Bulletin of Botanical Research ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (2): 277-286.doi: 10.7525/j.issn.1673-5102.2025.02.013
• Original Paper • Previous Articles
Changli ZHAO, Liwei ZHOU, Kerou ZHOU, Yueqi YOU, Zhixiang ZHANG
Received:2024-10-31
Online:2025-03-20
Published:2025-04-07
CLC Number:
Changli ZHAO, Liwei ZHOU, Kerou ZHOU, Yueqi YOU, Zhixiang ZHANG. Population Variation of Leaf Traits and Its Correlation with Environmental Factors of Caragana halodendron[J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2025, 45(2): 277-286.
Table 1
Sampling sites information of 18 populations of Caragana halodendron
居群 Population | 采集地点 Collection site | 样本数量 Sample number | 经度(E) Longitude/(°) | 纬度(N) Latitude/(°) | 海拔 Elevation/m |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 新疆北屯市 Beitun City,Xinjiang | 6 | 87.86 | 47.26 | 537.00 |
| 2 | 新疆阿勒泰地区阿勒泰市 Altay City,Altay Prefecture,Xinjiang | 6 | 87.71 | 47.70 | 705.00 |
| 3 | 新疆阿勒泰地区布尔津县 Burqin County,Altay Prefecture,Xinjiang | 6 | 87.23 | 47.75 | 490.00 |
| 4 | 新疆阿勒泰地区哈巴河县 Habahe County,Altay Prefecture,Xinjiang | 6 | 86.50 | 48.03 | 469.00 |
| 5 | 新疆塔城地区额敏县 Emin County,Tarbagatay Prefecture,Xinjiang | 6 | 83.57 | 46.42 | 423.00 |
| 6 | 新疆塔城地区精河县 Jinghe County,Tarbagatay Prefecture,Xinjiang | 6 | 82.18 | 44.44 | 815.00 |
| 7 | 新疆塔城地区精河县 Jinghe County,Tarbagatay Prefecture,Xinjiang | 6 | 82.18 | 44.44 | 795.00 |
| 8 | 新疆阜康市 Fukang City,Xinjiang | 6 | 87.89 | 44.29 | 407.00 |
| 9 | 新疆昌吉玛纳斯县 Manas County,Changji City,Xinjiang | 6 | 85.99 | 43.88 | 1 403.00 |
| 10 | 新疆伊犁地区巩留县 Gongliu County,Ili Prefecture,Xinjiang | 6 | 82.52 | 43.34 | 876.00 |
| 11 | 新疆沙湾市 Shawan City,Xinjiang | 6 | 85.72 | 44.36 | 462.00 |
| 12 | 新疆吐鲁番市 Turpan City,Xinjiang | 6 | 88.75 | 43.01 | 238.00 |
| 13 | 新疆喀什地区英吉沙县 Yingjisha County,Kashgar Prefecture,Xinjiang | 6 | 76.15 | 39.03 | 1 245.00 |
| 14 | 新疆和田地区和田县 Hotan County,Hotan Prefecture,Xinjiang | 6 | 80.00 | 37.39 | 1 236.00 |
| 15 | 新疆阿拉尔市 Aral City,Xinjiang | 6 | 81.35 | 40.55 | 948.00 |
| 16 | 新疆阿勒泰地区青河县 Qinghe County,Altay Prefecture,Xinjiang | 6 | 90.24 | 46.53 | 1 158.00 |
| 17 | 新疆阿勒泰地区富蕴县 Fuyun County,Altay Prefecture,Xinjiang | 6 | 88.75 | 46.36 | 698.00 |
| 18 | 新疆北屯市 Beitun City,Xinjiang | 6 | 87.83 | 47.37 | 505.00 |
Table 2
Variation in leaf traits of Caragana halodendron
描述性统计量 Descriptive statistics | 叶面积 Leaf area /mm2 | 叶长宽比 Leaf aspect ratio | 叶周长 Leaf perimeter /mm | 叶宽 Leaf width /mm | 叶长 Leaf length /mm | 叶含水量 Leaf water content/% | 干物质含量 Dry matter content/% | 比叶面积 Specific leaf area /(mm2·g-1) | 叶轴长度 Length of rachis/mm | 托叶刺长度 Length of stipulate spines/mm | 小叶数量 Number of leaflets | 均值Mean |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 均值Mean | 97.41 | 3.02 | 51.40 | 7.20 | 21.21 | 64.53 | 35.47 | 296.78 | 32.20 | 4.00 | 4.96 | |
| 标准差SD | 49.43 | 0.69 | 14.87 | 2.01 | 6.18 | 6.08 | 6.08 | 149.01 | 11.00 | 2.20 | 1.09 | |
| 最小值Min value | 16.99 | 0.49 | 18.85 | 3.02 | 6.19 | 42.43 | 21.41 | 71.63 | 8.00 | 0 | 2.00 | |
| 最大值Max value | 385.34 | 10.64 | 297.33 | 20.87 | 116.50 | 78.60 | 57.58 | 735.81 | 84.00 | 11.00 | 8.00 | |
| 极差Range | 368.35 | 10.15 | 278.49 | 17.86 | 110.31 | 36.17 | 36.17 | 664.18 | 76.00 | 11.00 | 6.00 | |
| 变异系数CV/% | 50.74 | 22.99 | 28.94 | 27.95 | 29.12 | 9.42 | 17.14 | 50.21 | 34.24 | 53.22 | 21.96 | 34.17 |
Table 3
Coefficient of variation of leaf traits of Caragana halodendron in different populations
居群 Population | 叶面积 Leaf area | 长宽比 Leaf aspect ratio | 叶周长 Leaf perimeter | 叶宽 Leaf width | 叶长 Leaf length | 叶含水量 Leaf water content | 干物质含量 Dry matter content | 比叶面积 Specific leaf area | 叶轴长度 Length of leaf rachis | 托叶刺长度 Length of stipulate spines | 小叶数量 Number of leaflets | 均值 Mean |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 40.02 | 19.84 | 23.14 | 25.98 | 21.02 | 10.83 | 18.48 | 31.52 | 25.59 | 55.04 | 20.16 | 26.51 |
| 2 | 56.37 | 15.10 | 27.79 | 26.75 | 28.27 | 4.29 | 8.58 | 46.70 | 33.00 | 51.62 | 18.76 | 28.84 |
| 3 | 41.06 | 13.81 | 21.30 | 24.01 | 20.32 | 1.58 | 5.22 | 24.12 | 18.20 | 48.42 | 19.69 | 21.61 |
| 4 | 36.75 | 22.32 | 21.26 | 21.35 | 21.20 | 4.81 | 9.49 | 31.00 | 24.68 | 42.45 | 20.49 | 23.26 |
| 5 | 35.97 | 14.88 | 19.20 | 20.64 | 19.42 | 2.31 | 3.42 | 24.43 | 40.24 | 37.73 | 23.28 | 21.96 |
| 6 | 36.52 | 14.66 | 21.14 | 21.93 | 20.85 | 4.09 | 8.71 | 33.70 | 23.26 | 59.07 | 19.47 | 23.95 |
| 7 | 30.14 | 17.22 | 16.41 | 19.64 | 17.41 | 5.61 | 8.67 | 22.20 | 27.03 | 37.29 | 19.14 | 20.07 |
| 8 | 39.87 | 18.02 | 20.16 | 21.91 | 20.04 | 7.51 | 16.61 | 30.93 | 26.70 | 41.98 | 23.32 | 24.28 |
| 9 | 30.96 | 13.19 | 15.40 | 17.26 | 15.02 | 2.91 | 5.91 | 18.31 | 33.77 | 19.82 | 22.01 | 17.69 |
| 10 | 24.89 | 13.96 | 14.28 | 15.85 | 14.94 | 3.48 | 5.49 | 13.39 | 13.46 | 33.46 | 16.07 | 15.39 |
| 11 | 31.69 | 14.23 | 16.13 | 17.98 | 16.64 | 3.14 | 6.24 | 12.53 | 23.33 | 45.74 | 15.87 | 18.50 |
| 12 | 24.24 | 10.67 | 12.78 | 12.49 | 14.16 | 5.33 | 7.57 | 14.30 | 25.28 | 32.63 | 20.16 | 16.33 |
| 13 | 41.06 | 19.83 | 31.79 | 22.89 | 30.02 | 2.93 | 7.40 | 21.47 | 29.39 | 47.25 | 9.71 | 23.98 |
| 14 | 31.79 | 20.03 | 18.93 | 17.73 | 20.32 | 14.35 | 19.39 | 23.37 | 24.96 | 31.23 | 21.70 | 22.16 |
| 15 | 41.90 | 16.83 | 21.75 | 20.81 | 21.79 | 14.03 | 22.47 | 43.40 | 21.34 | 41.25 | 12.91 | 25.32 |
| 16 | 32.31 | 13.33 | 18.62 | 18.37 | 16.61 | 2.12 | 3.47 | 21.17 | 26.74 | 36.55 | 19.67 | 19.00 |
| 17 | 30.21 | 15.78 | 19.28 | 19.49 | 19.30 | 4.61 | 8.01 | 19.40 | 22.18 | 50.13 | 20.58 | 20.81 |
| 18 | 40.39 | 23.13 | 23.59 | 22.80 | 23.83 | 5.70 | 9.14 | 30.64 | 20.28 | 41.68 | 20.55 | 23.79 |
| 最小值Min | 24.24 | 10.67 | 12.78 | 12.49 | 14.16 | 1.58 | 3.42 | 12.53 | 13.46 | 19.82 | 9.71 | 16.33 |
| 最大值Max | 56.37 | 23.13 | 31.79 | 26.75 | 30.02 | 14.35 | 22.47 | 46.70 | 40.24 | 59.07 | 23.32 | 21.84 |
| 均值Ave | 35.90 | 16.49 | 20.16 | 20.44 | 20.06 | 5.53 | 9.68 | 25.70 | 25.52 | 41.85 | 19.09 | 21.86 |
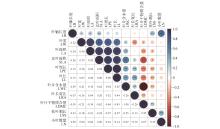
Fig.1
Correlation analysis of leaf traits in Caragana halodendronTrait correlations were represented by colors, which blue indicating positive correlations and red indicating negative correlations. The color gradient represented different Pearson correlation coefficients. An asterisk(*) denoted the level of significance(**.P<0.01,*.0.01<P<0.05).
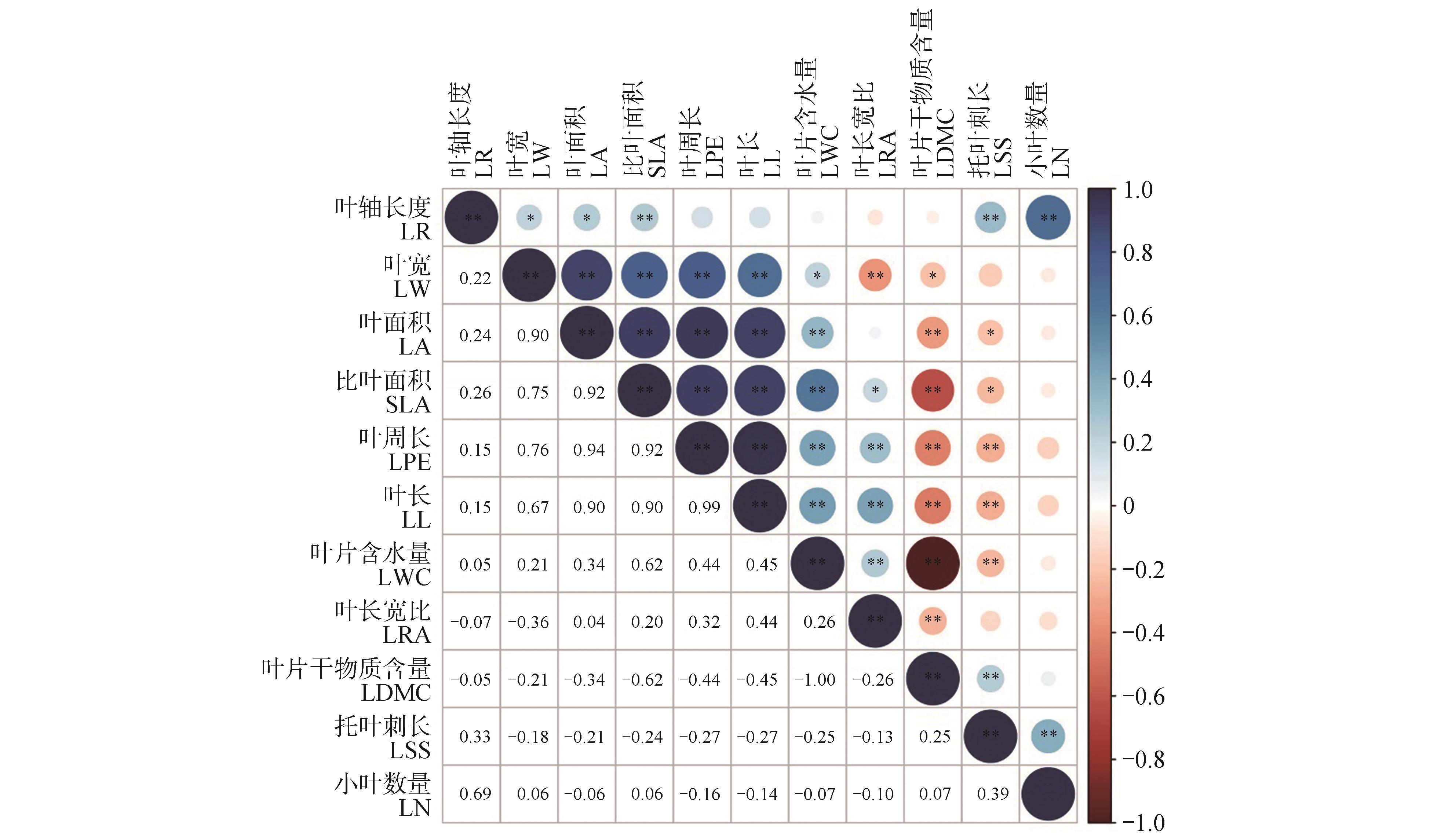
Table 4
Principal component analysis of leaf-related traits of Caragana halodendron
性状 Trait | 第一主成分 PC1 | 第二主成分 PC2 | 第三主成分 PC3 | 第四主成分 PC4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 叶片含水量LWC | 8.01 | 3.93 | 20.87 | 14.11 |
| 叶片干物质含量LDMC | 8.00 | 3.93 | 20.89 | 14.12 |
| 比叶面积SLA | 18.14 | 0.48 | 0.05 | 0.03 |
| 叶面积LA | 16.17 | 2.72 | 4.76 | 0.30 |
| 叶长宽比LRA | 1.18 | 8.13 | 13.53 | 49.90 |
| 叶周长LPE | 17.44 | 0.10 | 1.33 | 4.74 |
| 叶宽LW | 10.93 | 5.84 | 14.41 | 5.53 |
| 叶长LL | 16.97 | 0.00 | 0.26 | 9.17 |
| 叶轴长度LR | 0.62 | 31.79 | 7.65 | 0.30 |
| 托叶刺长度LSS | 2.18 | 15.57 | 3.18 | 1.75 |
| 小叶数量LN | 0.35 | 27.52 | 13.04 | 0.05 |
| 特征值Eigenvalue | 5.23 | 2.08 | 1.62 | 1.10 |
| 贡献率Contribution rate/% | 47.57 | 18.89 | 14.70 | 9.97 |
| 累计贡献率Cumulative contribution rate/% | 47.57 | 66.46 | 81.16 | 91.13 |

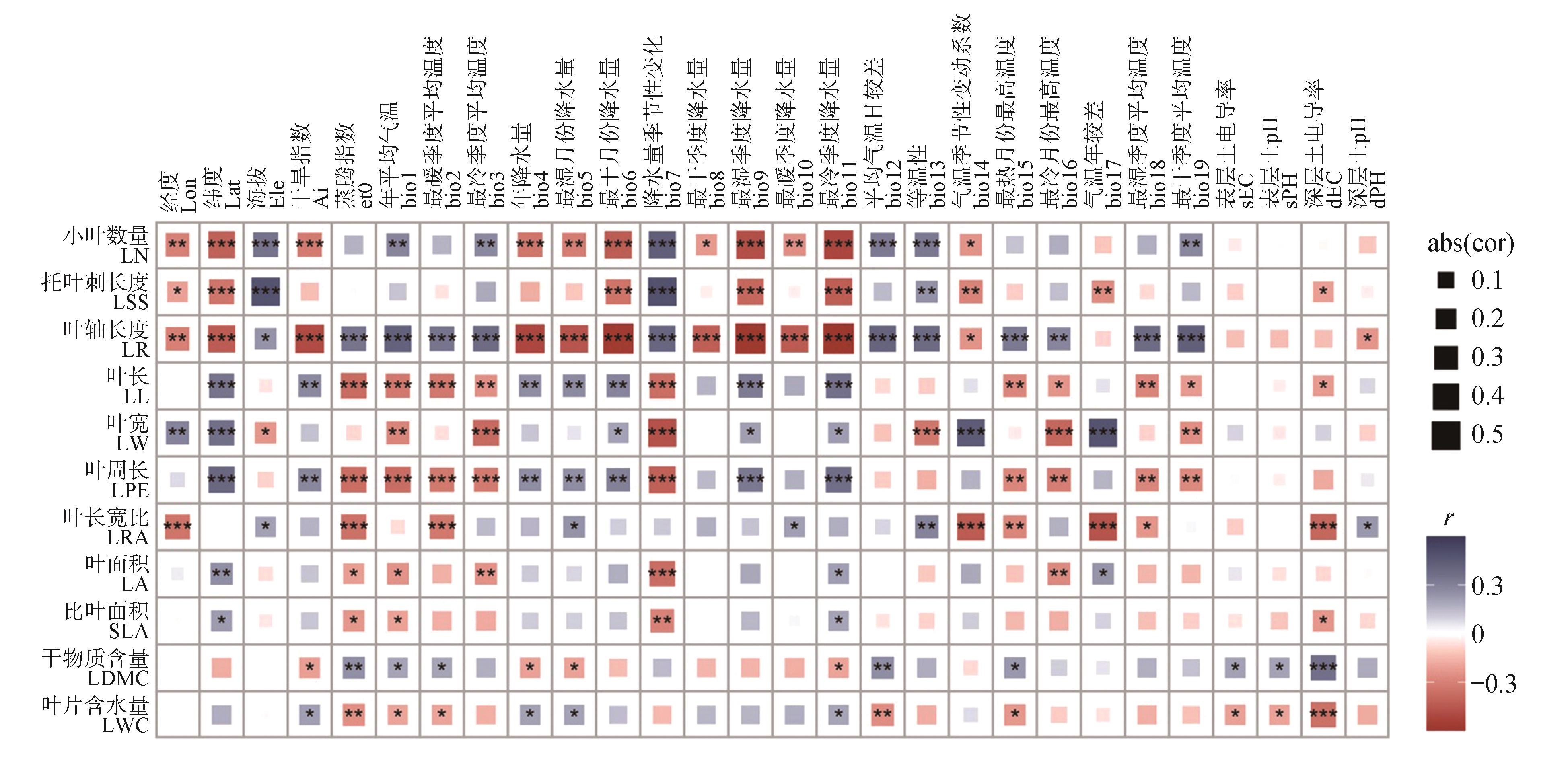
Fig.2
Correlation analysis between leaf traits and environmental factors of Caragana halodendronThe correlation between leaf traits and environmental factors was represented by color and the size of the color blocks. Blue indicated a positive correlation,and red indicated a negative correlation;the color gradient and the size of the blocks represented different Pearson correlation coefficients; the larger the block and the deeper the color, the higher the correlation coefficient(r). An asterisk(*) denoted the level of significance(***.P<0.001, **.0.001<P<0.01,*.0.01<P<0.05).
| 1 | CORNELISSEN J H C, LAVOREL S, GARNIER E,et al.A handbook of protocols for standardised and easy measurement of plant functional traits worldwide[J].Australian Journal of Botany,2003,51(4):335-380. |
| 2 | 潘映红.论植物表型组和植物表型组学的概念与范 畴[J].作物学报,2015,41(2):175-186. |
| PAN Y H.Analysis of concepts and categories of plant phenome and phenomics[J].Acta Agronomica Sinica,2015,41(2):175-186. | |
| 3 | 高强.17种荒漠植物形态结构与环境的适应性研 究[D].呼和浩特:内蒙古农业大学,2008. |
| GAO Q.Adaptability research of morphological structure to the desert plants and environment[D].Hohhot:Inner Mongolia Agricultural University,2008. | |
| 4 | 高春娟,夏晓剑,师恺,等.植物气孔对全球环境变化的响应及其调控防御机制[J].植物生理学报,2012, 48(1):19-28. |
| GAO C J, XIA X J, SHI K,et al.Response of stomata to global climate changes and the underlying regulation mechanism of stress responses[J].Plant Physiology Journal,2012,48(1):19-28. | |
| 5 | 李耀琪,王志恒.植物叶片形态的生态功能、地理分布与成因[J].植物生态学报,2021,45(10):1154-1172. |
| LI Y Q, WANG Z H.Leaf morphological traits:ecological function,geographic distribution and drivers[J].Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology,2021,45(10):1154-1172. | |
| 6 | JI D L, LI Q X, GUO Y J,et al.NADP+ supply adjusts the synthesis of photosystem I in Arabidopsis chloroplasts[J].Plant Physiology,2022,189(4):2128-2143. |
| 7 | ZHANG J Y, HE S B, LI L,et al.Auxin inhibits stomatal development through MONOPTEROS repression of a mobile peptide gene STOMAGEN in mesophyll[J].Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America,2014,111(29):E3015-E3023. |
| 8 | 毛桂莲,许兴,徐兆桢.植物耐盐生理生化研究进展[J].中国生态农业学报,2004,12(1):43-46. |
| MAO G L, XU X, XU Z Z.Advances in physiological and biochemical research of salt tolerance in plant[J].Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture,2004,12(1):43-46. | |
| 9 | 王佺珍,刘倩,高娅妮,等.植物对盐碱胁迫的响应机制研究进展[J].生态学报,2017,37(16):5565-5577. |
| WANG Q Z, LIU Q, GAO Y N,et al.Review on the mechanisms of the response to salinity-alkalinity stress in plants[J].Acta Ecologica Sinica,2017,37(16):5565-5577. | |
| 10 | 姚仁秀,陈燕,吕晓琴,等.海拔及环境因子影响杜鹃属植物的表型特征和化学性状[J].生物多样性,2023,31(2):22259. |
| YAO R X, CHEN Y, LÜ X Q,et al.Altitude-related environmental factors shape the phenotypic characteristics and chemical profile of Rhododendron [J].Biodiversity Science,2023,31(2):22259. | |
| 11 | 刘文倩,李家湘,龚俊伟,等.柯-青冈常绿阔叶林优势树种叶片性状变异及适应策略[J].生态学报,2022,42(17):7256-7265. |
| LIU W Q, LI J X, GONG J W,et al.Variation in leaf functional traits and adaptation strategies of dominant tree species in a Lithocarpus glaber-Cyclobalanopsis glauca evergreen broad-leaved forest[J].Acta Ecologica Sinica,2022,42(17):7256-7265. | |
| 12 | XU R, CHENG S D, ZHOU J,et al.Intraspecific variations in leaf functional traits of Cunninghamia lanceolata provenances[J].BMC Plant Biology,2023,23(1):92. |
| 13 | JIN N, YU X C, DONG J L,et al.Vertical variation in leaf functional traits of Parashorea chinensis with different canopy layers[J].Frontiers in Plant Science,2024,15:1335524. |
| 14 | GONG H M, YANG M, WANG C C,et al.Leaf phenotypic variation and its response to environmental factors in natural populations of Eucommia ulmoides [J].BMC Plant Biology,2023,23(1):562. |
| 15 | 刘学森,李娜,张雪云,等.新疆单叶蔷薇居群表型变异及多样性研究[J].北京林业大学学报,2024,46(2):51-61. |
| LIU X S, LI N, ZHANG X Y,et al.Phenotypic variation and diversity of natural Rosa persica populations in Xinjiang of northwestern China[J].Journal of Beijing Forestry University,2024,46(2):51-61. | |
| 16 | 吕亮雨,刘青青,蔡宗程,等.三江源地区小花棘豆表型多样性及其与环境因子的相关性[J].植物资源与环境学报,2024,33(2):50-57. |
| LÜ L Y, LIU Q Q, CAI Z C,et al.Phenotypic diversity of Oxytropis glabra in Sanjiangyuan region and its correlations with environmental factors[J].Journal of Plant Resources and Environment,2024,33(2):50-57. | |
| 17 | 胡夏宇,刘玉萍,苏旭,等.苦豆子不同居群染色体数目及核型分析[J].植物研究,2023,43(1):9-19. |
| HU X Y, LIU Y P, SU X,et al.Chromosome number and karyotype analysis of different populations in Sophora alopecuroides(Fabaceae)[J].Bulletin of Botanical Research,2023,43(1):9-19. | |
| 18 | Historical climate data:WorldClim 1 documentation[EB/OL].[2024-08-30].. |
| 19 | ABRÀMOFF M D, MAGALHÃES P J, RAM S J.Image processing with ImageJ[J].Biophotonics International,2004,11(7):36-42. |
| 20 | 中华人民共和国环境保护部.土壤 电导率的测定 电极法:HJ 802—2016[EB/OL].(2016-08-01)[2024-08-30].. |
| Ministry of Environmental Protection of the People’s Republic of China.Soil quality:determination of conductivity:electrode method:HJ 802-2016[EB/OL].(2016-08-01)[2024-08-30].. | |
| 21 | 中华人民共和国生态环境部.土壤pH值的测定 电位法:HJ 962—2018[EB/OL].(2019-01-01)[2024-08-30].. |
| Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China.Soil:determination of pH:potentiometry:HJ 962-2018[EB/OL].(2019-01-01)[2024-08-30].. | |
| 22 | 姚程程,王俊臣,胡继文,等.香椿种质生长及叶部表型性状的遗传变异分析[J].植物科学学报,2020, 38(1):112-122. |
| YAO C C, WANG J C, HU J W,et al.Genetic variation of growth and leaf phenotypic traits of Toona sinensis(A.Juss.) Roem.germplasms[J].Plant Science Journal,2020,38(1):112-122. | |
| 23 | ALBERT C H, THUILLER W, YOCCOZ N G,et al.Intraspecific functional variability:extent,structure and sources of variation[J].Journal of Ecology,2010,98(3):604-613. |
| 24 | HENN J J, BUZZARD V, ENQUIST B J,et al.Intraspecific trait variation and phenotypic plasticity mediate alpine plant species response to climate change[J].Frontiers in Plant Science,2018,9:1548. |
| 25 | 柳江群,尹明宇,左丝雨,等.长柄扁桃天然种群表型变异[J].植物生态学报,2017,41(10):1091-1102. |
| LIU J Q, YIN M Y, ZUO S Y,et al.Phenotypic variations in natural populations of Amygdalus pedunculata [J].Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology,2017,41(10):1091-1102. | |
| 26 | 许恒,刘艳红.极小种群梓叶槭种群结构及动态特征[J].南京林业大学学报(自然科学版),2019,43(2):47-54. |
| XU H, LIU Y H.The population structure,dynamics features and protection strategy of Acer catalpifolium extremely small population[J].Journal of Nanjing Forestry University (Natural Science Edition),2019,43(2):47-54 | |
| 27 | ZHANG X W, GÉLIN U, SPICER R A,et al.Rapid Eocene diversification of spiny plants in subtropical woodlands of central Tibet[J].Nature Communications,2022,13(1):3787. |
| 28 | 来凯凯,张光恒,胡江,等.水稻叶片与光合效率的相关特性研究分析[J].分子植物育种,2011,9(1):1401-1410. |
| LAI K K, ZHANG G H, HU J,et al.Study of relationship between leaf and photosynthetic efficiency in rice[J].Molecular Plant Breeding,2011,9(1):1401-1410. | |
| 29 | 何雅琴,史晓洁,陈国杰,等.滨柃叶功能性状对环境因子的响应[J].生态学报,2022,42(6):2418-2429. |
| HE Y Q, SHI X J, CHEN G J,et al.Response and adaptation of leaf functional traits of Eurya emarginata to environmental factors[J].Acta Ecologica Sinica,2022, 42(6):2418-2429. | |
| 30 | 郭文文,卓么草,何竹,等.藏东南色季拉山不同海拔川滇高山栎叶解剖结构及环境适应性[J].西南林业大学学报(自然科学),2022,42(2):33-38. |
| GUO W W, ZHUO M C, HE Z,et al.Anatomical characteristics and environmental adaptability of Quercus aquifolioides leaf in Sejila Mountain,southeastern Tibet[J].Journal of Southwest Forestry University,2022,42(2):33-38. | |
| 31 | ZHANG Z J, WANG X, GUO S J,et al.Divergent patterns and drivers of leaf functional traits of Robinia pseudoacacia and Pinus tabulaeformis plantations along a precipitation gradient in the Loess plateau,China[J].Journal of Environmental Management,2023,348:119318. |
| 32 | WANG Z Q, HUANG H, WANG H,et al.Leaf water content contributes to global leaf trait relationships[J].Nature Communications,2022,13(1):5525. |
| 33 | 牛婷,艾里西尔·库尔班,玉米提·哈力克,等.干旱区胡杨叶片含水量和叶绿素含量特征[J].生态学杂志,2012,31(6):1353-1360. |
| NIU T, KURBAN A, HALIK U,et al.Characteristics of Populus euphratica leaf water and chlorophyll contents in an arid area of Xinjiang,Northwest China[J].Chinese Journal of Ecology,2012,31(6):1353-1360. |
| [1] | Ying WANG, Yujie ZHANG, Zihui JIAO, Xueli LI, Kai WANG, Xiaowei DA, Kun SUN, Hui ZHANG. Preliminary Study on Cross Fertility in ‘Kushui’ Rose [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2022, 42(3): 403-411. |
| [2] | Si-Han WANG, Tao YANG, Jin-Zhu ZHANG, Jie DONG, Zhi-Ling KOU, Dai-Di CHE. Effects of Changes in Seed Cell Tissue Structure and Endogenous Hormones on Dormancy of Wild Rosa rugosa Fruit during Development [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2021, 41(3): 387-394. |
| [3] | Zhi-Yuan LIU, Li ZENG, Xi-Wu DU, PENG-Yong-Zheng, Yi-Wei TAO, Yu-Qing LI, Jun QIN. Flower Bud Differentiation and Endogenous Hormone Changes of Rosa ‘Angela’ [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2021, 41(1): 37-43. |
| [4] | DENG Jun-Jie, ABDUL MAJEED BALOCH, HOU Xue-Yue, LI Jia-Zhe, CHA Xin-You, ZHANG Rong-Shu. Effect of Trichoderma harzianum T6 on Rosa chinensis ‘Shi-Jie-Mei’ Growth [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2020, 40(5): 666-672. |
| [5] | ZHOU Li-Jun, YU Chao, CHANG Xiao, WAN Hui-Hua, LUO Le, PAN Hui-Tang, ZHANG Qi-Xiang. Variation Analysis of Phenotypic Traits in F1 Population of Rosa spp [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2019, 39(1): 131-138. |
| [6] | YUAN Yuan;WANG Yue;TANG Dong-Qin*;LIAN Fang-Qing. Cloning and Characterization of ACC Synthase FhACS1 Gene from Fressia [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2011, 31(4): 422-428. |
| [7] | BAI Jin-Rong;ZHANG Qi-Xiang*;LUO Le;PAN Hui-Tang;YU Chao. Pollen Morphology of Some Chinese Traditional Roses [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2011, 31(1): 15-23. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||