植物研究 ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (5): 731-744.doi: 10.7525/j.issn.1673-5102.2025.05.008
收稿日期:2025-02-19
出版日期:2025-09-20
发布日期:2025-09-28
通讯作者:
郑志民
E-mail:zmzheng@nefu.edu.cn
作者简介:武思尧(1999—),女,硕士研究生,主要从事林木遗传育种研究。
基金资助:
Siyao WU, Xinyu WANG, Ziteng SUN, Zhimin ZHENG( )
)
Received:2025-02-19
Online:2025-09-20
Published:2025-09-28
Contact:
Zhimin ZHENG
E-mail:zmzheng@nefu.edu.cn
摘要:
白桦(Betula platyphylla)作为多年生木本植物因生长周期较长、基因型复杂等问题,育种过程中难以获得纯合植株和家系,进而导致育种工作进展较慢。双单倍体(doubled haploid,DH)育种技术是近年来兴起的一种育种方法,只需要两代即可得到纯合的植物家系。因此,DH育种技术可以大大缩短林木育种周期并获得纯合家系,而DMP基因的发现与应用为双单倍育种开辟了一个新的研究方向。该研究旨在通过生物信息学分析揭示白桦BpDMPs基因家族的理化性质、蛋白结构、系统进化、基因结构、染色体分布及其在白桦生长发育过程中潜在的功能;通过表达模式分析鉴定该基因家族中具有单倍体诱导功能的白桦DMP基因,并通过拟南芥(Arabidopsis thaliana)回补试验验证基因功能。生物信息学分析结果显示:在白桦中,DMP基因包含14个基因家族成员,分布在6条染色体上;系统发育分析表明,BpDMPs基因家族中14个基因分属5个分支;对启动子顺式作用元件的预测分析表明,BpDMPs基因家族的启动子中包含生长发育、激素代谢、胁迫响应等相关的反应元件。qRT-PCR结果显示,BpDMPs在白桦各组织中表达水平差异较大,其中,BpDMP2和BpDMP7在雄蕊中表达量较高,拟南芥回补试验证明,BpDMP7基因可以回补拟南芥dmp8dmp9突变体籽粒败育的表型。为进一步验证BpDMP7诱导白桦产生单倍体,用CRISPER/Cas9基因编辑技术将该基因进行靶向敲除并获得突变体植株。该研究为进一步研究白桦BpDMPs基因家族的功能和调控机制提供了基础信息,并为理解这些基因在植物生长发育及环境适应过程中扮演的角色提供了新的视角。
中图分类号:
武思尧, 王新宇, 孙子腾, 郑志民. 白桦BpDMPs基因家族生物信息学及BpDMP7功能分析[J]. 植物研究, 2025, 45(5): 731-744.
Siyao WU, Xinyu WANG, Ziteng SUN, Zhimin ZHENG. Bioinformatics Analysis of the BpDMPs Gene Family in Betula platyphylla and Exploration of the Function of BpDMP7 gene[J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2025, 45(5): 731-744.
表1
白桦 BpDMPs 基因家族编码蛋白理化性质
基因名称 Gene name | 基因ID Gene ID | 所在染色体 Chromosome | 基因位置 Gene location | 氨基酸数目 Number of amino acids | 分子质量 Molecular mass/Da | 等电点 Isoelectric point | 总平均亲水性 Total average hydrophilicity | 亚细胞定位 Subcellular location |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BpDMP1 | BPChr08G17023 | 8 | 38650991-38651641 | 216 | 23 342.28 | 6.50 | 0.292 | CP |
| BpDMP2 | BPChr07G18894 | 7 | 22585554-22586180 | 208 | 22 727.21 | 5.61 | 0.279 | CM |
| BpDMP3 | BPChr11G17728 | 11 | 3219693-3220379 | 228 | 24 285.32 | 9.18 | 0.347 | CM |
| BpDMP4 | BPChr11G13419 | 11 | 25274063-25274683 | 206 | 22 923.87 | 9.03 | 0.264 | CP,Mito,Nucleus |
| BpDMP5 | BPChr08G05126 | 8 | 10638147-10638761 | 204 | 21 735.80 | 8.54 | 0.093 | CM,CW |
| BpDMP6 | BPChr01G23597 | 1 | 6378106-6378753 | 215 | 24 248.03 | 8.15 | 0.191 | CM |
| BpDMP7 | BPChr06G30721 | 6 | 19021326-19021925 | 199 | 21 589.71 | 5.84 | 0.232 | CM |
| BpDMP8 | BPChr08G05134 | 8 | 10612115-10612687 | 190 | 20 441.58 | 8.66 | 0.357 | CM |
| BpDMP9 | BPChr12G26817 | 12 | 3237953-3238363 | 156 | 17 233.41 | 9.13 | 0.160 | CP |
| BpDMP10 | BPChr06G30778 | 6 | 19025688-19026779 | 363 | 39 524.96 | 5.56 | -0.182 | CM |
| BpDMP11 | BPChr10G03440 | 10 | 10633218-10633790 | 190 | 20 246.45 | 8.79 | 0.297 | CM |
| BpDMP12 | BPChr10G03567 | 10 | 10667452-10668458 | 198 | 21 427.86 | 9.08 | 0.360 | CM |
| BpDMP13 | BPChr10G03436 | 10 | 10671858-10672481 | 207 | 22 453.96 | 6.25 | 0.561 | CM |
| BpDMP14 | BPChr10G03476 | 10 | 10661594-10661917 | 107 | 11 381.06 | 9.64 | -0.040 | CM |
表2
基因编辑植株信息统计
载体名称 Vector name | 外植体数量 Number of explants | 阳性植株数量 Number of positive plants | 转化效率 Transformation efficiency/% | 基因编辑数量 (Indel或有意义突变) Number of gene edits (Indel or significant mutation) | 基因编辑效率 (Indel或有意义突变) Gene editing efficiency (Indel or significant mutation)/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 合计 | 175 | 131 | 74.06 | 4 | 3.05 |
| pSC1-CRISPR-BpU6-2-sgRNA1 | 76 | 56 | 73.68 | 2 | 3.57 |
| pSC1-CRISPR-BpU6-2-sgRNA2 | 66 | 52 | 78.79 | 2 | 3.85 |
| pSC1-CRISPR-BpU6-2-sgRNA3 | 33 | 23 | 69.70 | — | — |
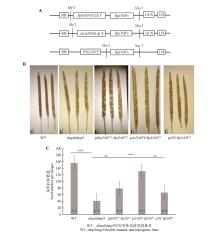
图3
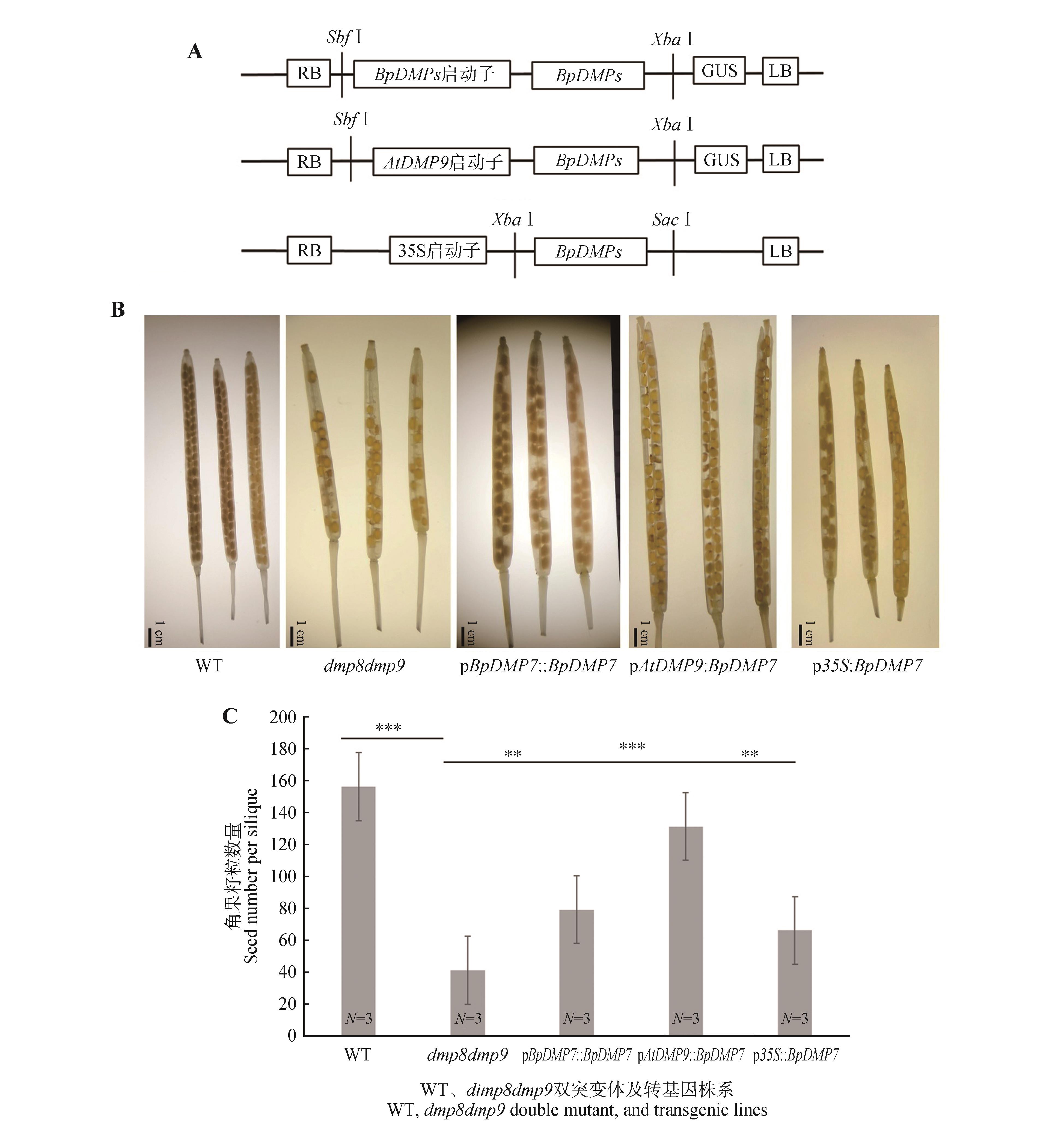
BpDMP7基因回补dmp8dmp9双突变体A.BpDMP7基因回补系载体构建;B.dmp8dmp9双突变体和BpDMP7基因回补系在dmp8dmp9双突变体背景下的角果图片;C.dmp8dmp9双突变体和BpDMP7基因回补系中角果内籽粒数量。WT.野生型株系,dmp8dmp9代表拟南芥DMP基因双突变体,pBpDMP7::BpDMP7、pAtDMP9::BpDMP7、p35s::BpDMP7分别代表3个回补株系。误差线代表3个生物学重复的标准误差。显著性为WT与dmp8dmp9、dmp8dmp9与pBpDMP7::BpDMP7、dmp8dmp9与pAtDMP9::BpDMP7、dmp8dmp9与p35s::BpDMP7分别通过Student’s t-test得到(**.P<0.01,***.P<0.001)。N.生物学重复次数。
| [1] | CHANG M T, COE E H. Doubled haploids[M]//KRIZ A L,LARKINS B A.Molecular genetic approaches to maize improvement.Heidelberg: Springer Berlin Heidelberg,2009:127-142. |
| [2] | KALINOWSKA K, CHAMAS S, UNKEL K,et al.State-of-the-art and novel developments of in vivo haploid technologies[J].Theoretical and Applied Genetics,2019,132:593-605. |
| [3] | DWIVEDI S L, BRITT A B, TRIPATHI L,et al.Haploids:constraints and opportunities in plant breeding[J].Biotechnology Advances,2015,33(6):812-829. |
| [4] | GUHA S, MAHESHWARI S C. In vitro production of embryos from anthers of Datura [J].Nature,1964,204:497. |
| [5] | DAVEY M R.Advances in haploid production in higher plants[J].Annals of Botany,2009,104(7):10. |
| [6] | MALUSZYNSKI M, KASHA K J, FORSTER B P,et al.Doubled haploid production in crop plants:a manual[M].New York:Springer Dordrecht,2003:309-335. |
| [7] | BAJAJ Y P S. In vitro production of haploids and their use in cell genetics and plant breeding[M]//BAJAJ Y P S.Haploids in crop improvement I:from fundamentals to quantum computing.New York:Springer Berlin Heidelberg,1990:3-30. |
| [8] | MOHAN JAIN S, SOPORY S K, VEILLEUX R E. In vitro haploid production in higher plants[M].Dordrecht:Springer Dordrecht,1996. |
| [9] | JACQUIER N M A, GILLES L M, PYOTT D E,et al.Puzzling out plant reproduction by haploid induction for innovations in plant breeding[J].Nature Plants,2020,6:610-619. |
| [10] | 王敬驹,朱至清,孙敬三.杨树花粉植株的诱导[J].植物学报,1975(1):56-59. |
| WANG J J, ZHU Z Q, SUN J S.The induction of Populus pollen-plants[J].Journal of Integrative Plant Biology,1975(1):56-59. | |
| [11] | DEUTSCH F, KUMLEHN J, ZIEGENHAGEN B,et al.Stable haploid poplar callus lines from immature pollen culture[J].Physiologia Plantarum,2004,120(4):613-622. |
| [12] | LI Y, LI H, CHEN Z,et al.Haploid plants from anther cultures of poplar(Populus×beijingensis)[J].Plant Cell,Tissue and Organ Culture,2013,114:39-48. |
| [13] | YANG J L, LI K, LI C Y,et al. In vitro anther culture and Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of the AP1 gene from Salix integra Linn.in haploid poplar(Populus simonii×P.nigra)[J].Journal of Forestry Research,2017,29:321-330. |
| [14] | LIU B, WANG S, TAO X Y,et al.Molecular karyotyping on Populus simonii × P.nigra and the derived doubled haploid[J].International Journal of Molecular Sciences,2021,22(21):11424. |
| [15] | GHARYAL P K, RASHID A, MAHESHWARI S C.Production of haploid plantlets in anther cultures of Albizzia lebbeck L.[J].Plant Cell Reports,1983,2:308-309. |
| [16] | SERAN T H, HIRIMBUREGAMA K, SHANMUGARAJAH V.Regeneration of plantlets from cultured anthers of tea (Camellia sinenesis (L.) O.Kuntze)[J].Journal of Tropical Agricultural Research,1998,10:271-281. |
| [17] | SRIVASTAVA P, CHATURVEDI R.Increased production of azadirachtin from an improved method of androgenic cultures of a medicinal tree Azadirachta indica A.Juss[J].Plant Signaling & Behavior,2011,6(7):974-981. |
| [18] | PINTOS B, MANZANERA J A, GÓMEZ-GARAY A.Production of doubled haploid embryos from cork oak anther cultures by antimitotic agents and temperature stress[J].Methods in Molecular Biology,2021,2289:199-219. |
| [19] | AROCKIASAMY S, PATIL M, YEPURI V,et al.Anther culture in Jatropha curcas L.:a tree species[J].Methods in Molecular Biology,2021,2289:221-233. |
| [20] | MISHRA V K, BAJPAI R, CHATURVEDI R.Androgenic haploid plant development via embryogenesis with simultaneous determination of bioactive metabolites in Cambod tea (Camellia assamica ssp.lasiocalyx)[J].Plant Cell,Tissue and Organ Culture,2022,148:515-531. |
| [21] | CARDEMIL L, JORDAN M.Light and electron microscopic stuay of in vitro cultured female gametophyte of Araucaria araucaria (Mol.) Koch[J].Zeitschrift für Pflanzenphysiologie,1982,107(4):329-338. |
| [22] | LI Y L, HUANG S W, ZHANG J Y,et al.A protocol of homozygous haploid callus induction from endosperm of Taxus chinensis Rehd.var.mairei [J].SpringerPlus,2016,5:659. |
| [23] | WINTON L L, EINSPAHR D W.The use of heat-treated pollen for aspen haploid production[J].Forest Science,1968,14(4):406-407. |
| [24] | LI Y, WEI H R, YANG J,et al.High-quality de novo assembly of the Eucommia ulmoides haploid genome provides new insights into evolution and rubber biosynthesis[J].Horticulture Research,2020,7:183. |
| [25] | HOOGHVORST I, NOGUÉS S.Opportunities and challenges in doubled haploids and haploid inducer-mediated genome-editing systems in cucurbits[J].Agronomy,2020,10(9):1441. |
| [26] | HOOGHVORST I, NOGUÉS S.Chromosome doubling methods in doubled haploid and haploid inducer-mediated genome-editing systems in major crops[J].Plant Cell Reports,2021,40:255-270. |
| [27] | Jr E H COE.A line of maize with high haploid frequency[J].The American Naturalist,1959,93:381-382. |
| [28] | BARRET P, BRINKMANN M, BECKERT M.A major locus expressed in the male gametophyte with incomplete penetrance is responsible for in situ gynogenesis in maize[J].Theoretical and Applied Genetics,2008,117:581-594. |
| [29] | PRIGGE V, XU X W, LI L,et al.New insights into the genetics of in vivo induction of maternal haploids,the backbone of doubled haploid technology in maize[J].Genetics,2012,190(2):781-793. |
| [30] | LIU C X, LI W, ZHONG Y,et al.Fine mapping of qhir8 affecting in vivo haploid induction in maize[J].Theoretical and Applied Genetics,2015,128:2507-2515. |
| [31] | DONG X, XU X, MIAO J,et al.Fine mapping of qhir1 influencing in vivo haploid induction in maize[J].Theoretical and Applied Genetics,2013,126:1713-1720. |
| [32] | KELLIHER T, STARR D, RICHBOURG L,et al. MATRILINEAL,a sperm-specific phospholipase,triggers maize haploid induction[J].Nature,2017,542:105-109. |
| [33] | LIU C X, LI X, MENG D X,et al.A 4-bp insertion at ZmPLA1 encoding a putative phospholipase a generates haploid induction in maize[J].Molecular Plant,2017,10(3):520-522. |
| [34] | JANG J H, SEO H S, WIDIEZ T,et al.Loss-of-function of gynoecium-expressed phospholipase pPLAIIγ triggers maternal haploid induction in Arabidopsis [J].New Phytologist,2023,238(5):1813-1824. |
| [35] | ZHONG Y, LIU C X, QI X L,et al.Mutation of ZmDMP enhances haploid induction in maize[J].Nature Plants,2019,5:575-580. |
| [36] | YAO L, ZHANG Y, LIU C X,et al. OsMATL mutation induces haploid seed formation in indica rice[J].Nature Plants,2018,4:530-533. |
| [37] | LIU C X, ZHONG Y, QI X L,et al.Extension of the in vivo haploid induction system from diploid maize to hexaploid wheat[J].Plant Biotechnology Journal,2020,18(2):316-318. |
| [38] | LIU H Y, WANG K, JIA Z M,et al.Efficient induction of haploid plants in wheat by editing of TaMTL using an optimized Agrobacterium-mediated CRISPR system[J].Journal of Experimental Botany,2020,71(4):1337-1349. |
| [39] | CYPRYS P, LINDEMEIER M, SPRUNCK S.Gamete fusion is facilitated by two sperm cell-expressed DUF679 membrane proteins[J].Nature Plants,2019,5:253-257. |
| [40] | KASARAS A, KUNZE R.Expression,localisation and phylogeny of a novel family of plant-specific membrane proteins[J].Plant Biology,2010,12(s1):140-152. |
| [41] | ZHONG Y, CHEN B J, LI M R,et al.A DMP-triggered in vivo maternal haploid induction system in the dicotyledonous Arabidopsis [J].Nature Plants,2020,6:466-472. |
| [42] | ZHONG Y, CHEN B J, WANG D,et al. In vivo maternal haploid induction in tomato[J].Plant Biotechnology Journal,2022,20:250-252. |
| [43] | WANG N, XIA X Z, JIANG T,et al. In planta haploid induction by genome editing of DMP in the model legume Medicago truncatula [J].Plant Biotechnology Journal,2022,20(1):22-24. |
| [44] | CHEN X E, LI Y X, AI G L,et al.Creation of a watermelon haploid inducer line via ClDMP3-mediated single fertilization of the central cell[J].Horticulture Research,2023,10(6):uhad081. |
| [45] | YIN S, LI S, SUN L,et al.Mutating the maternal haploid inducer gene CsDMP in cucumber produces haploids in planta [J].Plant Physiology,2024,194(3):1282-1285. |
| [46] | ZHONG Y, WANG Y W, CHEN B J,et al.Establishment of a DMP based maternal haploid induction system for polyploid Brassica napus and Nicotiana tabacum [J].Journal of Integrative Plant Biology,2022,64(6):1281-1294. |
| [47] | LONG L, FENG Y M, SHANG S Z,et al. In vivo maternal haploid induction system in cotton[J].Plant Physiology,2024,194(3):1286-1289. |
| [48] | ZHANG J Z, YIN J, LUO J Y,et al.Construction of homozygous diploid potato through maternal haploid induction[J].aBIOTECH,2022,3:163-168. |
| [49] | CHEN S, WANG Y C, YU L L,et al.Genome sequence and evolution of Betula platyphylla [J].Horticulture Research,2021,8:37. |
| [50] | LIU Z Y, WANG P L, ZHANG T Q,et al.Comprehensive analysis of BpHSP genes and their expression under heat stresses in Betula platyphylla [J].Environmental and Experimental Botany,2018,152:167-176. |
| [51] | SONG Q X, LI Q T, LIU Y F,et al.Soybean GmbZIP123 gene enhances lipid content in the seeds of transgenic Arabidopsis plants[J].Journal of Experimental Botany,2013,64(14):4329-4341. |
| [52] | CHENG D W, LIU Y Y, WANG Y,et al.Establishment of high-efficiency genome editing in white birch (Betula platyphylla Suk.)[J].Plant Biotechnology Journal,2024,22:7-9. |
| [53] | TAKAHASHI T, MORI T, UEDA K,et al.The male gamete membrane protein DMP9/DAU2 is required for double fertilization in flowering plants[J].Development,2018,145(23):dev170076. |
| [54] | KOSKI V, ROUSI M.A review of the promises and constraints of breeding silver birch (Betula pendula Roth) in Finland[J].Forestry:An International Journal of Forest Research,2005,78(2):187-198. |
| [55] | KELLIHER T, STARR D, SU X J,et al.One-step genome editing of elite crop germplasm during haploid induction[J].Nature Biotechnology,2019,37:287-292. |
| [56] | WANG B B, ZHU L, ZHAO B B,et al.Development of a haploid-inducer mediated genome editing system for accelerating maize breeding[J].Molecular Plant,2019,12(4):597-602. |
| [57] | WANG C, LIU Q, SHEN Y,et al.Clonal seeds from hybrid rice by simultaneous genome engineering of meiosis and fertilization genes[J].Nature Biotechnology,2019,37:283-286. |
| [58] | MARIMUTHU M P A, JOLIVET S, RAVI M,et al.Synthetic clonal reproduction through seeds[J].Science,2011,331(6019):876. |
| [59] | GENG W L, LI Y Y, SUN D Q,et al.Prediction of the potential geographical distribution of Betula platyphylla Suk.in China under climate change scenarios[J].PLoS One,2022,17(3):e0262540. |
| [60] | 陈柄华,张杰,刘桂丰,等.白桦半同胞家系纸浆材优良家系选择及选择方法评价[J].植物研究,2023,43(5):690-699. |
| CHEN B H, ZHANG J, LIU G F,et al.Selection of excellent families and evaluation of selection method for pulpwood half-siblin families of Betula platyphylla [J].Bulletin of Botanical Research,2023,43(5):690-699. | |
| [61] | 孙子腾,王新宇,侯丽丽,等.白桦BpGRFs基因鉴定与功能初步分析[J].植物研究,2025,45(2):191-201. |
| SUN Z T, WANG X Y, HOU L L,et al. Identification and prelimina functional analysis of the BpGRFs gene in Betula platyphylla [J].Bulletin of Botanical Research,2025,45(2):191-201. |
| [1] | 孙子腾, 王新宇, 侯丽丽, 刘月影, 郑志民. 白桦BpGRFs基因鉴定与功能初步分析[J]. 植物研究, 2025, 45(2): 191-201. |
| [2] | 喻心怡, 冀慧玥, 路萍萍, 周嘉裕, 廖海. 植物IPP基因的生物信息学分析[J]. 植物研究, 2024, 44(5): 774-782. |
| [3] | 王珊珊, 王瑞, 樊二勤, 付鹏跃, 曲冠证, 王楠. 楸树DELLA基因家族生信分析及CbuGRAS9的功能分析[J]. 植物研究, 2024, 44(1): 139-151. |
| [4] | 陈柄华, 张杰, 刘桂丰, 李思婷, 高元科, 李慧玉, 李天芳. 白桦半同胞家系纸浆材优良家系选择及选择方法评价[J]. 植物研究, 2023, 43(5): 690-699. |
| [5] | 郑占敏, 商玉冰, 周广波, 肖迪, 刘轶, 由香玲. PsnHB13与PsnHB15在小黑杨中的遗传转化与功能分析[J]. 植物研究, 2023, 43(3): 340-350. |
| [6] | 王景哲, 牛朝奎, 梁馨元, 申晨静, 尹静. 水杨酸在白桦苗期抵御盐碱胁迫中的调控作用[J]. 植物研究, 2023, 43(3): 379-387. |
| [7] | 廖诗贤, 王宇婷, 董立本, 顾咏梅, 贾丰璘, 姜廷波, 周博如. 小黑杨转录因子PsnbZIP1应答盐胁迫功能分析[J]. 植物研究, 2023, 43(2): 288-299. |
| [8] | 刘森尧, 贾丰璘, 国庆, 樊高锋, 周博如, 姜廷波. 小黑杨转录因子PsnbHLH162基因在盐和低温胁迫下应答分析[J]. 植物研究, 2023, 43(2): 300-310. |
| [9] | 杜金霞, 申婷婷, 王浩然, 林一萍, 李慧玉, 张连飞. 白桦BpSPL9基因抑制表达载体的构建及遗传转化研究[J]. 植物研究, 2023, 43(1): 30-35. |
| [10] | 黄安瀛, 夏德安, 张洋, 那冬晨, 燕青, 魏志刚. PtrWRKY51基因的克隆及抗旱表达特性分析[J]. 植物研究, 2022, 42(6): 1005-1013. |
| [11] | 陈华峰, 代龙军, 刘明洋, 郭冰冰, 杨洪, 王立丰. 橡胶树胶乳高表达热激蛋白HbHSP90.4基因抗逆功能分析[J]. 植物研究, 2022, 42(6): 1023-1032. |
| [12] | 李登高, 林睿, 穆青慧, 周娜, 张焱如, 白薇. 马铃薯StCRKs基因家族的鉴定分析及响应逆境信号的表达[J]. 植物研究, 2022, 42(6): 1033-1043. |
| [13] | 刘明洋, 肖化兴, 王立丰, 梁晓宇, 张宇, 王萌. 橡胶树热激蛋白HbHSP90.8-1基因的克隆与功能分析[J]. 植物研究, 2022, 42(5): 811-820. |
| [14] | 王宏鹏, 李一丹, 汪耀, 谭晓宇, 陈成彬, 张力鹏. 菊叶薯蓣DcPMK基因克隆及互作蛋白筛选[J]. 植物研究, 2022, 42(5): 855-865. |
| [15] | 陈坤, 方功桂, 穆怀志, 姜静. 白桦BpPIN3基因启动子序列及应答特性分析[J]. 植物研究, 2022, 42(4): 592-601. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||