Bulletin of Botanical Research ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (4): 518-532.doi: 10.7525/j.issn.1673-5102.2025.04.005
• Original Paper • Previous Articles Next Articles
Hao GUO1,2, Caixia CHEN2, Xiaojing AN1,2, Xian’en LI2, Haiying WANG1( ), Zhongting XIA3(
), Zhongting XIA3( )
)
Received:2025-02-05
Online:2025-07-20
Published:2025-07-25
Contact:
Haiying WANG, Zhongting XIA
E-mail:haiyingwang-99@163.com;Hexinshang-1@hotmail.com
CLC Number:
Hao GUO, Caixia CHEN, Xiaojing AN, Xian’en LI, Haiying WANG, Zhongting XIA. Effect of Environmental Factors on the Active Ingredients of Codonopsis pilosula[J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2025, 45(4): 518-532.
Table 1
The information of Codonopsis pilosula collected
编号 Number | 采样点 Sampling site | 基源 Origin plant | 经纬度 Latitude and longitude | 海拔 Elevation/m | 党参炔苷质量分数 Lobetyolin mass fraction/(mg·g-1) | 党参多糖质量分数 Codonopsis pilosula polysaccharide mass fraction/(mg·g-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D1 | 重庆市巫溪县双阳乡双阳村 | 党参 | 31°28′28″N,109°49′34″E | 1 650 | 2.147±0.064b | 128±35ij |
| D2 | 重庆市奉节县太和乡石板村 | 党参 | 30°24′6″N,109°9′4″E | 1 500 | 2.192±0.074a | 223±3efgh |
| D3 | 重庆市巫山县红椿乡红椿村 | 党参 | 30°31′28″N,109°39′14″E | 1 600 | 2.017±0.015c | 254±29bcdef |
| D4 | 重庆市奉节县长安乡五坝村 | 党参 | 30°25′24″N,109°21′8″E | 1 700 | 1.234±0.006f | 368±19a |
| D5 | 重庆市巫山县红椿乡西槽村 | 党参 | 30°28′57″N,109°21′13″E | 1 500 | 1.391±0.042e | 254±11cdef |
| D6 | 赤峰市阿鲁科尔沁旗三山村 | 党参 | 43°55′24″N,120°3′47″E | 452 | 0.396±0.010v | 389±54a |
| D7 | 定西市陇西县福星镇 | 党参 | 35°7′59″N,104°37′14″E | 2 160 | 0.586±0.003s | 228±28efgh |
| D8 | 定西市渭源县庆坪镇 | 党参 | 35°17′54″N,104°9′52″E | 2 407 | 0.763±0.011n | 298±21b |
| D9 | 定西市临洮县连儿湾乡 | 党参 | 35°24′26″N,104°8′18″E | 2 469 | 0.972±0.023i | 268±6bcde |
| D10 | 定西市漳县四族镇 | 党参 | 34°42′7″N,104°24′39″E | 2 181 | 0.923±0.008k | 277±19bcd |
| D11 | 定西市漳县石川镇 | 党参 | 34°37′23″N,104°19′10″E | 2 123 | 0.740±0.010o | 229±11efgh |
| D12 | 定西市岷县蒲麻镇 | 党参 | 34°34′27″N,104°21′28″E | 2 257 | 0.988±0.004h | 152±11i |
| D13 | 定西市岷县闾井镇 | 党参 | 34°22′17″N,104°31′21″E | 2 480 | 1.028±0.015g | 212±36fgh |
| D14 | 定西市岷县梅川镇 | 党参 | 34°32′24″N,104°9′31″E | 2 659 | 0.900±0.010l | 227±1efgh |
| D15 | 定西市岷县西江镇 | 党参 | 34°28′20″N,103°56′3″E | 2 178 | 0.682±0.016p | 211±13fgh |
| D16 | 甘南藏族自治州临潭县新城镇 | 党参 | 34°41′21″N,103°34′58″E | 2 803 | 0.498±0.015t | 234±23defgh |
| D17 | 甘南藏族自治州临潭县羊永镇 | 党参 | 34°39′35″N,103°29′24″E | 2 669 | 0.428±0.009u | 209±12gh |
| D18 | 甘南藏族自治州卓尼县木耳镇 | 党参 | 34°33′32″N,103°32′59″E | 2 496 | 0.661±0.002q | 252±23cdefg |
| D19 | 甘南藏族自治州卓尼县纳浪镇 | 党参 | 34°30′3″N,103°44′57″E | 2 371 | 0.960±0.030i | 285±10bc |
| D20 | 定西市岷县西寨镇 | 党参 | 34°28′25″N,103°49′28″E | 2 343 | 0.626±0.006r | 243±11cdefgh |
| D21 | 定西市岷县麻子川镇 | 党参 | 34°16′57″N,104°6′29″E | 2 475 | 1.477±0.043d | 207±52h |
| D22 | 陇南市宕昌县庞家乡 | 党参 | 34°16′4″N,104°17′59″E | 2 236 | 0.853±0.005m | 235±4defgh |
| D23 | 晋城市陵川县平城镇和村村 | 党参 | 35°52′23″N,113°18′35″E | 1 397 | 0.940±0.014j | 78±24k |
| D24 | 晋城市陵川县平城镇和村村 | 党参 | 35°52′23″N,113°18′35″E | 1 397 | 0.351±0.005w | 105±9jk |
| D25 | 晋城市陵川县平城镇林峦岭村 | 党参 | 35°52′55″N,113°19′51″E | 1 370 | 0.664±0.009q | 139±7ij |
| D26 | 晋城市陵川县平城镇魏庄村 | 党参 | 35°52′39″N,113°20′15″E | 1 360 | 0.641±0.014r | 76±8k |
| D27 | 晋城市陵川县夺火乡 | 党参 | 35°36′32″N,113°18′15″E | 1 344 | 0.513±0.028t | 73±23k |
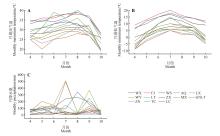
Fig.1
Meteorological data from different producing areas of Codonopsis pilosulaA.Monthly maximum temperature; B.Monthly minimum temperature; C.Monthly precipitation. WX. Wuxi County, Chongqing; FJ. Fengjie County, Chongqing; WS. Wushan County, Chongqing; AQ. Ar Horqin Banner, Chifeng City; LX. Longxi County, Dingxi City; WY. Weiyuan County, Dingxi City; LT. Lintao County, Dingxi City; ZX. Zhang County, Dingxi City; MX. Min County, Dingxi City; GNLT. Lintan County, Gannan Xizang Autonomous Prefecture; ZN. Zhuoni County, Gannan Xizang Autonomous Prefecture; TC. Tanchang County, Longnan City; LC. Lingchuan County, Jincheng City.
Fig.2
Mass fraction of active ingredients in Codonopsis pilosula from different producing areasA.Codonopsis pilosula polysaccharide mass fraction; B.Lobetyolin mass fraction. The upper edge of the box represented the upper quartile, and the lower edge represented the lower quartile. The white dots inside the box represented the median, and the white horizontal lines represented the mean. Different letters indicated significant differences among producing areas, P<0.05.WX. Wuxi County, Chongqing; FJ. Fengjie County, Chongqing; WS. Wushan County, Chongqing; AQ. Ar Horqin Banner, Chifeng City; LX. Longxi County, Dingxi City; WY. Weiyuan County, Dingxi City; LT. Lintao County, Dingxi City; ZX. Zhang County, Dingxi City; MX. Min County, Dingxi City; GNLT. Lintan County, Gannan Xizang Autonomous Prefecture; ZN. Zhuoni County, Gannan Xizang Autonomous Prefecture; TC. Tanchang County, Longnan City; LC. Lingchuan County, Jincheng City.
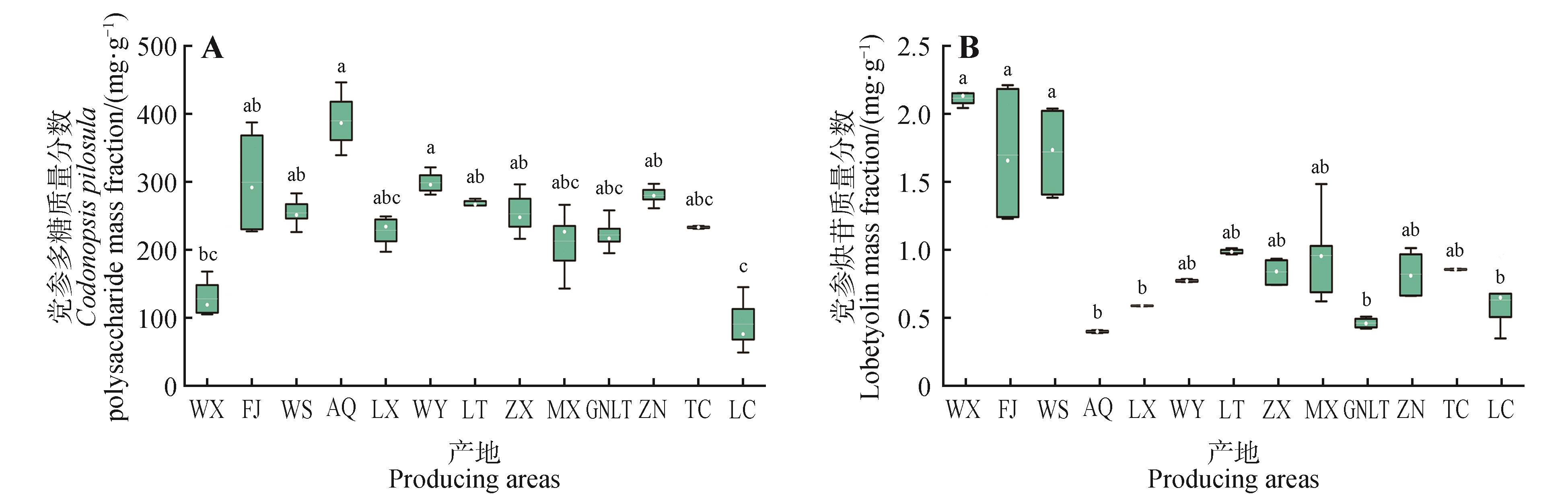
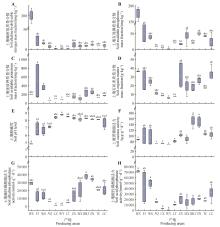
Fig.3
Physicochemical parameters of soils of Codonopsis pilosula root zone from different producing areasA.Soil alkaline-hydrolyzable nitrogen mass fraction; B.Soil available phosphorus mass fraction; C.Soil available potassium mass fraction; D.Soil organic matter mass fraction; E.Soil pH level; F.Soil sucrase activity; G.Soil alkaline phosphatase activity; H.Soil acid phosphatase activity. The upper edge of the box represented the upper quartile, and the lower edge represented the lower quartile. The white dots inside the box represented the median, and the white horizontal lines represented the mean. Different letters indicated significant differences among producing areas, P<0.05.WX. Wuxi County, Chongqing; FJ. Fengjie County, Chongqing; WS. Wushan County, Chongqing; AQ. Ar Horqin Banner, Chifeng City; LX. Longxi County, Dingxi City; WY. Weiyuan County, Dingxi City; LT. Lintao County, Dingxi City; ZX. Zhang County, Dingxi City; MX. Min County, Dingxi City; GNLT. Lintan County, Gannan Xizang Autonomous Prefecture; ZN. Zhuoni County, Gannan Xizang Autonomous Prefecture; TC. Tanchang County, Longnan City; LC. Lingchuan County, Jincheng City.
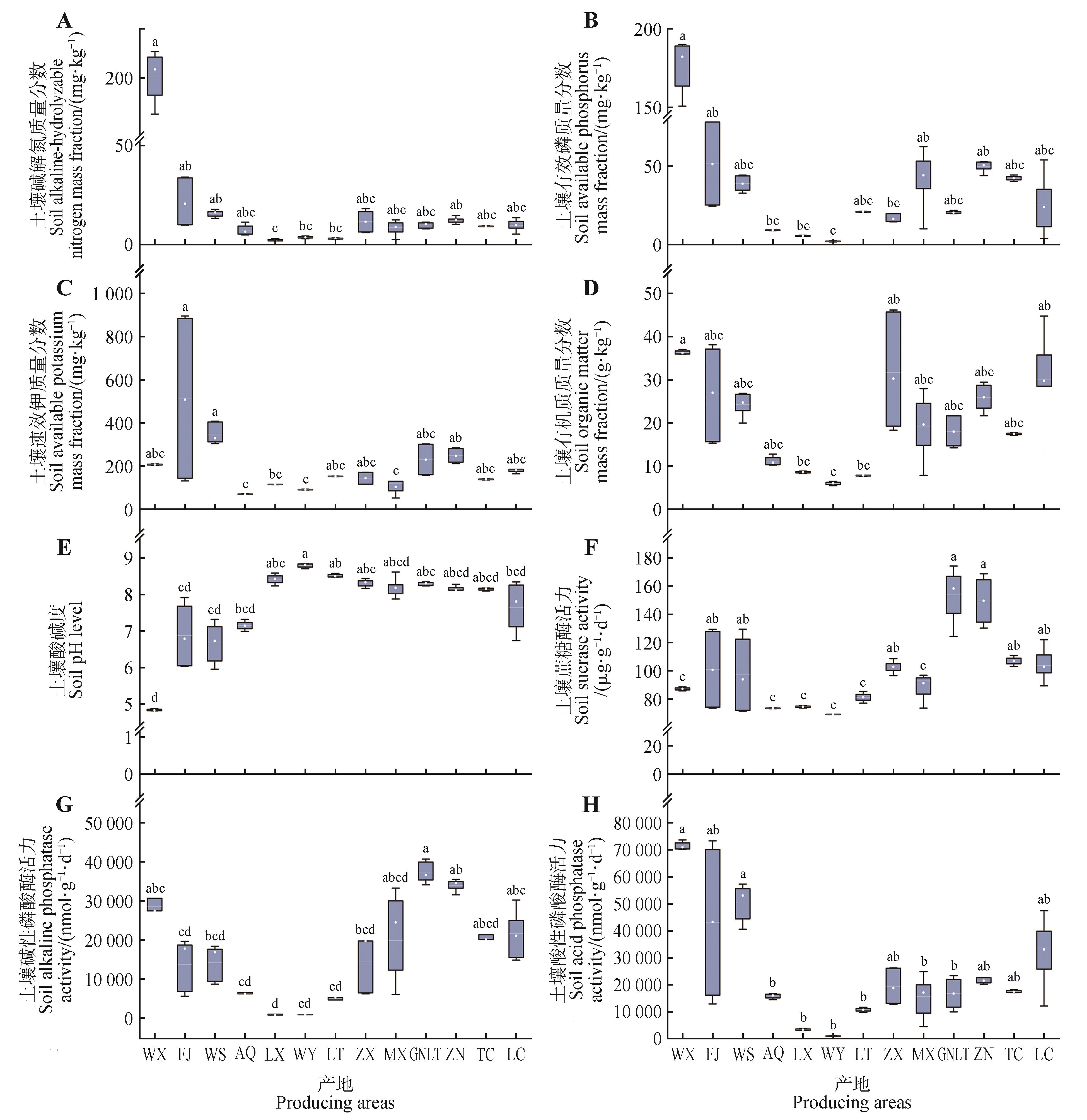
Table 2
Correlation analysis of the content of active ingredients in Codonopsis pilosula at different sampling sites based on longitude,latitude,and elevation
有效成分 Active ingredient | 地理因子 Geographical factors | 相关系数Correlation coefficient | P值 P value |
|---|---|---|---|
党参多糖 Codonopsis pilosula polysaccharide | 经度Longitude | -0.290 | 0.142 |
| 纬度Latitude | -0.275 | 0.164 | |
| 海拔Elevation | 0.242 | 0.221 | |
党参炔苷 Lobetyolin | 经度Longitude | 0.046 | 0.821 |
| 纬度Latitude | -0.714 | 0.000 | |
| 海拔Elevation | 0.049 | 0.809 |
Table 3
Principal component eigenvalues and variance contribution rate of active ingredients content in C. pilosula and environmental factors in different producing areas
主成分 Principal component | 特征值 Eigenvalue | 方差贡献率 Variance contribution rate/% | 累计方差贡献率 Cumulative variance contribution rate/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| PC1 | 16.4 | 53.0 | 53.0 |
| PC2 | 4.1 | 13.3 | 66.3 |
| PC3 | 3.1 | 9.9 | 76.3 |

Fig.4
Principal component analysis of active ingredients content in C. pilosula and environmental factors in different producing areasA.PCA score plot; B.PCA loading plot. Ellipses indicated 95% confidence intervals. cpp. Codonopsis pilosula polysaccharide; lob. Lobetyolin.SOM. Soil organic matter; pH. Soil pH value; AN.Available nitrogen in soil; AP. Available phosphorus in soil; AK. Available potassium in soil; fac1. Maximum temperature in April; fac2. Maximum temperature in May; fac3. Maximum temperature in June; fac4. Maximum temperature in July; fac5. Maximum temperature in August; fac6. Maximum temperature in September; fac7. Maximum temperature in October; fac8. Minimum temperature in April; fac9. Minimum temperature in May; fac10. Minimum temperature in June; fac11. Minimum temperature in July; fac12. Minimum temperature in August; fac13. Minimum temperature in September; fac14. Minimum temperature in October; fac15. Precipitation in April; fac16. Precipitation in May; fac17. Precipitation in June; fac18. Precipitation in July; fac19. Precipitation in August; fac20. Precipitation in September; fac21. Precipitation in October.
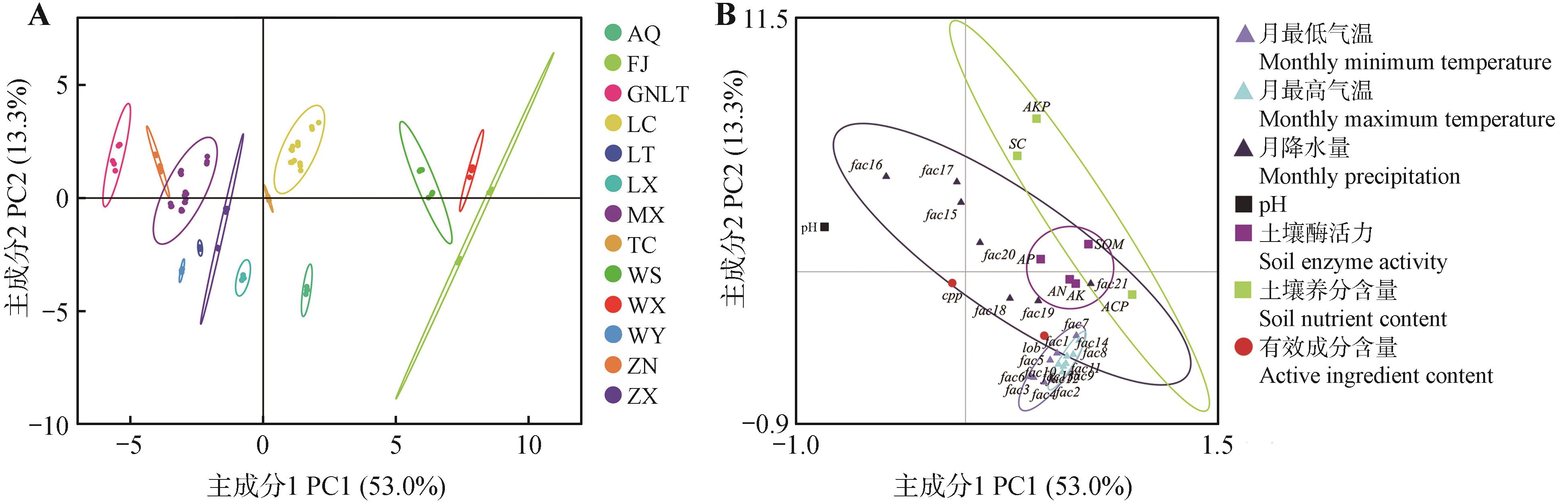
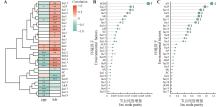
Fig.5
Correlation clustering heatmap and random forest model analysis between different environmental factors and active ingredient content in Codonopsis pilosulaA.Correlation clustering heatmap; B.Random forest model analysis of polysaccharide content in C. pilosula; C.Random forest model analysis of lobetyolin content in C. pilosula. *. P<0.05, **. P<0.01, ***. P<0.001. cpp. Codonopsis pilosula polysaccharide; lob. Lobetyolin.SOM. Soil organic matter; pH. Soil pH value; AN. Available nitrogen in soil; AP. Available phosphorus in soil; AK. Available potassium in soil; fac1. Maximum temperature in April; fac2. Maximum temperature in May; fac3. Maximum temperature in June; fac4. Maximum temperature in July; fac5. Maximum temperature in August; fac6. Maximum temperature in September; fac7. Maximum temperature in October; fac8. Minimum temperature in April; fac9. Minimum temperature in May; fac10. Minimum temperature in June; fac11. Minimum temperature in July; fac12. Minimum temperature in August; fac13. Minimum temperature in September; fac14. Minimum temperature in October; fac15. Precipitation in April; fac16. Precipitation in May; fac17. Precipitation in June; fac18. Precipitation in July; fac19. Precipitation in August; fac20. Precipitation in September; fac21. Precipitation in October.
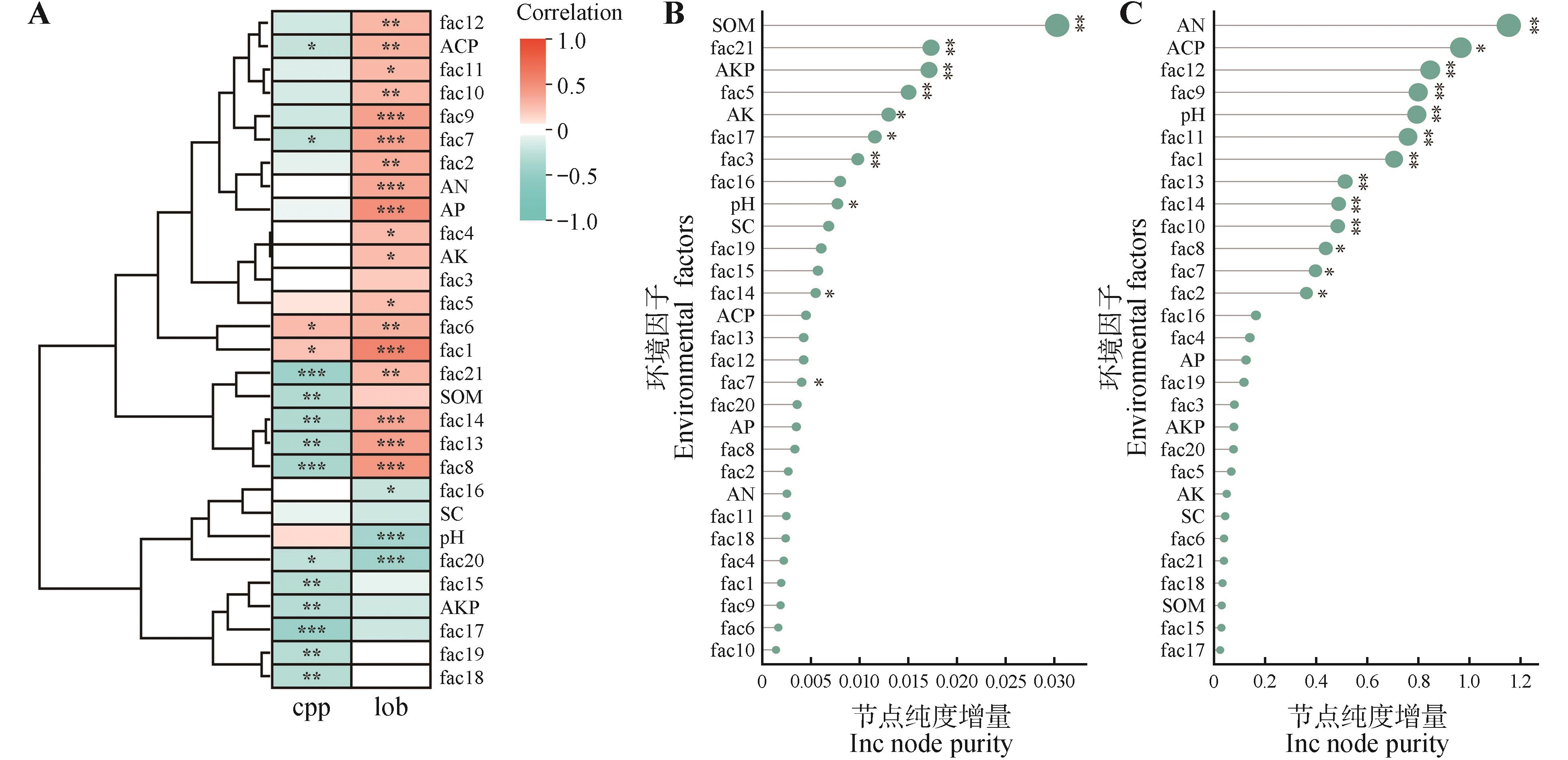
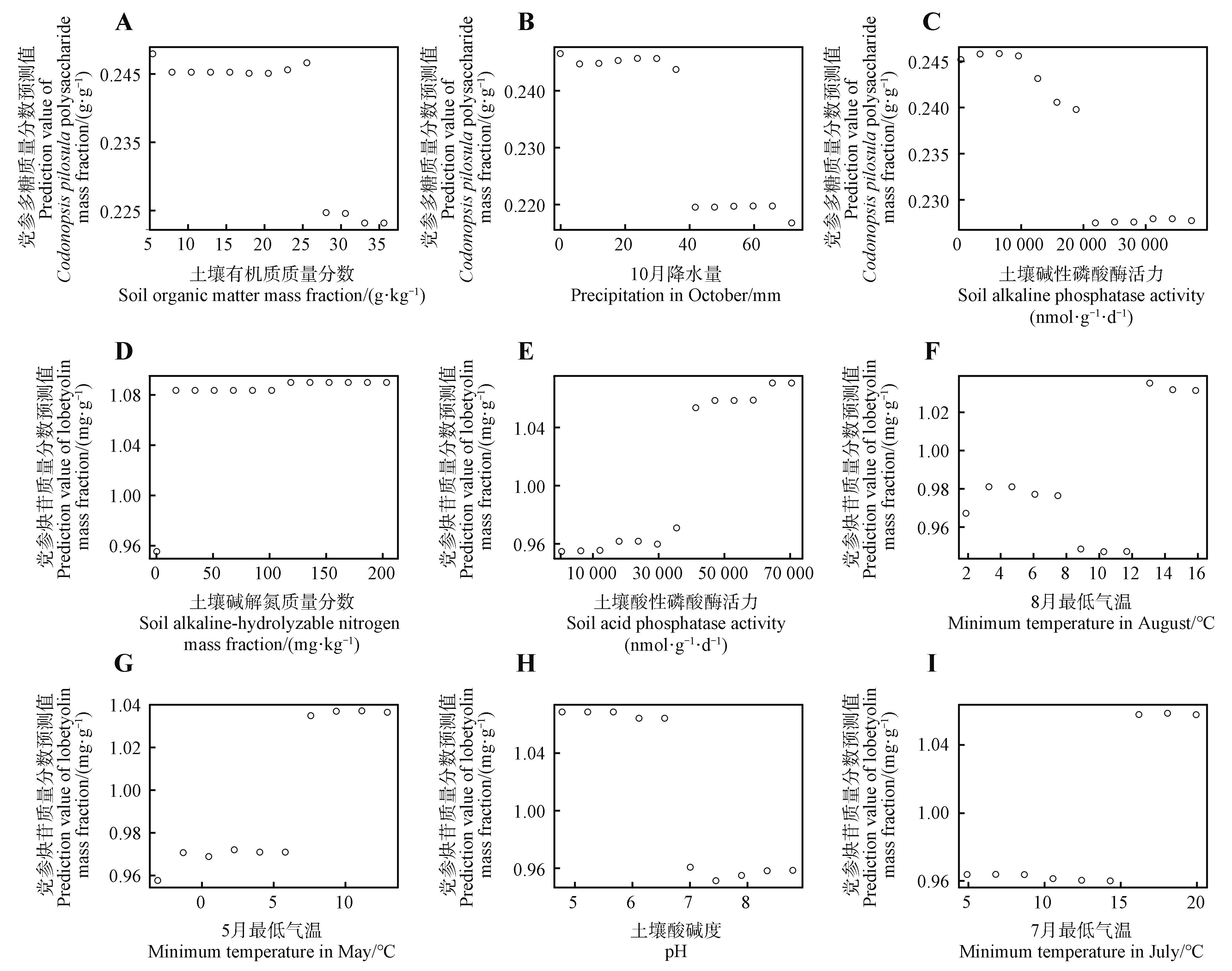
Fig.6
Partial dependence plot(PDP) of key environmental factors affecting the content of active ingredients in Codonopsis pilosulaA. PDP of polysaccharide mass fraction based on SOM; B. PDP of polysaccharide mass fraction based on fac21; C. PDP of polysaccharide mass fraction based on AKP; D. PDP of lobetyolin mass fraction based on AN; E. PDP of lobetyolin mass fraction based on ACP; F. PDP of lobetyolin mass fraction based on fac12; G. PDP of lobetyolin mass fraction based on fac9; H. PDP of lobetyolin mass fraction based on pH; I. PDP of lobetyolin mass fraction based on fac11.
| [1] | 苏圆锦,奚佳玉,史奇,等.药食同源中药党参的研究进展[J].中草药,2023,54(8):2607-2617. |
| SU Y J, XI J Y, SHI Q,et al.Research progress on Codonopsis Radix as medicinal and edible traditional Chinese medicine[J].Chinese Traditional and Herbal Drugs,2023,54(8):2607-2617. | |
| [2] | 张重阳,于淼,陈荣昌,等.党参药理作用的研究进展[J].中药新药与临床药理,2024,35(5):765-770. |
| ZHANG C Y, YU M, CHEN R C,et al.Research progress on the pharmacological effects of Codonopsis Radix [J].Traditional Chinese Drug Research and Clinical Pharmacology,2024,35(5):765-770. | |
| [3] | TANG S, LIU W, ZHAO Q Q,et al.Combination of polysaccharides from Astragalus membranaceus and Codonopsis pilosula ameliorated mice colitis and underlying mechanisms[J].Journal of Ethnopharmacology,2021,264:113280. |
| [4] | SHI Q, CHEN Z J, YANG J,et al.Review of Codonopsis Radix biological activities:a plant of traditional Chinese tonic[J].Journal of Ethnopharmacology,2024,332:118334. |
| [5] | 张开弦,姚秋阳,任艳,等.党参道地品种起源、变迁、现状研究进展[J].中成药,2024,46(1):211-216. |
| ZHANG K X, YAO Q Y, REN Y,et al.Research progress on the origin,change,and current status of the genuine species of Codonopsis Radix [J].Chinese Traditional Patent Medicine,2024,46(1):211-216. | |
| [6] | 段琦梅,梁宗锁,杨东风,等.党参质量评价体系的建立及不同产地党参质量差异性分析[J].中草药,2012,43(5):995-999. |
| DUAN Q M, LIANG Z S, YANG D F,et al.Establishment of quality evaluation system and difference analysis on roots of Codonopsis pilosula from different habitats[J].Chinese Traditional and Herbal Drugs,2012,43(5):995-999. | |
| [7] | 杨生超,赵昶灵,文国松,等.植物药材道地性的分子机制研究与应用[J].中草药,2007,38(11):1738-1741. |
| YANG S C, ZHAO C L, WEN G S,et al.Studies and applications on molecular mechanism of genuineness of traditional Chinese medicinal materials from plants[J].Chinese Traditional and Herbal Drugs,2007,38(11):1738-1741. | |
| [8] | 段耿婷,刘付松,张澜,等.不同产地党参的总硒、蛋白质、多糖含量及土壤总硒含量的相关性分析[J].中南药学,2023,21(3):777-783. |
| DUAN G T, LIU F S, ZHANG L,et al.Correlation between total selenium,protein and polysaccharide content of Codonopsis Radix and soil selenium content in different areas[J].Central South Pharmacy,2023,21(3):777-783. | |
| [9] | 牛天增,王玉龙,侯沁文,等.党参功效成分含量与土壤因子相关性分析[J].中国实验方剂学杂志,2022,28(11):164-172. |
| NIU T Z, WANG Y L, HOU Q W,et al.Correlation between functional components in Codonopsis pilosula roots and soil factors[J].Chinese Journal of Experimental Traditional Medical Formulae,2022,28(11):164-172. | |
| [10] | 栾青,郭建平,马雅丽,等.晋东南潞党参生态气候适生种植区划[J].生态学杂志,2020,39(9):2953-2962. |
| LUAN Q, GUO J P, MA Y L,et al.Division of eco-climate planting area of Codonopsis pilosula in southeastern Shanxi[J].Chinese Journal of Ecology,2020,39(9):2953-2962. | |
| [11] | 张定全,张娟.陇西县白条党参产量与生育期主要气象条件的相关性分析[J].甘肃农业科技,2012(8):11-13. |
| ZHANG D Q, ZHANG J.The relevance analysis of yield and the main meteorological condition of growth period of white dangshen[J].Gansu Agricultural Science and Technology,2012(8):11-13. | |
| [12] | 成铭,皮文霞,陆兔林,等.党参地上部分的党参炔苷、多糖含量测定及影响因素分析[J].中药材,2020,43(5):1092-1098. |
| CHENG M, PI W X, LU T L,et al.Determination of content of lobetyolin and polysaccharides in the aerial parts of Codonopsis Radix and analysis of influencing factors[J].Journal of Chinese Medicinal Materials,2020,43(5):1092-1098. | |
| [13] | 程泽京,张慧仙,黄高鉴,等.腐植酸型营养剂对潞党参产量与品质的影响[J].山西农业科学,2023,51(7):771-776. |
| CHENG Z J, ZHANG H X, HUANG G J,et al.Effects of humic acid conditioners on the yield and quality of Codonopsis pilosula(Lu Dangshen)[J].Journal of Shanxi Agricultural Sciences,2023,51(7):771-776. | |
| [14] | 针娴,高建平,曹玲亚.潞党参多糖含量测定[J].中华中医药学刊,2014,32(3):498-500. |
| ZHEN X, GAO J P, CAO L Y.Determination of contents of polysaccharide in Lu Dangshen[J].Chinese Archives of Traditional Chinese Medicine,2014,32(3):498-500. | |
| [15] | 中国土壤学会农业化学专业委员会.土壤农业化学常规分析方法[M].北京:科学出版社,1983:78. |
| Soil Agrochemistry Specialty Committee of the Soil Science Society of China.Routine analytical methods for soil agrochemistry[M].Beijing:Science Press,1983:78. | |
| [16] | QADERI M M, MARTEL A B, STRUGNELL C A.Environmental factors regulate plant secondary metabolites[J].Plants,2023,12(3):447. |
| [17] | 郭兰萍,周良云,康传志,等.药用植物适应环境胁迫的策略及道地药材“拟境栽培”[J].中国中药杂志,2020,45(9):1969-1974. |
| GUO L P, ZHOU L Y, KANG C Z,et al.Strategies for medicinal plants adapting environmental stress and “simulative habitat cultivation” of Dao-di herbs[J].China Journal of Chinese Materia Medica,2020,45(9):1969-1974. | |
| [18] | 田红怡,淳泽,王刚,等.生态因子与金钗石斛生理指标及有效成分的相关性研究[J].中药材,2020,43(3):558-563. |
| TIAN H Y, CHUN Z, WANG G,et al.Correlation study of ecological factors and the Dendrobium nobile physiology indexes and effective constituents[J].Journal of Chinese Medicinal Materials,2020,43(3):558-563. | |
| [19] | WANG Y L, LIU H C, YU S,et al.Effects of geographical,soil and climatic factors on the two marker secondary metabolites contents in the roots of Rubia cordifolia L.[J].Frontiers in Plant Science,2024,15:1419392. |
| [20] | 孙卫敏,曾伟民,贾向前,等.不同经纬度黄芩代谢差异的综合研究[J].中国药学杂志,2023,58(17):1554-1562. |
| SUN W M, ZENG W M, JIA X Q,et al.A comprehensive study on the differences between Scutellaria baicalensis Georgi metabolism at different latitudes and longitudes[J].Chinese Pharmaceutical Journal,2023,58(17):1554-1562. | |
| [21] | ÇΙRAK C, RADUŠIENĖ J, JANULIS V,et al.Secondary metabolites in Hypericum perfoliatum:variation among plant parts and phenological stages[J].Botanica Helvetica,2007,117:29-36. |
| [22] | BHATT N F, GUPTA R C, BANSAL Y.Secondary metabolites in Arctium lappa L.:variation among plant parts and phenological stages[J].Journal of Planar Chromatography,2019,32:461-465. |
| [23] | 郭杰,刘小平,张琴,等.基于Maxent模型的党参全球潜在分布区预测[J].应用生态学报,2017,28(3):992-1000. |
| GUO J, LIU X P, ZHANG Q,et al.Prediction for the potential distribution area of Codonopsis pilosula at global scale based on Maxent model[J].Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology,2017,28(3):992-1000. | |
| [24] | ATKIN O K, BRUHN D, HURRY V M,et al.The hot and the cold:unravelling the variable response of plant respiration to temperature[J].Functional Plant Biology,2005,32(2):87-105. |
| [25] | HAYASHI S, LEVINE C P, YU W,et al.Raising root zone temperature improves plant productivity and metabolites in hydroponic lettuce production[J].Frontiers in Plant Science,2024,15:1352331. |
| [26] | 李旭,刘莹,孙文松,等.不同产地五味子品质与气候因子的相关性分析[J].时珍国医国药,2022,33(5):1194-1197. |
| LI X, LIU Y, SUN W S,et al.Correlation analysis between climate factors and main components of Schisandra chinensis Baill with different areas[J].Lishizhen Medicine and Materia Medica Research,2022,33(5):1194-1197. | |
| [27] | 孟彤彤,赵涛涛,王永刚,等.季节驱动下的土壤微生态环境与党参生长的动态关系[J].基因组学与应用生物学,2023,42(7):744-756. |
| MENG T T, ZHAO T T, WANG Y G,et al.Dynamic relationship between soil micro-ecological environment and Codonopsis pilosula growth driven by seasons[J].Genomics and Applied Biology,2023,42(7):744-756. | |
| [28] | 何春雨,张延红,蔺海明.甘肃道地党参生长动态研究[J].中国中药杂志,2006,31(4):285-289. |
| HE C Y, ZHANG Y H, LIN H M.Study on dynamic growth of Codonopsis pilosula [J].China Journal of Chinese Materia Medica,2006,31(4):285-289. | |
| [29] | 王赞文.土壤水分对党参生长发育和成分积累的影响[D].杭州:浙江理工大学,2018. |
| WANG Z W.The effects of growth development and composition accumulation of Codonopsis pilosula under different soil moisture[D].Hangzhou:Zhejiang Sci-Tech University,2018. | |
| [30] | 张晓煜,刘静,袁海燕,等.枸杞多糖与土壤养分、气象条件的量化关系研究[J].干旱地区农业研究,2003(3):43-47. |
| ZHANG X Y, LIU J, YUAN H Y,et al.A study on quantified relationship between the polysaccharides concent of Lycium barbarum L. and soil nutrient and meteorological condition[J].Agricultural Research in the Arid Areas,2003(3):43-47. | |
| [31] | 林伟山,德科加,钱诗祎,等.高寒草甸植被-土壤养分含量与气象因子相关关系研究[J].草原与草坪,2023,43(6):109-120. |
| LIN W S, DE K J, QIAN S Y,et al.A study on the correlation between vegetation-soil nutrient content and meteorological factors in alpine meadows[J].Grassland and Turf,2023,43(6):109-120. | |
| [32] | 冼丽铧,吴道铭,隆曼迪,等.土壤养分、种植年限和种植方式对巴戟天寡糖含量的影响[J].华南农业大学学报,2021,42(3):75-85. |
| XIAN L H, WU D M, LONG M D,et al.Effects of soil nutrients,planting years and methods on oligosaccharide content of Morinda officinalis [J].Journal of South China Agricultural University,2021,42(3):75-85. | |
| [33] | 李卫建,李先恩.连翘有效成分含量与土壤养分的量化关系研究[J].中国中药杂志,2005,30(20):1577-1580. |
| LI W J, LI X E.Study on quantified relationship between contents of active components in Forsythia suspense and nutrition of soil[J].China Journal of Chinese Materia Medica,2005,30(20):1577-1580. | |
| [34] | 黄高鉴,孙晋鑫,张强,等.氮磷钾配施对潞党参产量与品质的影响及肥料效应[J].中国土壤与肥料,2022(9):26-31. |
| HUANG G J, SUN J X, ZHANG Q,et al.Effect of combined application of NPK fertilization on the yield and quality of Codonopsis piloula(Lu Dangshen)and its fertilizer interaction[J].Soil and Fertilizer Sciences in China,2022(9):26-31. | |
| [35] | YAN Z H, JIN H, YANG X Y,et al.Effect of rhizosphere soil microbial communities and environmental factors on growth and the active ingredients of Angelica sinensis in Gansu Province,China[J].Folia Microbiologica,2025,70(3):673-687. |
| [36] | 黄宇,张海伟,徐芳森.植物酸性磷酸酶的研究进展[J].华中农业大学学报,2008,27(1):148-154. |
| HUANG Y, ZHANG H W, XU F S.Research progress on plant acid phosphatase[J].Journal of Huazhong Agricultural University,2008,27(1):148-154. |
| [1] | Jiaying TANG, Jinkun ZHANG, Jiwen HU, Fude WANG, Peiyao XIN, Wenjun MA. Phenotypic Diversity Analysis of Natural Herbaceous Peony Populations in Great Khingan Mountains [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2025, 45(2): 299-314. |
| [2] | Xiangchen MA, Ping ZHANG, Yuxin CHEN, Lei JIN. Antioxidant Activity of Polyphenol Extracts from Ten Lily Bulbs and Its Correlation with Environmental Factors [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2025, 45(2): 315-328. |
| [3] | Chu HUANG, Mingyue HE, Meile SUN, Yanhong CHEN, Huizhen WANG. Silicon-mediated Regulation on Polysaccharides Synthesis of Codonopsis pilosula under Drought Stress Based on EMP and TCA cycle Pathways [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2025, 45(1): 98-110. |
| [4] | Yuping QIU, Yichuan WANG, Hongwei GUO. Research Progress on the Regulatory Mechanism of Plant Root Hair Development [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2023, 43(3): 321-332. |
| [5] | CAI Nian-Hui, WANG Da-Wei, HUANG Wen-Xue, WU Jun-Wen, WANG Jun-Min, CHEN Shi, XU Yu-Lan, DUAN An-An. Correlation and Path Analysis on Growth Traits and Biomass of Pinus yunnanensis Seedlings [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2019, 39(6): 853-862. |
| [6] | LIU Min-Xia, LI Li-Rong, CHE Ying-Di, JIAO Jiao. Functional Traits of Plant Leaves at Different Succession Stages in Alpine Meadow [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2019, 39(5): 760-769. |
| [7] | DUAN Yi-Zhong, DU Zhong-Yu, KANG Fu-Ren. Community Characteristics of Endangered Plant of Ammopiptanthus mongolicus to Environmental Factors in Northwest Arid Area of China [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2018, 38(6): 834-842. |
| [8] | CHANG Bo-Wen, LIU Jie, ZHONG Peng, GUO Xiao-Rui. Effects of Exogenous Ethylene on Physiology and Alkaloid Accumulations in Catharanthus roseus [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2018, 38(2): 284-291. |
| [9] | HAN Shu-Ting, TIAN Gui-Quan, HAN Shu-Mei. Species Diversity of Ground Bryophyte Communities in Different Vegetation in Daqinggou National Nature Reserve [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2017, 37(5): 664-672. |
| [10] | DU Qing-Xin, QING Jun, ZHU Jing-Le, DU Hong-Yan, DU Lan-Ying. Pigments and Active Ingredients in Leaves of Seven Eucommia ulmoides Variation-types [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2017, 37(3): 468-473. |
| [11] | HUNG Wen-Juan, JIAO Pei-Pei, HUANG Jin-Hua, ZHANG Dan. Leaf Anatomical Structure of Populus euphratica in Tarim River Basin [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2016, 36(5): 669-675. |
| [12] | XU Bin1;PENG Li-Xia2;YANG Hui-Xiao1*;PAN Wen1;ZHANG Fang-Qiu1. Genetic Diversity Analysis for Leaf Main Traits of Camellia azalea [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2015, 35(5): 730-734. |
| [13] | LIU Dian-Kun1;LIU Meng-Ran1;LI Zhi-Xin1;WANG Guang-Yu2;LI Ying1;ZHENG Mi1;LIU Gui-Feng1;ZHAO Xi-Yang1*. Variation Analysis of Growth Traits of Transgenic Populus simonii×P.nigra Clones Carrying TaLEA Gene [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2015, 35(4): 540-546. |
| [14] | YANG Qing-Xiao;ZHU Liang-Jun;WANG Xiao-Chun. Development of Pinus koraiensis Tree-ring Chronology and Master Year Analysis in Liangshui National Natural Reserve,China [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2015, 35(3): 418-424. |
| [15] | ZHANG Zhong-Hua1,2;TANG Zhong-Hua1;YANG Feng-Jian1*;WANG Hua3;ZHANG Jun1;ZU Yuan-Gang1. Photosynthetic Characteristics and Its Micro-environmental Limiting Factors of Two Main Oil Peony [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2014, 34(6): 770-775. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||