Bulletin of Botanical Research ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (5): 755-768.doi: 10.7525/j.issn.1673-5102.2025.05.010
• Original Paper • Previous Articles Next Articles
Xi ZHANG1, Haifu FANG1, Hong ZHAO2, Jiacheng SHEN2, Liangying LIU1, Xintong XU1, Ling ZHANG1( )
)
Received:2024-11-21
Online:2025-09-20
Published:2025-09-28
Contact:
Ling ZHANG
E-mail:lingzhang09@126.com
CLC Number:
Xi ZHANG, Haifu FANG, Hong ZHAO, Jiacheng SHEN, Liangying LIU, Xintong XU, Ling ZHANG. The Effects of Soil Nitrogen and Microbial Community on Growth of Moso Bamboo and Japanese Cedar Seedlings: Potential Mechanisms of Bamboo Expansion[J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2025, 45(5): 755-768.
Table 1
Effects of nitrogen input, microbial regulation and planting patterns on biomass,plant height and root/shoot ratio of Japanese cedar in ANOVAs
处理 Treatments | 自由度 df | 生物量 Biomass | 苗高 Plant height | 根冠比 Root/shoot ratio | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F | P | F | P | F | P | ||
| N | 2 | 39.88 | <0.000 1 | 37.48 | <0.000 1 | 7.76 | 0.000 8 |
| B | 1 | 11.28 | 0.001 1 | 16.06 | 0.000 1 | 3.01 | 0.085 8 |
| F | 1 | 9.12 | 0.003 2 | 7.83 | 0.003 2 | 18.38 | <0.000 1 |
| P | 1 | 0.82 | 0.367 3 | 0.01 | 0.921 8 | 9.41 | 0.022 8 |
| N×B | 2 | 0.16 | 0.848 2 | 0.71 | 0.493 0 | 1.49 | 0.230 9 |
| N×F | 2 | 0.02 | 0.982 7 | 1.34 | 0.267 1 | 2.84 | 0.063 2 |
| B×F | 1 | 0.14 | 0.706 7 | 10.01 | 0.002 1 | 1.25 | 0.267 0 |
| N×B×F | 2 | 0.15 | 0.859 1 | 0.46 | 0.632 1 | 0.45 | 0.640 3 |
| N×P | 2 | 0.51 | 0.603 6 | 0.14 | 0.867 3 | 0.09 | 0.915 9 |
| B×P | 1 | 0.01 | 0.988 9 | 0.89 | 0.348 5 | 0.13 | 0.715 3 |
| F×P | 1 | 0.01 | 0.910 1 | 0.06 | 0.811 6 | 0.01 | 0.977 6 |
| N×B×P | 2 | 0.14 | 0.871 4 | 1.24 | 0.294 0 | 0.84 | 0.434 0 |
| N×F×P | 2 | 0.29 | 0.749 3 | 0.17 | 0.841 1 | 0.02 | 0.985 1 |
| B×F×P | 1 | 0.04 | 0.857 2 | 0.01 | 0.966 4 | 0.03 | 0.873 6 |
| N×B×F×P | 2 | 0.09 | 0.915 9 | 0.08 | 0.926 4 | 0.39 | 0.677 2 |
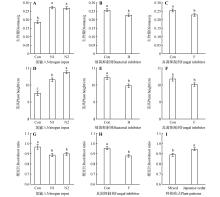
Fig.1
Effects of nitrogen input and microbial regulation on biomass(A,B,C), plant height(D,E,F),as well as the effects of nitrogen input,fungal inhibitors,and planting patterns on root/shoot ratio(G,H,I) of Japanese cedarCon. Control; N. Nitrogen input; N1. (NH4)2SO4; N2. KNO3; B. Bacterial inhibitors; F. Fungal inhibitors. Different lowercase letters indicated significant difference between treatments at P<0.05.
Table 2
Effects of nitrogen input,microbial regulation and planting patterns on biomass,plant height and root/shoot ratio of moso bamboo in ANOVAs
处理 Treatments | 自由度 df | 生物量 Biomass | 苗高 Plant height | 根冠比 Root/shoot ratio | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F | P | F | P | F | P | ||
| N | 2 | 16.11 | <0.000 1 | 28.62 | <0.000 1 | 8.35 | 0.000 5 |
| B | 1 | 9.58 | 0.002 6 | 34.60 | <0.000 1 | 5.31 | 0.023 3 |
| F | 1 | 12.64 | 0.000 5 | 18.14 | <0.000 1 | 23.96 | <0.000 1 |
| P | 1 | 4.32 | 0.040 3 | 30.89 | <0.000 1 | 11.32 | 0.001 1 |
| N×B | 2 | 0.90 | 0.408 2 | 0.53 | 0.593 1 | 1.93 | 0.150 4 |
| N×F | 2 | 0.58 | 0.564 1 | 0.31 | 0.737 1 | 3.15 | 0.047 1 |
| B×F | 1 | 8.90 | 0.003 6 | 2.39 | 0.125 2 | 1.97 | 0.163 9 |
| N×B×F | 2 | 1.47 | 0.235 6 | 2.37 | 0.098 8 | 0.71 | 0.494 1 |
| N×P | 2 | 0.26 | 0.768 0 | 1.56 | 0.215 6 | 0.23 | 0.794 1 |
| B×P | 1 | 0.07 | 0.787 9 | 2.28 | 0.134 6 | 0.16 | 0.688 4 |
| F×P | 1 | 0.02 | 0.899 2 | 0.27 | 0.607 3 | 0.01 | 0.961 0 |
| N×B×P | 2 | 0.02 | 0.980 3 | 2.01 | 0.139 5 | 0.78 | 0.462 8 |
| N×F×P | 2 | 0.03 | 0.969 3 | 0.15 | 0.862 7 | 0.02 | 0.975 4 |
| B×F×P | 1 | 0.01 | 0.949 5 | 0.33 | 0.568 0 | 0.02 | 0.883 3 |
| N×B×F×P | 2 | 0.01 | 0.993 0 | 0.66 | 0.521 6 | 0.26 | 0.770 2 |
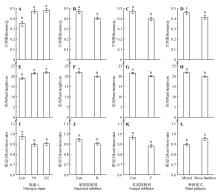
Fig. 2
Effects of nitrogen input, microbial regulation and planting patterns on biomass(A,B,C,D), plant height(E,F,G,H) and root/shoot ratio(I,J,K,L) of moso bambooCon. Control; N. Nitrogen input; N1. (NH4)2SO4; N2. KNO3; B. Bacterial inhibitor; F. Fungal inhibitor. Different lowercase letters indicated significant difference between treatments at P<0.05 .
Table 3
Effects of nitrogen input, microbial regulation and planting patterns on soil nutrient content of Japanese cedar and moso bamboo in ANOVAs
处理 Treatments | 自由度 df | F | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
有机碳 TOC | 全氮 TN | 全磷 TP | 铵态氮 | 硝态氮 | pH | ||
| N | 2 | 20.97 | 10.21 | 55.50 | 55.73 | 197.62 | 58.98 |
| B | 1 | 1.83 | 1.87 | 2.31 | 0.10 | 0.03 | 1.03 |
| F | 1 | 1.41 | 1.37 | 1.87 | 3.41 | 1.41 | 1.59 |
| P | 2 | 91.33 | 36.28 | 130.14 | 2.67 | 1.47 | 36.56 |
| N×B | 2 | 2.50 | 1.48 | 10.76 | 0.02 | 0.27 | 0.16 |
| N×F | 2 | 3.17 | 5.01 | 2.05 | 6.01 | 0.12 | 0.88 |
| B×F | 1 | 0.68 | 17.71 | 0.81 | 2.96 | 0.01 | 6.22 |
| N×B×F | 2 | 1.24 | 0.42 | 4.95 | 4.57 | 0.07 | 3.58 |
| N×P | 4 | 38.29 | 12.55 | 55.24 | 3.16 | 1.30 | 10.77 |
| B×P | 2 | 1.78 | 2.63 | 4.29 | 1.76 | 2.83 | 0.65 |
| F×P | 2 | 2.98 | 1.18 | 3.99 | 2.82 | 0.48 | 1.70 |
| N×B×P | 4 | 5.17 | 6.74 | 13.42 | 1.86 | 0.84 | 0.90 |
| N×F×P | 4 | 5.07 | 2.27 | 2.43 | 2.09 | 0.54 | 0.39 |
| B×F×P | 2 | 0.71 | 0.42 | 3.78 | 2.59 | 0.82 | 3.77 |
| N×B×F×P | 4 | 0.61 | 0.41 | 2.88 | 2.99 | 1.87 | 0.22 |
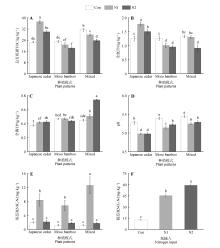
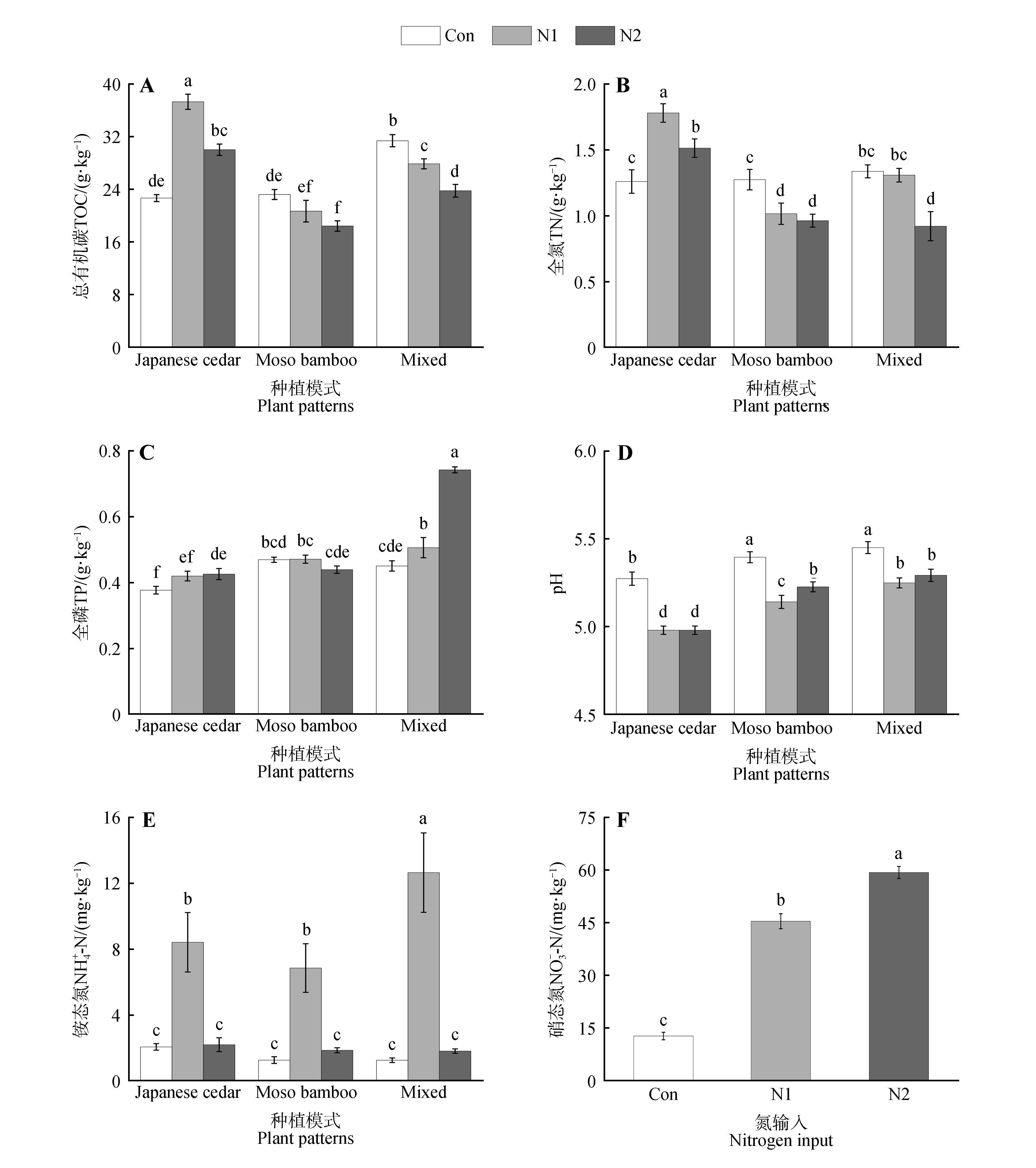
Fig.3
Effects of plant patterns and nitrogen input on soil physicochemical properties of Japanese cedar and moso bambooA. Total organic carbon(TOC); B. Total nitrogen(TN); C. Total phosphorus(TP); D. pH; E. Ammonium nitrogen(NH4+-N); F. Nitrate nitrogen (NO3--N). Different lowercase letters indicated significant difference between treatments at P<0.05.
| [1] | 刘喜帅.毛竹扩张对凋落物-土壤碳氮磷含量的影响及其微生物学机制研究[D].南昌:江西农业大学,2018. |
| LIU X S.The effect of Phyllostachys edulis expansion on the content of carbon,nitrogen and phosphorus in litter and soil and its microbiological mechanism[D].Nanchang:Jiangxi Agricultural University,2018. | |
| [2] | 史军义,易同培,马丽莎,等.中国引进竹亚科植物种类及特征[J].林业科学研究,2008,21(3):362-369. |
| SHI J Y, YI T P, MA L S,et al.Bambusoideae introduced in China and their bionomics[J].Forest Research,2008,21(3):362-369. | |
| [3] | 崔诚.毛竹扩张对土壤结构组成及碳氮磷化学计量特征的影响研究[D].南昌:江西农业大学,2018. |
| CUI C.The effects of Phyllostachys edulis expansion on soil structure composition and stoichiometric characteristics of carbon,nitrogen and phosphorus[D].Nanchang:Jiangxi Agricultural University,2018. | |
| [4] | 余雅迪,张茜,王皓,等.土壤二氧化碳及氧化亚氮排放对毛竹扩张的响应及机制[J].浙江农林大学学报,2024,41(3):659-668. |
| YU Y D, ZHANG X, WANG H,et al.Response of soil CO2 and N2O emissions to Phyllostachys edulis expansion and its mechanism[J].Journal of Zhejiang A&F University,2024,41(3):659-668. | |
| [5] | 方海富,江亮波,张毅,等.武功山日本柳杉林与草甸土壤碳氮特征和pH比较[J].福建农业学报,2019,34(6):705-710. |
| FANG H F, JIANG L B, ZHANG Y,et al.Carbon,nitrogen and pH in meadow soil at Cryptomeria japonica forests in Mt.Wugong[J].Fujian Journal of Agricultural Sciences,2019,34(6):705-710. | |
| [6] | LI Z Z, ZHANG L, DENG B L,et al.Effects of moso bamboo (Phyllostachys edulis) invasions on soil nitrogen cycles depend on invasion stage and warming[J].Environmental Science and Pollution Research,2017,24(32):24989-24999. |
| [7] | WU C S, MO Q F, WANG H K,et al.Moso bamboo (Phyllostachys edulis (Carriere) J.Houzeau) invasion affects soil phosphorus dynamics in adjacent coniferous forests in subtropical China[J].Annals of Forest Science,2018,75(1):24. |
| [8] | 吴家森,姜培坤,王祖良.天目山国家级自然保护区毛竹扩张对林地土壤肥力的影响[J].江西农业大学学报,2008,30(4):689-692. |
| WU J S, JIANG P K, WANG Z L.The effects of Phyllostachys pubescens expansion on soil fertility in National Nature Reserve of Mount Tianmu[J].Acta Agriculturae Universitatis Jiangxiensis,2008,30(4):689-692. | |
| [9] | 赵雨虹,罗嘉东,范少辉.毛竹扩张对常绿阔叶林土壤性质的影响及相关分析[J].林业科学研究,2017,30(2):354-359. |
| ZHAO Y H, LUO J D, FAN S H.The influence of Phyllostachys edulis expanding into evergreen broadleaf forest on soil property and its related analysis[J].Forest Research,2017,30(2):354-359. | |
| [10] | PAN J, LIU Y Q, YUAN X Y,et al.Root litter mixing with that of Japanese cedar altered CO2 emissions from Moso bamboo forest soil[J].Forests,2020,11(3):356. |
| [11] | 欧阳明,杨清培,陈昕,等.毛竹扩张对次生常绿阔叶林物种组成、结构与多样性的影响[J].生物多样性,2016,24(6):649-657. |
| OUYANG M, YANG Q P, CHEN X,et al.Effects of the expansion of Phyllostachys edulis on species composition,structure and diversity of the secondary evergreen broad-leaved forests[J].Biodiversity Science,2016,24(6):649-657. | |
| [12] | LIU X S, SIEMANN E, CUI C,et al.Moso bamboo (Phyllostachys edulis) invasion effects on litter,soil and microbial PLFA characteristics depend on sites and invaded forests[J].Plant and Soil,2019,438(1/2):85-99. |
| [13] | QIN H, NIU L M, WU Q F,et al.Bamboo forest expansion increases soil organic carbon through its effect on soil arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal community and abundance[J].Plant and Soil,2017,420(1/2):407-421. |
| [14] | 徐健鸿,周波,李凯,等.毛竹扩张对日本柳杉林土壤氮矿化速率温度敏感性的影响[J].江西农业大学学报,2023,45(6):1409-1417. |
| XU J H, ZHOU B, LI K,et al.Effects of moso bamboo (Phyllostachys edulis) expansion to Japanese cedar forest on temperature-sensitivity of soil nitrogen mineralization[J].Acta Agriculturae Universitatis Jiangxiensis,2023,45(6):1409-1417. | |
| [15] | 毛莹儿,周秀梅,王楠,等.毛竹扩张对杉木林土壤细菌群落的影响[J].生物多样性,2023,31(6):22659. |
| MAO Y E, ZHOU X M, WANG N,et al.Impact of Phyllostachys edulis expansion to Chinese fir forest on the soil bacterial community[J].Biodiversity Science,2023,31(6):22659. | |
| [16] | 张秦泽,郝广,李洪远.外源输入氮的有效性及形态对植物生长与生理影响的研究进展[J].生态学杂志,2024,43(3):878-887. |
| ZHANG Q Z, HAO G, LI H Y.Effects of availability and form of exogenous nitrogen on plant growth and physiology:progress and prospects[J].Chinese Journal of Ecology,2024,43(3):878-887. | |
| [17] | ZOU N, HUANG L, CHEN H J,et al.Nitrogen form plays an important role in the growth of moso bamboo (Phyllostachys edulis) seedlings[J].PeerJ,2020,8:e9938. |
| [18] | ZOU N, SHI W M, HOU L H,et al.Superior growth,N uptake and NH4 + tolerance in the giant bamboo Phyllostachys edulis over the broad-leaved tree Castanopsis fargesii at elevated NH4 + may underlie community succession and favor the expansion of bamboo[J].Tree Physiology,2020,40(11):1606-1622. |
| [19] | 刘宇馨,邹娜,颜卓佳,等.NH4 +-N浓度对毛竹和杉木幼苗生长及种间竞争的影响[J].江西农业大学学报,2023,45(3):526-539. |
| LIU Y X, ZOU N, YAN Z J,et al.Effects of NH4 +-N concentration on growth and interspecific competition of Phyllostachys edulis and Cunninghamia lanceolata seedlings[J].Acta Agriculturae Universitatis Jiangxiensis,2023,45(3):526-539. | |
| [20] | 邹欢欢,程明圣,邹娜,等.硝态氮对毛竹幼苗生长的抑制性研究[J].江西农业大学学报,2022,44(2):290-298. |
| ZOU H H, CHENG M S, ZOU N,et al.Inhibition of nitrate nitrogen on the growth of moso bamboo(Phyllostachys edulis)seedlings[J].Acta Agriculturae Universitatis Jiangxiensis,2022,44(2):290-298. | |
| [21] | 邓邦良,刘倩,刘喜帅,等.UV-B辐射增强和氮沉降对入侵植物乌桕生长的影响[J].植物生态学报,2017,41(4):471-479. |
| DENG B L, LIU Q, LIU X S,et al.Effects of enhanced UV-B radiation and nitrogen deposition on the growth of invasive plant Triadica sebifera [J].Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology,2017,41(4):471-479. | |
| [22] | 方海富,冯为迅,罗来聪,等.氮沉降背景下土壤微生物对入侵植物乌桕叶绿素荧光特征的影响[J].生态学报,2021,41(23):9377-9387. |
| FANG H F, FENG W X, LUO L C,et al.Effects of soil microorganisms on chlorophyll fluorescence characteristics of invasive Triadica sebifera with nitrogen deposition[J].Acta Ecologica Sinica,2021,41(23):9377-9387. | |
| [23] | REN G Q, LI Q, LI Y,et al.The enhancement of root biomass increases the competitiveness of an invasive plant against a co-occurring native plant under elevated nitrogen deposition[J].Flora,2019,261:151486. |
| [24] | ZOU J, ROGERS W E, SIEMANN E.Differences in morphological and physiological traits between native and invasive populations of Sapium sebiferum [J].Functional Ecology,2007,21(4):721-730. |
| [25] | BRADLEY B A, BLUMENTHAL D M, WILCOVE D S,et al.Predicting plant invasions in an era of global change[J].Trends in Ecology & Evolution,2010,25(5):310-318. |
| [26] | 陈彤,刘文莉,张崇邦,等.加拿大一枝黄花入侵对本土植物群落动态的影响及其机制[J].植物生态学报,2012,36(3):253-261. |
| CHEN T, LIU W L, ZHANG C B,et al.Effects of Solidago canadensis invasion on dynamics of native plant communities and their mechanisms[J].Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology,2012,36(3):253-261. | |
| [27] | 李艺雪,叶冬梅,郝龙飞,等.土壤灭菌、AM真菌接种与氮添加对柠条根际土壤的影响[J].植物研究,2024,44(4):590-601. |
| LI Y X, YE D M, HAO L F,et al.The responses of rhizosphere soil of Caragana korshinskii under soil sterilization,AM fungi inoculation and N addition[J].Bulletin of Botanical Research,2024,44(4):590-601. | |
| [28] | FOX C A, MACDONALD K B.Challenges related to soil biodiversity research in agroecosystems-issues within the context of scale of observation[J].Canadian Journal of Soil Science,2003,83(Sup.):231-244. |
| [29] | 严淑娴,刘茗,刘彩霞,等.毛竹纯林土壤微生物多样性高于杉木纯林[J].土壤学报,2022,59(6):1704-1717. |
| YAN S X, LIU M, LIU C X,et al.Soil microbial diversity is higher in pure stands of moso bamboo than in pure stands of Chinese fir[J].Acta Pedologica Sinica,2022,59(6):1704-1717. | |
| [30] | WANG C Q, KUZYAKOV Y.Mechanisms and implications of bacterial-fungal competition for soil resources[J].The ISME Journal,2024,18(1):wrae073. |
| [31] | 方海富.毛竹扩张对日本柳杉林土壤N2O排放的影响及微生物机制研究[D].南昌:江西农业大学,2021. |
| FANG H F.Effects of moso bamboo expansion into Japanese cedar forest on soil N2O emissions and the microbial mechanism[D].Nanchang:Jiangxi Agricultural University,2021. | |
| [32] | ZHANG L, ZHANG Y J, WANG H,et al.Chinese tallow trees (Triadica sebifera) from the invasive range outperform those from the native range with an active soil community or phosphorus fertilization[J].PLoS One,2013,8(9):e74233. |
| [33] | ZHANG M Y, ZHANG W Y, BAI S H,et al.Minor increases in Phyllostachys edulis (moso bamboo) biomass despite evident alterations of soil bacterial community structure after phosphorus fertilization alone:based on field studies at different altitudes[J].Forest Ecology and Management,2019,451:117561. |
| [34] | 徐道炜,刘金福,何中声,等.毛竹向杉木林扩张对土壤活性有机碳及碳库管理指数影响[J].西部林业科学,2019,48(5):22-28. |
| XU D W, LIU J F, HE Z S,et al.Effect of Phyllostachys edulis to Cunninghamia lanceolata forest on soil active organic carbon and carbon management index[J].Journal of West China Forestry Science,2019,48(5):22-28. | |
| [35] | 童冉,周本智,姜丽娜,等.毛竹入侵对森林植物和土壤的影响研究进展[J].生态学报,2019,39(11):3808-3815. |
| TONG R, ZHOU B Z, JIANG L N,et al.Influence of moso bamboo invasion on forest plants and soil:a review[J].Acta Ecologica Sinica,2019,39(11):3808-3815. | |
| [36] | FANG H F, GAO Y, ZHANG Q,et al.Moso bamboo and Japanese cedar seedlings differently affected soil N2O emissions[J].Journal of Plant Ecology,2022,15(2):277-285. |
| [37] | NIJJER S, ROGERS W E, LEE C T A,et al.The effects of soil biota and fertilization on the success of Sapium sebiferum [J].Applied Soil Ecology,2008,38(1):1-11. |
| [38] | 鲍士旦.土壤农化分析[M].第3版.北京:中国农业出版社,2000. |
| BAO S D.Soil and agricultural chemistry analysis[M]. 3rd ed.Beijing:China Agricultural Publishing House,2000. | |
| [39] | XIE J Y, FANG H F, ZHANG Q,et al.Understory plant functional types alter stoichiometry correlations between litter and soil in Chinese fir plantations with N and P addition[J].Forests,2019,10(9):742. |
| [40] | 罗来聪,白健,高宇,等.油茶壳及凋落叶生物质炭对土壤温室气体排放的影响[J].江西农业大学学报,2022,44(5):1177-1187. |
| LUO L C, BAI J, GAO Y,et al.Effects of Camellia oleifera leaf litter and fruit shell-derived biochar on soil greenhouse gas emissions[J].Acta Agriculturae Universitatis Jiangxiensis,2022,44(5):1177-1187. | |
| [41] | 毛晋花,邢亚娟,闫国永,等.陆生植物生物量分配对模拟氮沉降响应的Meta分析[J].生态学报,2018,38(9):3183-3194. |
| MAO J H, XING Y J, YAN G Y,et al.A meta-analysis of the response of terrestrial plant biomass allocation to simulated N deposition[J].Acta Ecologica Sinica,2018,38(9):3183-3194. | |
| [42] | BOZZOLO F H, LIPSON D A.Differential responses of native and exotic coastal sage scrub plant species to N additions and the soil microbial community[J].Plant and Soil,2013,371(1/2):37-51. |
| [43] | 令狐克念,王姝.不同生长阶段苘麻生物量分配对种群密度和土壤水分的响应[J].植物研究,2023,43(2):272-280. |
| LINGHU K N, WANG S.Responses of biomass allocation to population density and soil water in Abutilon theophrasti at different growth stages[J].Bulletin of Botanical Research,2023,43(2):272-280. | |
| [44] | YANG Y H, FANG J Y, MA W H,et al.Large-scale pattern of biomass partitioning across China’s grasslands[J].Global Ecology and Biogeography,2010,19(2):268-277. |
| [45] | REYNOLDS H L, PACALA S W.An analytical treatment of root-to-shoot ratio and plant competition for soil nutrient and light[J].The American Naturalist,1993,141(1):51-70. |
| [46] | YANG Q, LI B, SIEMANN E.The effects of fertilization on plant-soil interactions and salinity tolerance of invasive Triadica sebifera [J].Plant and Soil,2015,394(1/2):99-107. |
| [47] | 王珍,金轲,丁勇,等.植物-土壤微生物反馈在草地演替过程中的作用机制[J].中国草地学报,2022,44(1):95-103. |
| WANG Z, JIN K, DING Y,et al.The mechanism of plants-soil microbial feedback in grassland succession[J].Chinese Journal of Grassland,2022,44(1):95-103. | |
| [48] | STRECKER T, BARNARD R L, NIKLAUS P A,et al.Effects of plant diversity,functional group composition,and fertilization on soil microbial properties in experimental grassland[J].PLoS One,2015,10(5):e0125678. |
| [49] | 沈仁芳,赵学强.土壤微生物在植物获得养分中的作用[J].生态学报,2015,35(20):6584-6591. |
| SHEN R F, ZHAO X Q.Role of soil microbes in the acquisition of nutrients by plants[J].Acta Ecologica Sinica,2015,35(20):6584-6591. | |
| [50] | ZHANG R F, VIVANCO J M, SHEN Q R.The unseen rhizosphere root-soil-microbe interactions for crop production[J].Current opinion in microbiology,2017,37:8-14. |
| [51] | 李欣欣,赖金莉,岳建华,等.毛竹各器官和根际土浸提液对杉木种子萌发的化感作用[J].生态学报,2018,38(22):8149-8157. |
| LI X X, LAI J L, YUE J H,et al.Allelopathy of Phyllostachys pubescens extract on the seed germination of Chinese fir[J].Acta Ecologica Sinica,2018,38(22):8149-8157. | |
| [52] | 陈娟,白尚斌,周国模,等.毛竹浸提液对苦槠幼苗生长的化感效应[J].生态学报,2014,34(16):4499-4507. |
| CHEN J, BAI S B, ZHOU G M,et al.Allelopathic effects of Phyllostachys edulis extracts on Castanopsis sclerophylla [J].Acta Ecologica Sinica,2014,34(16):4499-4507. | |
| [53] | DENG M F, LIU L L, SUN Z Z,et al.Increased phosphate uptake but not resorption alleviates phosphorus deficiency induced by nitrogen deposition in temperate Larix principis‐rupprechtii plantations[J].New Phytologist,2016,212(4):1019-1029. |
| [54] | CHANG E H, CHIU C Y.Changes in soil microbial community structure and activity in a cedar plantation invaded by moso bamboo[J].Applied Soil Ecology,2015,91(2):1-7. |
| [55] | TIAN J H, WEI K, CONDRON L M,et al.Impact of land use and nutrient addition on phosphatase activities and their relationships with organic phosphorus turnover in semi-arid grassland soils[J].Biology and Fertility of Soils,2016,52(5):675-683. |
| [56] | 吴金凤.氮沉降背景下凋落物对松嫩草地土壤磷循环的调节作用[D].长春:东北师范大学,2021. |
| WU J F.Regulation of litter on soil phosphorus cycling in Songnen grassland under the background of nitrogen deposition[D].Changchun:Northeast Normal University,2021. | |
| [57] | 宋庆妮,杨清培,刘骏,等.毛竹扩张对常绿阔叶林土壤氮素矿化及有效性的影响[J].应用生态学报,2013,24(2):338-344. |
| SONG Q N, YANG Q P, LIU J,et al.Effects of Phyllostachys edulis expansion on soil nitrogen mineralization and its availability in evergreen broadleaf forest[J].Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology,2013,24(2):338-344. | |
| [58] | PAN J, LIU Y Q, NIU J H,et al.Moso bamboo expansion reduced soil N2O emissions while accelerated fine root litter decomposition:contrasting non-additive effects[J].Plant and Soil,2024,501(1):7-21. |
| [59] | 张普河,姚佳,王雪韧,等.短期氮添加对荒漠草原土壤无机碳及土壤酸缓冲能力的影响[J].草地学报,2024,32(7):2081-2088. |
| ZHANG P H, YAO J, WANG X R,et al.Effects of short-term nitrogen addition on soil inorganic carbon and soil acid buffering capacity in desert grasslands[J].Acta Agrestia Sinica,2024,32(7):2081-2088. |
| [1] | Yixue LI, Dongmei YE, Longfei HAO, Tingyan LIU, Jiajing DUAN, Zhengying NIE. The Responses of Rhizosphere Soil of Caragana korshinskii under Soil Sterilization, AM Fungi Inoculation and N Addition [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2024, 44(4): 590-601. |
| [2] | Zhiqi CHEN, Haina ZHANG, Jiali LIU, Xianghui LU, Baocheng YANG. Effects of Nitrogen Addition on Root Growth, Biomass Allocation and Non-structural Carbohydrate Content of Cinnamomum bodinier Seedlings in Rare Earth Tailings [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2024, 44(1): 86-95. |
| [3] | GUO Hai-Xia, XU Bo, SHI Fu-Sun, WU Yan. Effects of Shading and Nitrogen Addition on the Growth and C-N Balance of Fritillaria unibracteata [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2017, 37(5): 738-743. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||