Bulletin of Botanical Research ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (4): 580-591.doi: 10.7525/j.issn.1673-5102.2025.04.010
• Original Paper • Previous Articles Next Articles
Qianwen MAO1,2, Guohua WANG1,2, Rong HAN1,2
Received:2025-02-21
Online:2025-07-20
Published:2025-07-25
CLC Number:
Qianwen MAO, Guohua WANG, Rong HAN. Response of Arabidopsis thaliana Histone Chaperone HIRA to Enhanced UV-B Radiation[J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2025, 45(4): 580-591.
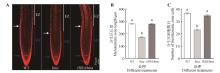
Fig.3
Statistical analysis of root meristem of Arabidopsis thalianaA. PI fluorescence staining; B. Length of root meristematic zone; C. Number of root cells at meristematic zone. MZ represented the meristem zone; EZ represented the elongation zone; the blue arrow pointed to the static center QC; the white arrow indicated the meristem-elongation transition zone. Different lowercase letters indicated significant difference(P<0.05).
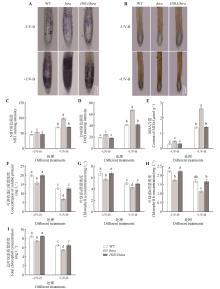
Fig.7
Effects of enhanced UV-B radiation on physiological and biochemical indexes of Arabidopsis thalianaA. NBT staining; B. DAB staining; C. Gray analysis of NBT staining; D. Gray analysis of DAB staining. Different lowercase letters indicated significant difference between treatments (P<0.05).
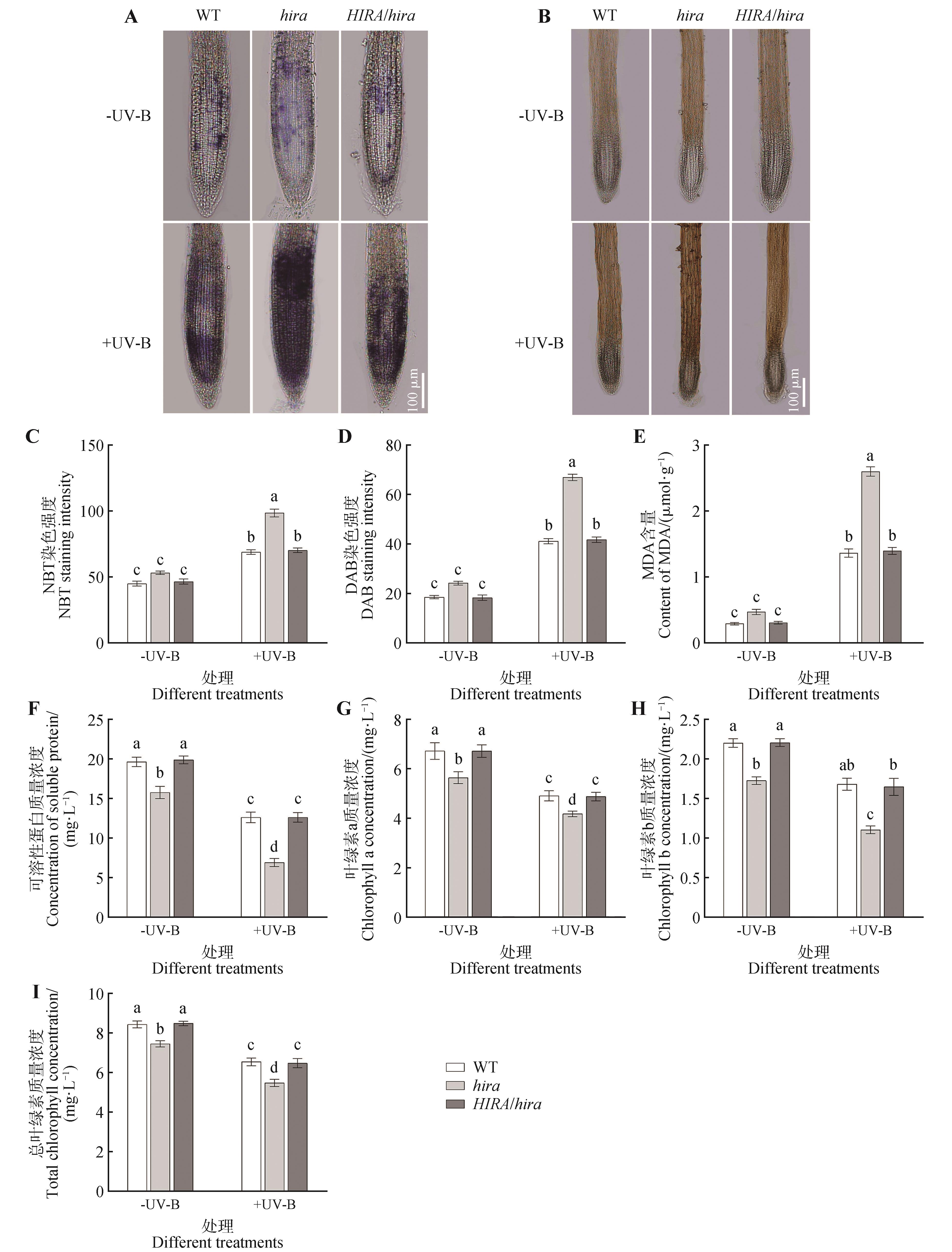
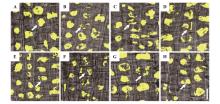
Fig.9
Effect of enhanced UV-B radiation on mitosis of hira mutant root cellsAfter UV-B radiation treatment, the root cells of hira mutants showed abnormal mitosis. A. Micronucleus; B. Chromosome bridge; C. Lagging chromosome; D. Free chromosome; E-F. Equatorial plate deflection; G. Multiple beam splitting; H. Unequal division. The white arrow indicated the undergoing cells mitosis.
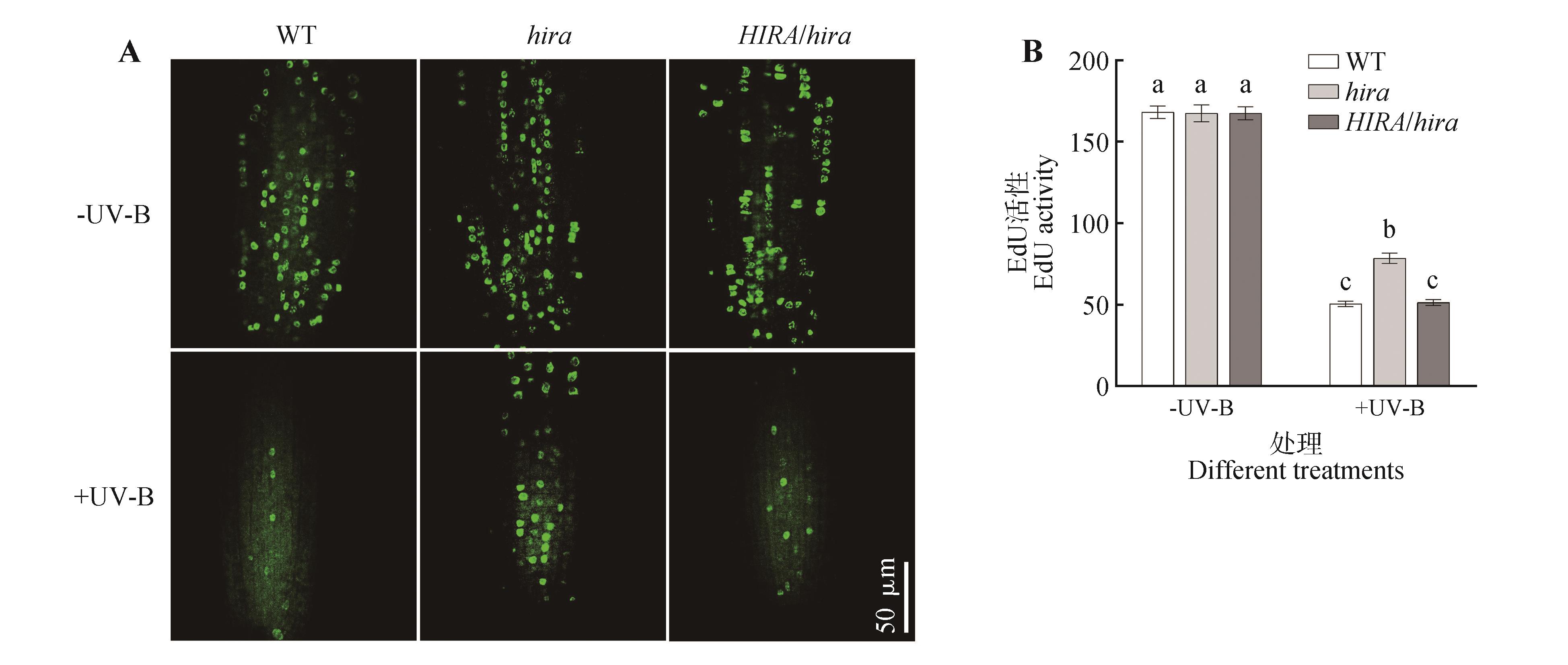
Fig.11
Effects of enhanced UV-B radiation on DNA synthesis in Arabidopsis thalianaA. EdU fluorescence staining under UV-B radiation treatment; B. Statistical analysis of EdU activity under UV-B radiation treatment. Different lowercase letters indicated significant difference between treatments(P<0.05).
| [1] | 韩榕.He-Ne激光对小麦增强UV-B辐射损伤的修复效应及机理[D].西安:西北大学,2002. |
| HAN R.Repair effect and mechanism of He-Ne laser on enhanced UV-B radiation damage in Triticum aestivum [D].Xi’an:Northwest University,2002. | |
| [2] | TURUNEN M, LATOLA K.UV-B radiation and acclimation in timberline plants[J].Environmental Pollution,2005,137(3):390-403. |
| [3] | LIU W, GIURIANI G, HAVLIKOVA A,et al.Phosphorylation of Arabidopsis UVR8 photoreceptor modulates protein interactions and responses to UV-B radiation[J].Nature Communications,2024,15(1):1221. |
| [4] | SHI C, LIU H T.How plants protect themselves from ultraviolet-B radiation stress[J].Plant Physiology,2021,187(3):1096-1103. |
| [5] | JIANG L, WANG Y, BJÖRN L O,et al.UV-B-induced DNA damage mediates expression changes of cell cycle regulatory genes in Arabidopsis root tips[J].Planta,2011,233(4):831-841. |
| [6] | SUZUKI G, NISHIUCHI C, TSURU A,et al.Cellular localization of mitotic RAD21 with repetitive amino acid motifs in Allium cepa [J].Gene,2013,514(2):75-81. |
| [7] | LI X, HEYER W D.Homologous recombination in DNA repair and DNA damage tolerance[J].Cell Research,2008,18(1):99-113. |
| [8] | WETERINGS E, CHEN D J.The endless tale of non-homologous end-joining[J].Cell Research,2008,18(1):114-124. |
| [9] | FRIEDMAN N, VARDI S, RONEN M,et al.Precise temporal modulation in the response of the SOS DNA repair network in individual bacteria[J].PLoS Biology,2005,3(7):e238. |
| [10] | WARMERDAM D O, KANAAR R.Dealing with DNA damage:relationships between checkpoint and repair pathways[J].Mutation Research,2010,704(1/3):2-11. |
| [11] | HÄDER D P, SINHA R P.Solar ultraviolet radiation-induced DNA damage in aquatic organisms:potential environmental impact[J].Mutation Research,2005,571(1/2):221-233. |
| [12] | SZENKER E, LACOSTE N, ALMOUZNI G.A developmental requirement for HIRA-dependent H3.3 deposition revealed at gastrulation in Xenopus [J].Cell Reports,2012,1(6):730-740. |
| [13] | SKENE P J, HENIKOFF S.Histone variants in pluripotency and disease[J].Development,2013,140(12):2513-2524. |
| [14] | MISOVA I, PITELOVA A, BUDIS J,et al.Repression of a large number of genes requires interplay between homologous recombination and HIRA[J].Nucleic Acids Research,2021,49(4):1914-1934. |
| [15] | ADAM S, POLO S E, ALMOUZNI G.Transcription recovery after DNA damage requires chromatin priming by the H3.3 histone chaperone HIRA[J].Cell,2013,155(1):94-106. |
| [16] | NIE X, WANG H F, LI J,et al.The HIRA complex that deposits the histone H3.3 is conserved in Arabidopsis and facilitates transcriptional dynamics[J].Biology Open,2014,3(9):794-802. |
| [17] | BORCHERS A, PIELER T.Programming pluripotent precursor cells derived from Xenopus embryos to generate specific tissues and organs[J].Genes,2010,1(3):413-426. |
| [18] | 林艳,郭伟珍,徐振华,等.大叶女贞抗寒性及冬季叶片丙二醛和可溶性糖含量的变化[J].中国农学通报,2012,28(25):68-72. |
| LIN Y, GUO W Z, XU Z H,et al.Cold resistance and changes on MDA and soluble sugar of leaves of Ligustrum lucidum Ait in winter[J].Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin,2012,28(25):68-72. | |
| [19] | GUO D P, GUO Y P, ZHAO J P,et al.Photosynthetic rate and chlorophyll fluorescence in leaves of stem mustard (Brassica juncea var. tsatsai) after turnip mosaic virus infection[J].Plant Science,2005,168(1):57-63. |
| [20] | OVIEDO M J, QUESTER K, HIRATA G A,et al.Determination of conjugated protein on nanoparticles by an adaptation of the Coomassie blue dye method[J].MethodsX,2019,6:2134-2140. |
| [21] | HAN T T, LIU W C, LU Y T.General control non-repressible 20 (GCN20) functions in root growth by modulating DNA damage repair in Arabidopsis [J].BMC Plant Biology,2018,18(1):274. |
| [22] | RŮŽIČKA K, LJUNG K, VANNESTE S,et al.Ethylene regulates root growth through effects on auxin biosynthesis and transport-dependent auxin distribution[J].Plant Cell,2007,19(7):2197-2212. |
| [23] | SPARKES I A, RUNIONS J, KEARNS A,et al.Rapid,transient expression of fluorescent fusion proteins in tobacco plants and generation of stably transformed plants[J].Nature Protocols,2006,1(4):2019-2025. |
| [24] | ZUK-GOLASZEWSKA K, UPADHYAYA M K, GOLASZEWSKI J.The effect of UV-B radiation on plant growth and development[J].Plant,Soil and Environment,2003,49(3):135-140. |
| [25] | SHIN R, BERG R H, SCHACHTMAN D P.Reactive oxygen species and root hairs in Arabidopsis root response to nitrogen,phosphorus and potassium deficiency[J].Plant and Cell Physiology,2005,46(8):1350-1357. |
| [26] | LIDON F C, RAMALHO J C.Impact of UV-B irradiation on photosynthetic performance and chloroplast membrane components in Oryza sativa L.[J].Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology B:Biology,2011,104(3):457-466. |
| [27] | GILL S S, TUTEJA N.Reactive oxygen species and antioxidant machinery in abiotic stress tolerance in crop plants[J].Plant Physiology and Biochemistry,2010,48(12):909-930. |
| [28] | JANSEN M A K, GABA V, GREENBERG B M.Higher plants and UV-B radiation:balancing damage,repair and acclimation[J].Trends in Plant Science,1998,3(4):131-135. |
| [29] | 陈慧泽,韩榕.植物响应UV-B辐射的研究进展[J].植物学报,2015,50(6):790-801. |
| CHEN H Z, HAN R.Plants respond to UV-B radiation:a review[J].Chinese Bulletin of Botany,2015,50(6):790-801. | |
| [30] | RAY-GALLET D, RICKETTS M D, SATO Y,et al.Functional activity of the H3.3 histone chaperone complex HIRA requires trimerization of the HIRA subunit[J].Nature Communications,2018,9(1):3103. |
| [31] | LI X, TYLER J K.Nucleosome disassembly during human non-homologous end joining followed by concerted HIRA- and CAF-1-dependent reassembly[J].eLife,2016,5:e15129. |
| [32] | HALL C, NELSON D M, YE X F,et al.HIRA,the human homologue of yeast Hir1p and Hir2p,is a novel cyclin-cdk2 substrate whose expression blocks S-phase progression[J].Molecular and Cellular Biology,2001,21(5):1854-1865. |
| [33] | LEWIS P W, ELSAESSER S J, NOH K M,et al.Daxx is an H3.3-specific histone chaperone and cooperates with ATRX in replication-independent chromatin assembly at telomeres[J].Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America,2010,107(32):14075-14080. |
| [34] | RAY-GALLET D, QUIVY J P, SCAMPS C,et al.HIRA is critical for a nucleosome assembly pathway independent of DNA synthesis[J].Molecular Cell,2002,9(5):1091-1100. |
| [35] | TAGAMI H, RAY-GALLET D, ALMOUZNI G,et al.Histone H3.1 and H3.3 complexes mediate nucleosome assembly pathways dependent or independent of DNA synthesis[J].Cell,2004,116(1):51-61. |
| [36] | ADAM S, POLO S E.Chromatin dynamics during nucleotide excision repair:histones on the move[J].International Journal of Molecular Sciences,2012,13(9):11895-11911. |
| [37] | POLO S E, ALMOUZNI G.Chromatin dynamics after DNA damage:the legacy of the access-repair-restore model[J].DNA Repair,2015,36:114-121. |
| [38] | ZHU Y, WENG M J, YANG Y,et al. Arabidopsis homologues of the histone chaperone ASF1 are crucial for chromatin replication and cell proliferation in plant development[J].The Plant Journal,2011,66(3):443-455. |
| [1] | Jianhua WANG, Huize CHEN, Rong HAN. Alleviative Effects of Foliar TiO2-NPs Pretreatment on Wheat Seedling Growth under UV-B Stress [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2025, 45(4): 592-602. |
| [2] | Zhihui HUANG, Yining ZHANG, Nana LI, Baojiang ZHENG, Yuhong ZHANG. Responses of Supplemental UV-B Radiation to Physiological Properties and Secondary Metabolites of Thlaspi arvense [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2022, 42(6): 1079-1087. |
| [3] | Qing-Yan GAI, Zi-Ying WANG, Yu-Jie FU, Jiao JIAO, Hui-Mei WANG, Yao LU, Jing LIU, Jin-Xian FU, Xiao-Jie XU, Lan YAO. Effects of UV-B Radiation on Phenolic Acid Accumulation and Physiological and Biochemical Characters in 84K Poplar [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2021, 41(6): 878-887. |
| [4] | WEI Xiao-Li;ZHENG Na;LI Xiao-Yang;HAN Rong*. Effect of Enhanced UV-B Radiation on Arabidopsis Mesophyll Cell Protein [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2013, 33(2): 186-190. |
| [5] | MENG Qing-Huan;ZU Yuan-Gang;GUO Xiao-Rui;DUAN Xi-Hua;*. Effect of Exogenous Nitric Oxide on Photosynthetic Pigments and Chlorophyll Fluorescence under Enhanced UV-B Radiation in Larix gmelinii [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2013, 33(2): 181-185. |
| [6] | GUO Xiao-Rui;WANG Hong-Ling;WANG Hua-Nan;DUAN Xi-Hua*. The Effects of Supplementary UV-B Radiation and Nitrogen Levels on the Growth and Physiological Metabolism of Catharanthus roseus [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2011, 31(5): 592-596. |
| [7] | AN Xu-Liang;HAN Rong*. Renovation of ROP GTPase in Young Seedlings of Wheats by He-Ne Laser under Enhanced UV-B Radiation [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2010, 30(6): 725-730. |
| [8] | GUO Jun-Yu;ZHANG Qin;HAN Rong*. Effects of He-Ne Laser on Chloroplast of Wheat Seedling Exposed to Enhanced UV-B Radiation [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2009, 29(2): 204-208. |
| [9] | MA Xiao-Li;HAO Jin-Hua;HAN Rong*. The Influence on Peroxidase Activity and Polyamine Oxidase Activity of Leaves in Wheat Seedings Exposed to Enhanced Ultraviolet-B Radiation and Irradiated by He-Ne Laser [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2007, 27(6): 669-673. |
| [10] | YI Hui-lan, HAN Shu-ju. STUDIES ON MICRONUCLEI AND ABNORMOL DIVISION OF HORDEUM VULGARE BREEDED IN NACL SOLUTION [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2000, 20(2): 156-161. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||