Bulletin of Botanical Research ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (2): 211-216.doi: 10.7525/j.issn.1673-5102.2025.02.007
• Original Paper • Previous Articles
Qi ZHANG, Jiayin LI, Haiyan WANG, Ziqin MA, Fu HE( )
)
Received:2024-11-28
Online:2025-03-20
Published:2025-04-07
Contact:
Fu HE
E-mail:hefu@ctgu.edu.cn
CLC Number:
Qi ZHANG, Jiayin LI, Haiyan WANG, Ziqin MA, Fu HE. Sporogenesis and Gametogenesis of Polygonatum cyrtonema[J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2025, 45(2): 211-216.
Fig.1
Anther wall development of P. cyrtonemaA. Anther wall at the secondary sporogenous cell stage; B. Anther wall at the microspore mother cell stage; C. Anther wall in dyad period; D. Anther wall in mononuclear microspore stage; E. Anther wall at the pollen grain development stage; F. Residual anther wall; Ep. Epidermis; En. Endothecium; Ml. Middle layer; Ta. Tapetum.
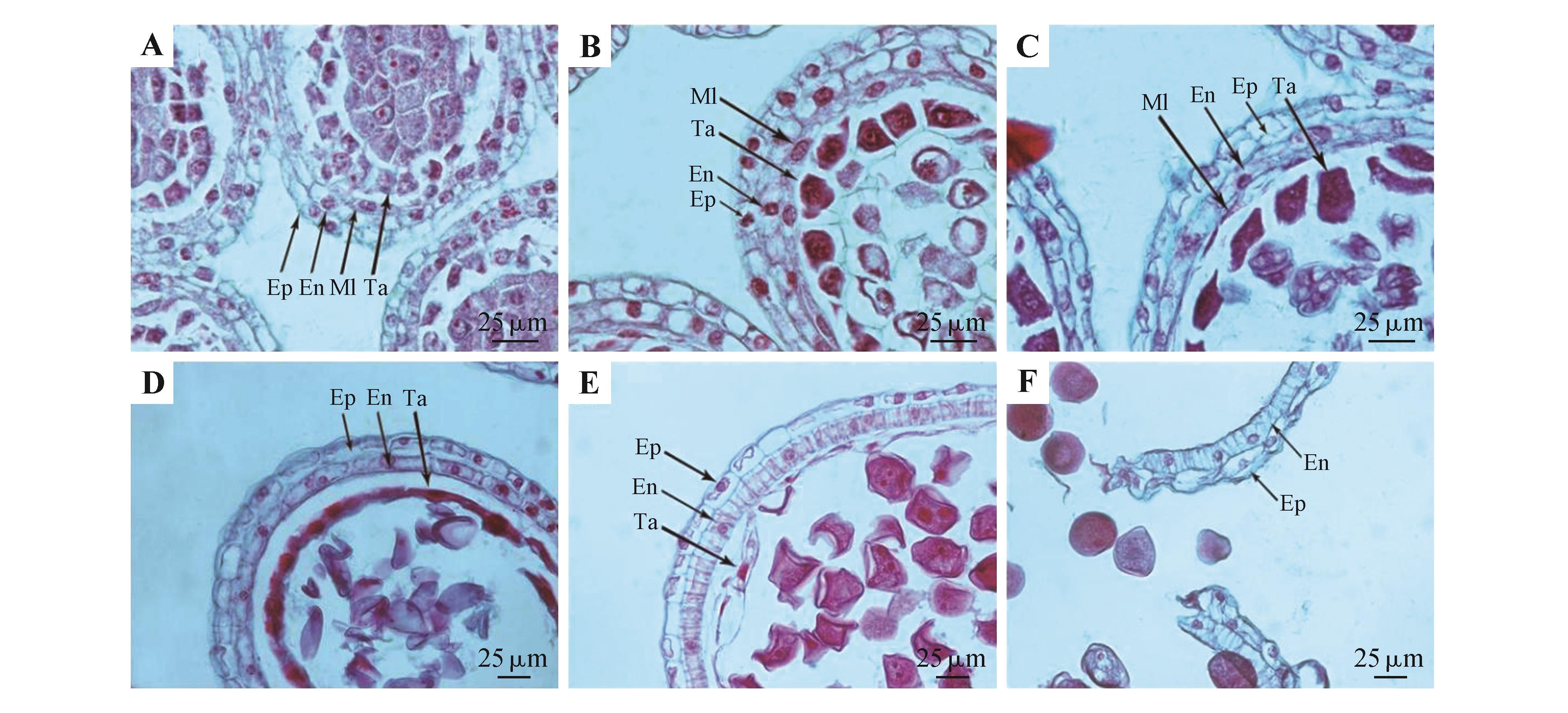
Fig.2
Microsporogenesis and development of male gametophyte of P. cyrtonemaA. Secondary sporogenous cell stage; B. Microspore mother cell stage; C. The tetrad stage; D. Mononuclear microspore stage; E. Developing pollen grain (the red arrow indicated the three-celled pollen grain); F. Matured pollen grain (the red arrow indicated the three-celled pollen grain); Ssc. Secondary sporogenous cell; Mmc. Microspore mother cell; Te. Tetrad; Mm. Mononuclear microspore; Mp. Mature pollen.
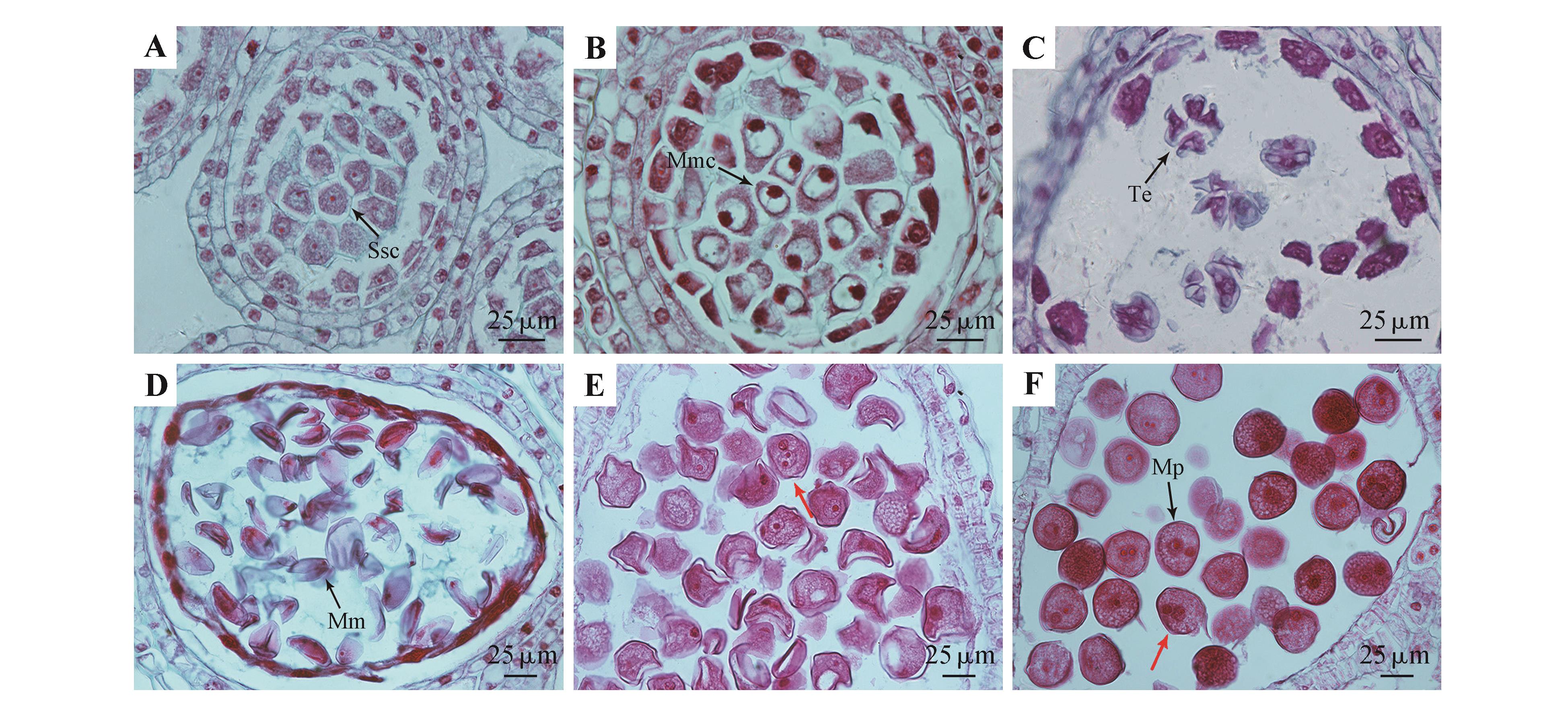
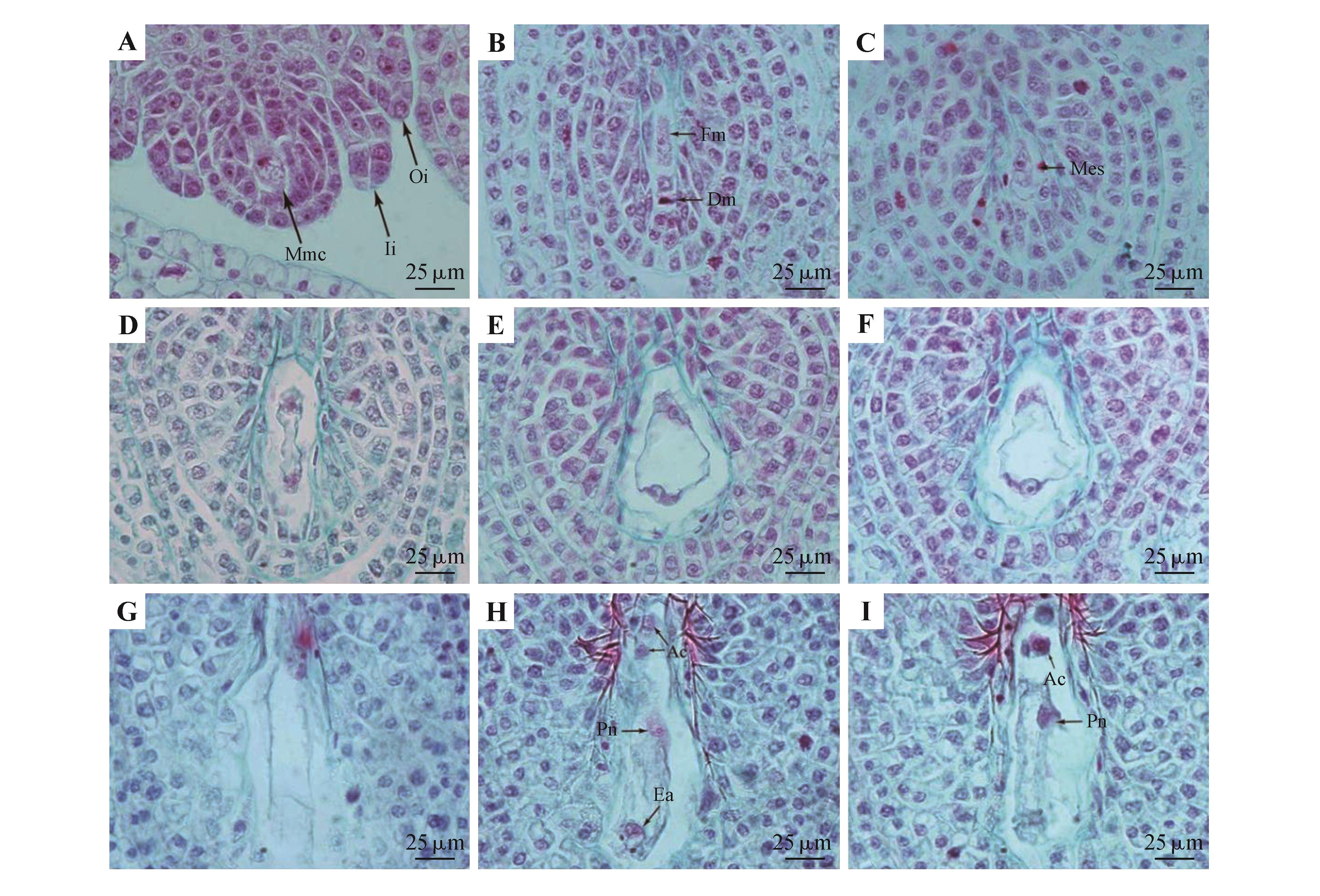
Fig.3
Megasporogenesis and development of female gametophyte of P. cyrtonemaA. Megasporocyte stage; B. Terminal tetrad; C. Mononuclear embryo sac; D. Two nuclear embryo sac; E-F. Successive sections showing four nuclear embryo sac; G. Eight-nucleate embryo sac, showing four nuclei at the chalazal end; H-I. Successive sections showing eight nuclear embryo sac; Mmc. Megaspore mother cell; Fm. Functional megaspore; Dm. Degenerated megaspore; Mes. Mononuclear embryo sac; Ac. Antipodal cell; Pn. Polar nuclei; Ea. Egg apparatus; Oi. Outer integument; Ii. Inner integument.
| 1 | 龙志望.多花黄精的特征特性及林下种植技术[J].种子科技,2024,42(7):66-68. |
| LONG Z W.Characteristics and cultivation techniques of Polygonatum cyrtonema Hua in shaded forest[J].Seed Science & Technology,2024,42(7):66-68. | |
| 2 | 雷云仙.多花黄精的特征特性及林下栽培技术[J].现代农业科技,2020(22):54-55. |
| LEI Y X.Characteristics and cultivation techniques of Polygonatum cyrtonema Hua[J].Modern Agricultural Science and Technology,2020(22):54-55. | |
| 3 | 罗敏,章文伟,邓才富,等.药用植物多花黄精研究进展[J].时珍国医国药,2016,27(6):1467-1469. |
| LUO M, ZHNAG W W, DENG C F,et al.Advances in studies of medicinal crop Polygonatum cyrtonema Hua[J].Lishizhen Medicine and Materia Medica Research,2016,27(6):1467-1469. | |
| 4 | XIAO J D, XIE L M, ZHENG B,et al. Polygonatum cyrtonema saponin supplementation ameliorated DSS-induced intestinal barrier injury via targeting the PI3K/AKT/mTOR-mediated autophagy/microbiota axis[J].Food Bioscience,2024,61(22):104727. |
| 5 | 陈祖铿.植物的生殖讲座(八):植物生殖生物学研究进展[J].生物学通报,1996,31(10):29-31. |
| CHEN Z K.Lecture on plant reproduction (VIII):research progress in plant reproductive biology[J].Bulletin of Biology,1996,31(10):29-31. | |
| 6 | 王康鑫,王仕沁,王毅敏,等.濒危植物小勾儿茶大小孢子发生和雌雄配子体发育[J].植物研究,2024,44(5):662-669. |
| WANG K X, WANG S Q, WANG Y M,et al.Megasporogenesis,microsporogenesis and development of male and female gametophytes of endangered Berchemiella wilsonii [J].Bulletin of Botanical Research,2024,44(5):662-669. | |
| 7 | 施慧嫒,陈发菊,梁宏伟,等.濒危植物瑶山苣苔的大小孢子发生和雌雄配子体发育研究[J].植物研究,2021,41(3):329-335. |
| SHI H A, CHEN F J, LIANG H W,et al.Sporogenesis and gametogenesis on endangered Dayaoshania cotinifolia [J].Bulletin of Botanical Research,2021,41(3):329-335. | |
| 8 | 王金子.玉簪大小孢子发生及雌雄配子体发育[J].华中农业大学学报,2011,30(3):295-299. |
| WANG J Z.The mega-/micro-sporogenesis and female-/male-gametogenesis of Hosta plantaginea Aschers[J].Journal of Huazhong Agricultural University,2011,30(3):295-299. | |
| 9 | BARRANCO-GUZMÁN Á M, RODRÍGUEZ-GARAY B.Development of the female gametophyte of Agave colimana,subgenus Littaea (Asparagaceae)[J].The Journal of the Torrey Botanical Society,2020,147(3):281-288. |
| 10 | 宫丽婷,吕东明,王天媛,等.玉竹小孢子发育的研究[J].人参研究,2016,28(3):38-41. |
| GONG L T, LÜ D M, WANG T Y,et al.Interrelation of cytological development period of Polygonatum odoratum microspore and the morphology of flower organ[J].Ginseng Research,2016,28(3):38-41. | |
| 11 | SONG Y Y, ZHAO Y Y, LIU J X.Embryology of Polygonatum (Asparagaceae) and its systematic significance[J].Phytotaxa,2018,350(3):235-246. |
| 12 | 李华荣,周财,魏薇,等.湖北黄精大小孢子发生及雌雄配子体发育[J].西北植物学报,2024,44(5):813-823. |
| LI H R, ZHOU C, WEI W,et al.The reproductive biology theory of sporogenesis and gametogenesis in Polygonatum zanlanscianense Pamp[J].Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica,2024,44(5):813-823. | |
| 13 | MOSER M, GROVES N R, MEIER I.The Arabidopsis KASH protein SINE3 is involved in male and female gametogenesis[J].Plant Reproduction,2024,37(4):521-534. |
| 14 | HUANG X R, SUN M X.Epigenetic regulation and intercellular communication during male gametophyte development[J].Journal of Plant Physiology,2021,258:153391. |
| 15 | WANG X Y, WANG X Q, GAO F,et al.Polysaccharides from Polygonatum cyrtonema Hua prevent depression-like behaviors in mice with chronic unpredictable mild stress through refining gut microbiota-lipopolysaccharide-paraventricular nucleus signal axis[J].Heliyon,2024,10(19):e38554. |
| 16 | 孙思宇,王华磊,陈松树,等.不同品系多花黄精药理和食用成分比较研究[J].食品安全质量检测学报,2022,13(22):7272-7278. |
| SUN S Y, WANG H L, CHEN S S,et al.Comparative study on pharmacological and ediable components of different strains of Polygonatum polyflora [J].Journal of Food Safety and Quality,2022,13(22):7272-7278. | |
| 17 | 田雪丽,冉舞,陆红霞,等.油茶林下黄精高产栽培技术及病虫害防治措施[J].种子科技,2024,42(15):4-6. |
| TIAN X L, RAN W, LU H X,et al.Cultivation techniques of high-yield yellow essence under Polygonatum sibiricum oleifolia forest and measures of pest control[J].Seed Science & Technology,2024,42(15):4-6. | |
| 18 | 白洁,周涛,马江,等.三叶木通大小孢子发生和雌雄配子体发育研究[J].植物研究,2022,42(6):946-955. |
| BAI J, ZHOU T, MA J,et al.Sporogenesis and gametogenesis of Akebia trifoliata [J].Bulletin of Botanical Research,2022,42(6):946-955. | |
| 19 | 王瑞,胡玥,崔宏安,等.19种菊科植物花药结构及绒毡层的发育类型研究[J].草业学报,2020,29(6):182-190. |
| WANG R, HU Y, CUI H A,et al.Anther structures and tapetum development types of 19 species of Asteraceae[J].Acta Prataculturae Sinica,2020,29(6):182-190. | |
| 20 | ZHANG H Y, ZHANG X Y, NING K,et al.Stamen and pollen development in Menispermaceae with contrasting androecium structure[J].Plant Systematics and Evolution,2022,308(5):36. |
| 21 | GAO X L, YANG Y, YE J W,et al.Abnormal calcium accumulation and ROS homeostasis-induced tapetal programmed cell death lead to pollen abortion of petaloid-type cytoplasmic male sterility in Camellia oleifera [J].Agronomy,2024,14(3):585. |
| 22 | DAVIS G L.Systematic embryology of the angiosperms[M].Hoboken:John Wiley & Sons,1967. |
| 23 | AKITA K, TAKAGI T, KOBAYASHI K,et al.Ultrastructural characterization of microlipophagy induced by the interaction of vacuoles and lipid bodies around generative and sperm cells in Arabidopsis pollen[J].Protoplasma,2021,258(1):129-138. |
| 24 | XIA C, WANG Y J, LIANG Y,et al.The ARID-HMG DNA-binding protein AtHMGB15 is required for pollen tube growth in Arabidopsis thaliana [J].The Plant Journal,2014,79(5):741-756. |
| 25 | 孙颖,王蕾,杨雪,等.侧金盏大小孢子发生及雌雄配子体发育[J].东北林业大学学报,2017,45(7):61-65. |
| SUN Y, WANG L, YANG X,et al.Megasporogenesis,microsporogenesis and development of male and female gametophytes of Adonis amurensis Regel et Radde[J].Journal of Northeast Forestry University,2017,45(7):61-65. | |
| 26 | 孙豪愽,孔冬瑞,胡德昌.砂引草(紫草科)大小孢子发生和雌雄配子体发育及其分类学意义[J].植物研究,2024,44(1):27-33. |
| SUN H B, KONG D R, HU D C.Sporogenesis and gametogenesis of Messerschmidia sibirica L.(Boraginaceae) and their taxonomic implications[J].Bulletin of Botanical Research,2024,44(1):27-33. | |
| 27 | 付琳,徐凤霞,曾庆文,等.广西含笑的小孢子发生及雄配子体形成的研究[J].广西植物,2011,31(3):312-317. |
| FU L, XU F X, ZENG Q W,et al.Studies of microsporogenesis and male gametophyte formation of Michelia guangxiensis [J].Guihaia,2011,31(3):312-317. |
| [1] | ZHANG Bo;LI Li-Ping;MAO Wei-Bing;WANG Chang-Lan;CHEN Fa-Ju*. Development of Male and Female Gametophytes between Fertile Line and Male Sterile Line’s Flowers of Catalpa bungei C.A.Meyer. [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2015, 35(6): 812-818. |
| [2] | LI Li-Ping;LIU Hai-Yan;CHEN Fa-Ju*. Observation on Megasporogenesis, Microsporogenesis and Development of Female and Male Gametophytes of Catalpa speciosa Warder [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2013, 33(2): 145-148. |
| [3] | WANG Ying;LI Fu-Rong;GUAN Li-Ping;LI Feng-Lan*. Comparative Studies on the Development of Male and Female Gametophytes Between Fertile Line and Male Sterile Line’s Flowers of Tagetes erecta L. [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2009, 29(4): 391-396. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||