density | 树种组成 Tree species composition | 林龄 Stand age/a | 平均树高 Mean canopy height/m | 平均胸径 Mean diameter at breast height /cm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
先锋群落 Pioneer community(PC) | 天然枫桦 次生林 | 上 | 西 | 20 | 520 | 0.95 | 3枫2杨2山1红1黄+色+ 白+稠+落+钻-核-花-糠 | 39 | 7.63 | 9.24 |
| 中 | 西 | 13 | 498 | 0.95 | 8.46 | 9.32 | ||||
| 下 | 西 | 15 | 484 | 0.95 | 7.34 | 9.81 | ||||
中期群落 Middle community(MC) | 次生 阔叶林 | 上 | 北 | 16 | 535 | 0.85 | 6枫1红1白+青+色+ 紫-冷-核-云-花 | 69 | 10.19 | 14.14 |
| 中 | 西北 | 15 | 493 | 0.80 | 10.03 | 14.99 | ||||
| 下 | 西北 | 16 | 454 | 0.85 | 12.97 | 15.24 | ||||
稳定群落 Stable community(SC) | 次生针阔 混交林 | 上 | 西北 | 13 | 373 | 0.85 | 4红2枫1紫1榆1色+ 水+冷-白-青 | 125 | 8.08 | 16.88 |
| 中 | 西 | 12 | 361 | 0.80 | 8.78 | 17.69 | ||||
| 下 | 西 | 13 | 356 | 0.90 | 10.39 | 21.05 | ||||
顶极群落 Climax community(CC) | 原始阔叶 红松林 | 上 | 西北 | 24 | 476 | 0.85 | 7红1冷1枫+色+ 紫-花-青 | 230 | 10.07 | 25.04 |
| 中 | 北 | 23 | 473 | 0.85 | 10.65 | 28.43 | ||||
| 下 | 北 | 24 | 471 | 0.80 | 14.60 | 29.82 |
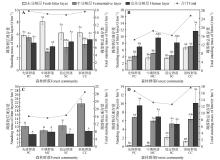
Fig.1
Litter standing mass in different forest communities and decomposition stagesA. July 2021; B. October 2021; C. May 2022; D. August 2022. Because of the lack of litter in the L layer in May 2022, the difference analysis between different decomposition degrees of the same forest community was not conducted. Different capital letters indicated significant differences(P<0.05) in the same degree of decomposition of litter among different forest communities; different lowercase letters indicated significant differences(P<0.05) in different decomposition degrees of litter under the same forest community.
Fig.2
Organic carbon mass fraction of litter in different forest communities and different decomposition layersA.July,2021;B.October,2021;C.May,2022;D.August,2022. Because of the lack of litter in the L layer in May 2022, the difference analysis between different decomposition degrees of the same forest community was not conducted. Different capital letters indicated the significant differences between forest communities of the same decomposition degree of litter(P<0.05); different lowercase letters indicated the significant differences between decomposition degrees of litter within the same forest community(P<0.05).
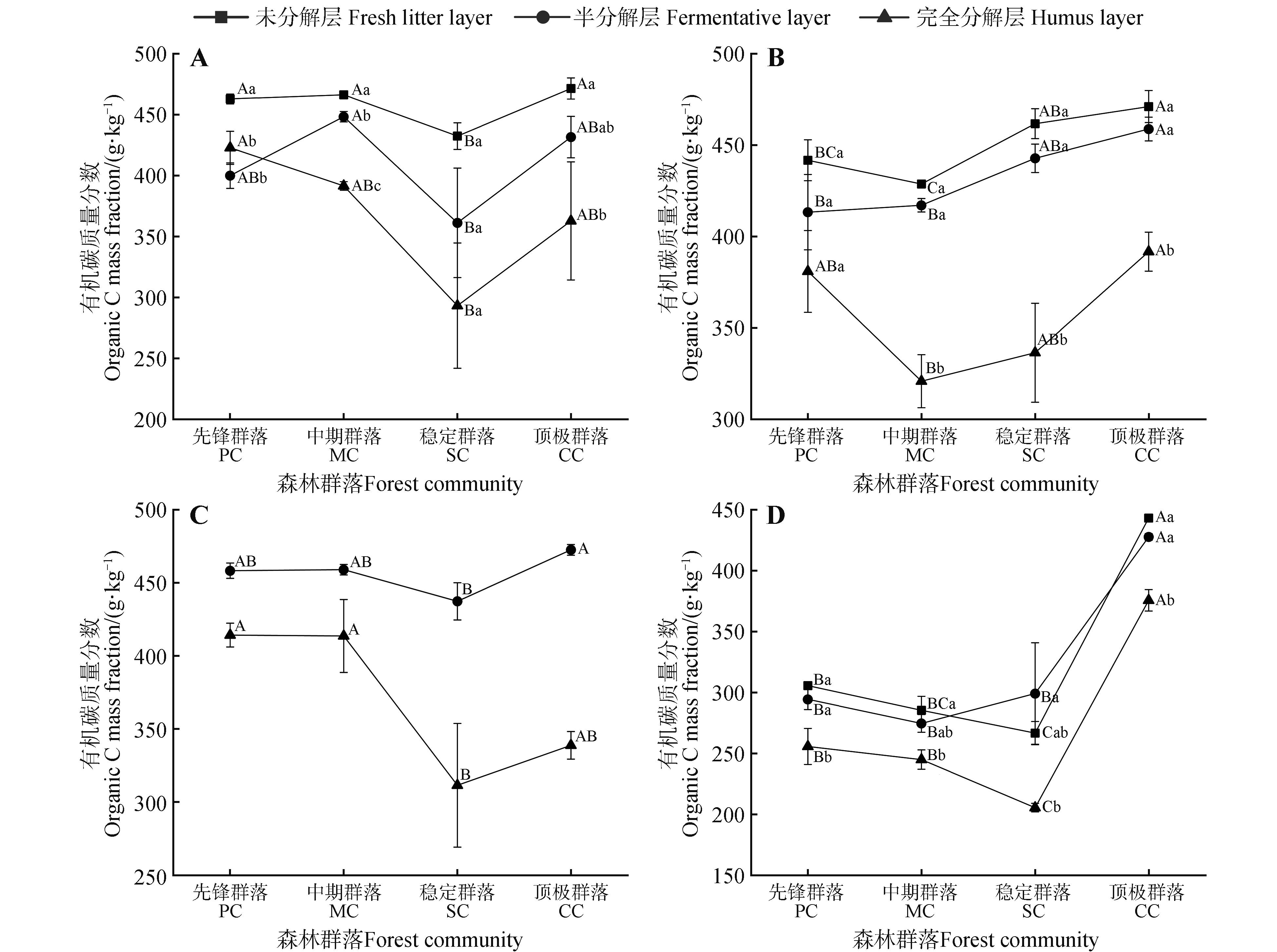
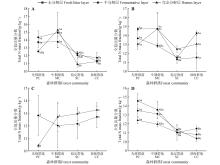
Fig.3
Total nitrogen mass fraction of litter in different forest communities and different decomposition layersA. July 2021; B. October 2021; C. May 2022; D. August 2022. Because of the lack of litter in the L layer in May 2022, the difference analysis between different decomposition degrees of the same forest community was not conducted. Different capital letters indicated significant differences(P<0.05) in the same degree of decomposition of litter among different forest communities; different lowercase letters indicated significant differences(P<0.05) in different decomposition degrees of litter under the same forest community.
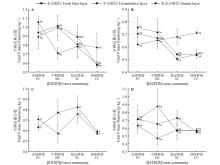
Fig.4
Total phosphorus mass fraction of litter in different forest communities and different decomposition layersA. July 2021; B. October 2021; C. May 2022; D. August 2022. Because of the lack of litter in the L layer in May 2022, the difference analysis between different decomposition degrees of the same forest community was not conducted. Different capital letters indicated significant differences(P<0.05) in the same degree of decomposition of litter among different forest communities; different lowercase letters indicated significant differences(P<0.05) in different decomposition degrees of litter under the same forest community.
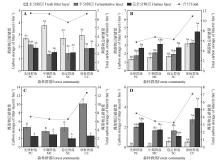
Fig.6
Carbon storage of litter in different forest types and decomposition stagesA. July 2021; B. October 2021; C. May 2022; D. August 2022. Because of the lack of litter in the L layer in May 2022, the difference analysis between different decomposition degrees of the same forest community was not conducted. Different capital letters indicated significant differences(P<0.05) in the same degree of decomposition of litter among different forest types; different lowercase letters indicated significant differences(P<0.05) in different decomposition degrees of litter under the same forest type.
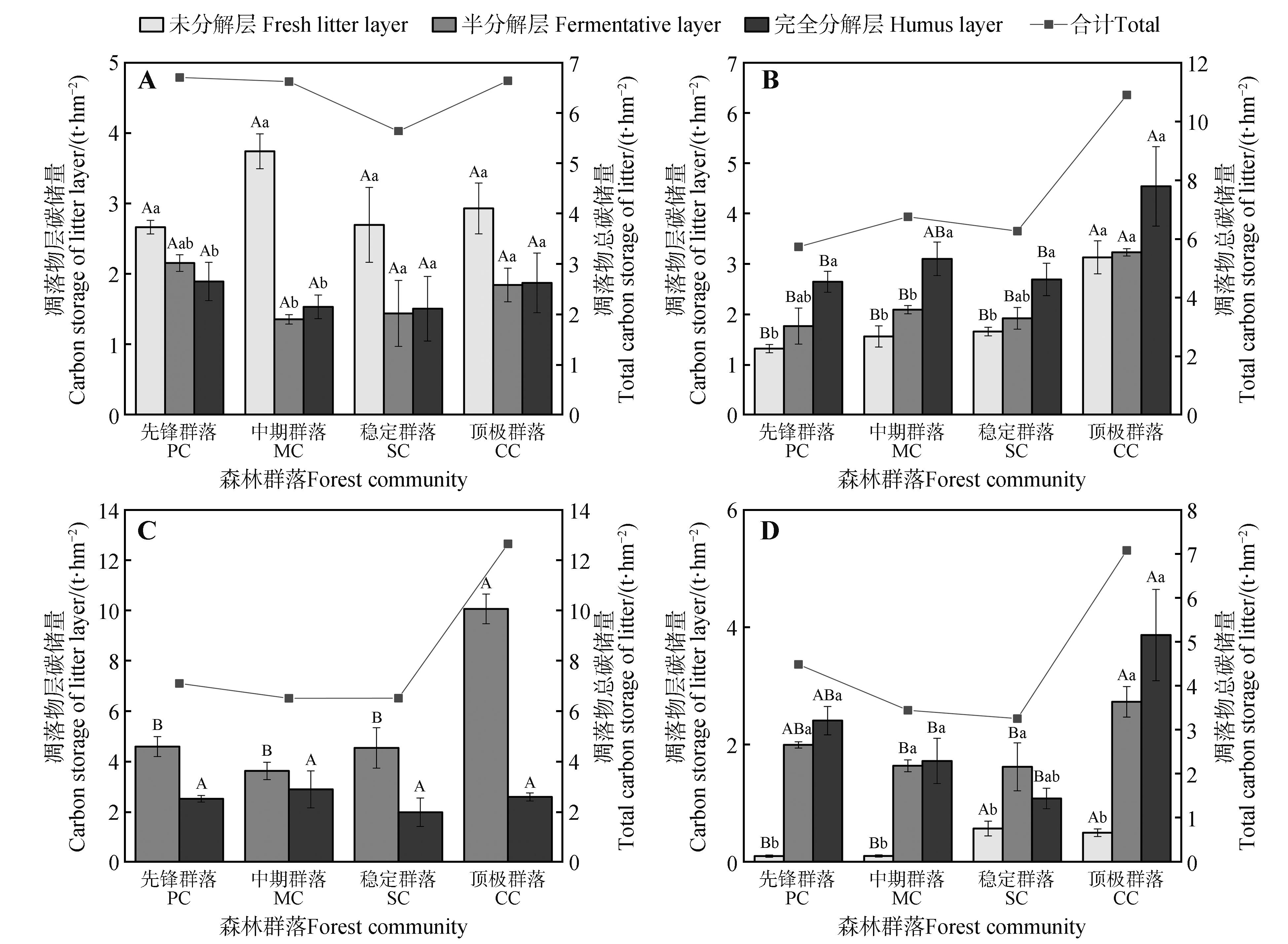
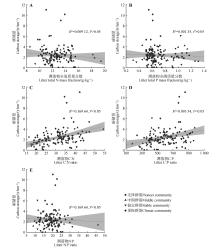
Fig.8
Relationships between the stoichiometric characteristics of litter and litter carbon storageA. TN mass fraction; B. TP mass fraction; C. C∶N ratio; D. C∶P ratio; E. N∶P ratio. The solid line and grey interval were the best fitting line and its 95% confidence interval obtained by linear regression model. R2 represented the adjusted fitting coefficient, and P value represented the significance of the whole model.
| [1] | SONG Z H, SHI P, LI P,et al.Effects of forest type on carbon storage in the hilly region of Loess Plateau,China[J].Frontiers in Forests and Global Change,2024,7:1349047. |
| [2] | PAN Y D, BIRDSEY R A, FANG J Y,et al.A large and persistent carbon sink in the world’s forests[J].Science,2011,333(6045):988-993. |
| [3] | DOMKE G M, PERRY C H, WALTERS B F,et al.Estimating litter carbon stocks on forest land in the United States[J].Science of the Total Environment,2016,557:469-478. |
| [4] | MIAO R H, MA J, LIU Y Z,et al.Variability of aboveground litter inputs alters soil carbon and nitrogen in a coniferous-broadleaf mixed forest of central China[J].Forests,2019,10(2):188. |
| [5] | SPOHN M.Microbial respiration per unit microbial biomass depends on litter layer carbon-to-nitrogen ratio[J].Biogeosciences,2015,12(3):817-823. |
| [6] | ZOU J L, LI Q Y, OSBORNE B,et al.Dominant role of nitrogen stoichiometric flexibility in ecosystem carbon storage under elevated CO2 [J].Science of the Total Environment,2020,747:141308. |
| [7] | YANG J, WU F Z, NI X Y,et al.Responses of soil nitrogen pools to litter input under nitrogen addition:a meta-analysis[J].Journal of Geophysical Research-Biogeosciences,2024,129(1):e2023JG007699. |
| [8] | SONG T J, AN Y, TONG S Z,et al.Soil water conditions together with plant nitrogen acquisition strategies control vegetation dynamics in semi-arid wetlands undergoing land management changes[J].Catena,2023,227:107115. |
| [9] | WANG B, XU G C, MA T T,et al.Effects of vegetation restoration on soil aggregates,organic carbon,and nitrogen in the Loess Plateau of China[J].Catena,2023,231:107340. |
| [10] | HU Q J, SHENG M Y, BAI Y X,et al.Response of C,N,and P stoichiometry characteristics of Broussonetia papyrifera to altitude gradients and soil nutrients in the karst rocky ecosystem,SW China[J].Plant and Soil,2022,475(1/2):123-136. |
| [11] | 周以良.中国小兴安岭植被[M].北京:科学出版社,1994. |
| ZHOU Y L.Vegetation of Xiaoxing’an Mountains in China[M].Beijing:Science Press,1994. | |
| [12] | 王亚飞,蒋乙东,段文标,等.小兴安岭南部2种红松天然林优势树种的空间结构和生态位特征[J].中南林业科技大学学报,2023,43(10):117-128. |
| WANG Y F, JIANG Y D, DUAN W B,et al.Spatial structure and niche characteristics of dominant species in natural Pinus koraiensis forest in southern Xiaoxing’an Mountains[J].Journal of Central South University of Forestry & Technology,2023,43(10):117-128. | |
| [13] | 王美娟,段文标,陈立新,等.模拟氮磷沉降和凋落物处理对红松林土壤全氮和有机氮的影响[J].中国水土保持科学(中英文),2022,20(5):56-65. |
| WANG M J, DUAN W B, CHEN L X,et al.Effects of simulated nitrogen and phosphorus deposition and litter treatment on the soil total nitrogen and organic nitrogen in Pinus koraiensis forest[J].Science of Soil and Water Conservation,2022,20(5):56-65. | |
| [14] | 郑路,卢立华.我国森林地表凋落物现存量及养分特征[J].西北林学院学报,2012,27(1):63-69. |
| ZHENG L, LU L H.Standing crop and nutrient characteristics of forest floor litter in China[J].Journal of Northwest Forestry University,2012,27(1):63-69. | |
| [15] | 陈金磊,张仕吉,李雷达,等.亚热带不同植被恢复阶段林地凋落物层现存量和养分特征[J].生态学报,2020,40(12):4073-4086. |
| CHEN J L, ZHANG S J, LI L D,et al.Stock and nutrient characteristics of litter layer at different vegetation restoration stages in subtropical region,China[J].Acta Ecologica Sinica,2020,40(12):4073-4086. | |
| [16] | 李明军,喻理飞,杜明凤,等.不同林龄杉木人工林植物-凋落叶-土壤C、N、P化学计量特征及互作关系[J].生态学报,2018,38(21):7772-7781. |
| LI M J, YU L F, DU M F,et al.C,N,and P stoichiometry and their interaction with plants,litter,and soil in a Cunninghamia lanceolata plantation with different ages[J].Acta Ecologica Sinica,2018,38(21):7772-7781. | |
| [17] | GENG Q W, MUHAMMAD A, YUAN Z X,et al.Plant species composition and diversity along successional gradients in arid and semi-arid regions of China[J].Forest Ecology and Management,2022,524:120542. |
| [18] | WANG Y F, CHEN L X, QU M X,et al.Response of soil aggregate composition and stability to secondary succession and plantation of a broad-leaved Korean pine forest after clear-cutting and its causes[J].Forests,2023,14(10):2010. |
| [19] | FANG J Y, WANG G G, LIU G H,et al.Forest biomass of China:an estimate based on the biomass-volume relationship[J].Ecological Applications,1998,8(4):1084-1091. |
| [20] | XIONG Y M, ZENG H, XIA H P,et al.Interactions between leaf litter and soil organic matter on carbon and nitrogen mineralization in six forest litter-soil systems[J].Plant and Soil,2014,379(1/2):217-229. |
| [21] | ZHANG J W, QIN T L, XIAO S B,et al.Research advances on carbon-water relationship of forest litter-soil interface [J].Polish Journal of Environmental Studies,2022,31(4):3919-3928. |
| [22] | 尹宝丝,史常青,贺康宁,等.高寒区华北落叶松林生长季内地表凋落物层碳氮磷化学计量特征[J].应用与环境生物学报,2019,25(2):268-274. |
| YIN B S, SHI C Q, HE K N,et al.Litter carbon,nitrogen,and phosphorus stoichiometry of Larix principis- rupprechtii in alpine region during growing season[J].Chinese Journal of Applied and Environmental Biology,2019,25(2):268-274. | |
| [23] | ZAN P, MAO Z J, SUN T.Effects of soil fauna on litter decomposition in Chinese forests:a meta-analysis[J].PeerJ,2022,10:e12747. |
| [24] | 武仁杰,邢玮,葛之葳,等.4种林分凋落叶不同分解阶段化学计量特征[J].浙江农林大学学报,2023,40(1):155-163. |
| WU R J, XING W, GE Z W,et al.Stoichiometric characteristics of leaf litter at different decomposition stages in 4 forest types[J].Journal of Zhejiang A&F University,2023,40(1):155-163. | |
| [25] | 赵畅,龙健,李娟,等.茂兰喀斯特原生林不同坡向及分解层的凋落物现存量和养分特征[J].生态学杂志,2018,37(2):295-303. |
| ZHAO C, LONG J, LI J,et al.Litter stock and nutrient characteristics of decomposing litter layers in Maolan karstprimary forest in different slope directions[J].Chinese Journal of Ecology,2018,37(2):295-303. | |
| [26] | AYRES E, STELTZER H, BERG S,et al.Soil biota accelerate decomposition in high-elevation forests by specializing in the breakdown of litter produced by the plant species above them[J].Journal of Ecology,2009,97(5):901-912. |
| [27] | WU P, ZHOU H, CUI Y C,et al.Stoichiometric characteristics of leaf,litter and soil during vegetation succession in Maolan National Nature Reserve,Guizhou,China[J].Sustainability,2022,14(24):16517. |
| [28] | YOU C M, WU F Z, YANG W Q,et al.The National Key Forestry Ecology Project has changed the zonal pattern of forest litter production in China[J].Forest Ecology and Management,2017,399:37-46. |
| [29] | 李雪峰,韩士杰,郭忠玲,等.红松阔叶林内凋落物表层与底层红松枝叶的分解动态[J].北京林业大学学报,2006,28(3):8-13. |
| LI X F, HAN S J, GUO Z L,et al.Decomposition of pine needles and twigs on and under the litter layer in the natural Korean pine broadleaved forests[J].Journal of Beijing Forestry University,2006,28(3):8-13. | |
| [30] | MAO R C, SONG J X, TANG B,et al.Vegetation variation regulates soil moisture sensitivity to climate change on the Loess Plateau[J].Journal of Hydrology,2023,617:128763. |
| [31] | 秦立厚,刘琪璟,孙震,等.长白山阔叶红松林主要树种凋落叶分解速率及其与叶性状的关系[J].生态学报,2022,42(14):5894-5905. |
| QIN L H, LIU Q J, SUN Z,et al.Leaf litter decomposition rate of main tree species in broad-leaved Korean pine forest and its relationship with leaf traits[J].Acta Ecologica Sinica,2022,42(14):5894-5905. | |
| [32] | 董凌勃,海旭莹,汪晓珍,等.黄土高原退耕还草地植物群落动态对生态系统碳储量的影响[J].生态学报,2020,40(23):8559-8569. |
| DONG L B, HAI X Y, WANG X Z,et al.Effects of plant community dynamics on ecosystem carbon stocks since returning farmlands to grasslands on the Loess Plateau [J].Acta Ecologica Sinica,2020,40(23):8559-8569. | |
| [33] | 李勋,张艳,宋思梦,等.马尾松与乡土阔叶树种凋落叶混合分解过程中全碳释放的动态变化[J].植物研究,2022,42(2):309-320. |
| LI X, ZHANG Y, SONG S M,et al.Dynamic changes of total carbon release during mixed decomposition of leaf litter of Pinus massoniana and native broad-leaved tree species[J].Bulletin of Botanical Research,2022,42(2):309-320. | |
| [34] | 谌贤,刘洋,邓静,等.川西亚高山森林凋落物不同分解阶段碳氮磷化学计量特征及种间差异[J].植物研究,2017,37(2):216-226. |
| CHEN X, LIU Y, DENG J,et al.C,N and P stoichiometry at different stages of litter decomposition in subalpine forest of western Sichuan Province and interspecies comparison[J].Bulletin of Botanical Research,2017,37(2):216-226. | |
| [35] | XIE J Y, FANG H F, ZHANG Q,et al.Understory plant functional types alter stoichiometry correlations between litter and soil in Chinese fir plantations with N and P addition[J].Forests,2019,10(9):742. |
| [36] | 梁星云.长白山阔叶红松林演替系列主要树种叶片功能性状与化学计量学研究[D].北京:中国林业科学研究院,2017. |
| LIANG X Y.Leaf functional traits and ecological stoichiometry of the dominant tree species along forest succession of Korean pine and broad-leaved mixed forest in Changbai Mountain,northeastern China[D].Beijing:Chinese Academy of Forestry,2017. | |
| [37] | SWIFT M J, HEAL O W, ANDERSON J M.Decomposition in terrestrial ecosystem[M].Oxford:Blackwell Scientific Publication,1979:56-57. |
| [38] | GÜSEWELL S, VERHOEVEN J T A.Litter N∶P ratios indicate whether N or P limits the decomposability of graminoid leaf litter[J].Plant and Soil,2006,287(1/2):131-143. |
| [39] | 王珂,尹昀洲,张明辉,等.林龄对红松人工林叶片-凋落物-土壤C、N、P生态化学计量特征的影响[J].西部林业科学,2023,52(2):55-61. |
| WANG K, YIN Y Z, ZHANG M H,et al.Effects of stand age on ecological stoichiometric characteristics of C,N and P in leaves,litter and soil of Pinus koraiensis plantation[J].Journal of West China Forestry Science,2023,52(2):55-61. | |
| [40] | KANG H Z, XIN Z J, BERG B,et al.Global pattern of leaf litter nitrogen and phosphorus in woody plants[J].Annals of Forest Science,2010,67(8):811. |
| [41] | 刘平,杨章旗,颜培栋,等.马尾松林下植被和凋落物的碳氮磷化学计量特征[J].森林与环境学报,2023,43(5):473-480. |
| LIU P, YANG Z Q, YAN P D,et al.C,N,P stoichiometric characteristics of vegetation and litter in the Pinus massoniana understory[J].Journal of Forest and Environment,2023,43(5):473-480. | |
| [42] | CHEN B, CHEN Y Y, JIANG L,et al.C∶N∶P stoichiometry of plant,litter and soil along an elevational gradient in subtropical forests of China[J].Forests,2022,13(3):372. |
| [1] | Yuwei GUO, Jing LIANG, Haibing WU, Chuanjie ZHOU, Linlin SUN, Zhibao WANG, Xiaoru LI, Xiangfeng CHEN, Mulan LI. Ecosystem Carbon Storage Distribution and Influencing Factors in Different-aged Poplar Plantations in the Yellow River Floodplain in Western Shandong, China [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2025, 45(2): 241-253. |
| [2] | Yuqi MA, Yuhui LI, Lin LIN, Yue SHEN, Yufeng GU, Faguo WANG. Phyto-community Characteristics of the Dependent Environment of Dipteris shenzhenensis [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2024, 44(1): 34-44. |
| [3] | Hongbo LI, Shi CHEN, Yaohua HUANG, Dingxu KANG, Jianrong WU, Huancheng MA. Ecological Stoichiometry and Homeostasis of Alpine Quercus semicarpifolia Leaves in Subalpine Zone of Hengduan Mountains [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2023, 43(6): 923-931. |
| [4] | Xun Li, Yan Zhang, Simeng Song, Yang Zhou, Jian Zhang. Dynamic Changes of Total Carbon Release During Mixed Decomposition of Leaf Litter of Pinus massoniana and Native Broad-leaved Tree Species [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2022, 42(2): 309-320. |
| [5] | Ke-Xin MA, Mei ZHANG, Xin FANG, Li-Li TANG, Jian-Hua HAN, Li-Fang YANG, Fu-Chen SHI. Effects of Invasive Plant Datura stramonium on the Functional Traits of Native Plants and the Stoichiometric Characteristics of Soil Carbon, Nitrogen and Phosphorus [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2020, 40(6): 867-875. |
| [6] | LIU Min-Xia, LI Li-Rong, CHE Ying-Di, JIAO Jiao. Functional Traits of Plant Leaves at Different Succession Stages in Alpine Meadow [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2019, 39(5): 760-769. |
| [7] | LIU Yan, MAO Zi-Jun. Root Biomass in Different Secondary Succession Forests inthe Broad-leaved Korean Pine Forest Areaof Xiaoxing'an Mountain [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2018, 38(4): 583-589. |
| [8] | LI Yuan-Yuan, WANG Zheng-Wen, SUN Tao. Response of Fine Root Decomposition to Long-term Nitrogen Addition in the Temperate Forest [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2017, 37(6): 848-854. |
| [9] | ZHANG Ming, LIU Fu-De, AN Shu-Qing, CAO Xue-Zhang. Leaf Traits of the Saplings of Later Successional Stage Tropical Montane Rain Forest in Hainan Island [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2017, 37(6): 907-914. |
| [10] | ZHANG Yang-Feng, YIN Guang-Tian, YANG Jin-Chang, LI Shao-Wei, LI Rong-Sheng, ZOU Wen-Tao. Effects of Planting Densities on Production and Dynamics of Litter of Mytilaria laosensis Plantation [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2017, 37(5): 768-777. |
| [11] | LI Ji-Mei, ZHANG Yu-Yao, LI Xiang, HAN Yan-Liang. Impact of Precipitation Intensity on the Decomposition of Floor Litter and the Fine Roots of Picea schrenkiana [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2017, 37(3): 360-369. |
| [12] | SHEN Xian, LIU Yang, DENG Jing, SHI Jia-Qi. C,N and P Stoichiometry at Different Stages of Litter Decomposition in Subalpine Forest of Western Sichuan Province and Interspecies Comparison [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2017, 37(2): 216-226. |
| [13] | GENG Zhao-Peng, MAO Zi-Jun, HUANG Wei, HAN Ying-Ying. Comparative Study on the Soil Respiration and Component Characteristics of Primary Broad-leaved Korean Pine Forest and Betula costata Secondary Forest in Xiaoxing'an Mountatins,China [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2017, 37(2): 312-320. |
| [14] | WEI Da-Ping, ZHANG Dan-Ju, LI Xun, ZHANG Yan, LI Chuan-Bei, ZHANG Jian. Dynamics of Leaf Litter and Mineral Soil Nutrients in Different Sized Pinus massoniana Forest Gaps [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2017, 37(1): 128-138. |
| [15] | HOU Dan, ZHANG Li, WEI Zhi-Gang, ZHOU Chun-Yan, XIA De-An. Genetic Variation of Pinus koraiensis from Provenances and High Carbon Storage Provenance Selection [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2016, 36(3): 452-460. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||