Bulletin of Botanical Research ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (4): 491-503.doi: 10.7525/j.issn.1673-5102.2025.04.003
• Original Paper • Previous Articles Next Articles
Guoju XU, Piaoxue GUO, Xunran ZHU, Zimei YANG, Huanyu CHENG, Wei QIANG( )
)
Received:2025-06-05
Online:2025-07-20
Published:2025-07-25
Contact:
Wei QIANG
E-mail:wayneqiang@126.com
CLC Number:
Guoju XU, Piaoxue GUO, Xunran ZHU, Zimei YANG, Huanyu CHENG, Wei QIANG. The Salicylic Acid Responsive UrSTR4 Gene is Involved in Rhynchophylline Biosynthesis in Uncaria rhynchophylla[J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2025, 45(4): 491-503.
Table 1
Primers for cloning of UrSTR candidate genes and qPCR analysis
引物名称 Primer name | 引物序列(5′—3′) Primer sequence(5′—3′) | 引物名称 Primer name | 引物序列(5′—3′) Primer sequence(5′—3′) |
|---|---|---|---|
| F-STR4-OE | cacgggggactcttgggatccGCAATGACGCTGACCGGAT | R-STR4-OE | cgatcggggaaattcgagctcTAGGGAACTATTTTGTCACTCTAATTGG |
| Fq-GAPDH | AGCAAGGACTGGAGAGGTGGAAG | Rq-GAPDH | CCGTTGAGGGCTGGAAGAACTTTC |
| Fq-STR1 | CTCCGCCATATAAAGGTG | Rq-STR1 | GACAGAAGAAGCCAATCC |
| Fq-STR2 | GGTAACAACTCCGAACAG | Rq-STR2 | CACCATTAGGACCAACTAC |
| Fq-STR3 | CCTCCTTACAGTGACTTC | Rq-STR3 | GTCCATCAGAACCGTTAC |
| Fq-STR4 | CAAGGACCTTATGCGAGCGTCTC | Rq-STR4 | TTGGTCCAAGGTCGGGATTTGTTG |
| Fq-STR5 | CATCCCTCTACCGTATAAAG | Rq-STR5 | GAAGAAGCCTCTCCATTC |
| Fq-STR6 | GATGGTCGGATTCTCAAG | Rq-STR6 | GATGAACACACTCCTTCC |
| Fq-STR7 | CTTCTTCTCCTCATCTTCG | Rq-STR7 | GACAACTCTGCCATCTTC |
| Fq-STR8 | GGTTCAAGACATCCTGAG | Rq-STR8 | GCCATCTCTGCTAACTTC |
| Fq-STR9 | CTCTCTCATCCTCCTCAA | Rq-STR9 | GTAGACCACAACTGCTAG |
Table 2
Physicochemical characteristics of the proteins encoded by UrSTRs
基因名称 Gene name | 氨基酸残基 Amino acid residues/aa | 相对分子质量 Molecular weight/Da | 不稳定系数 Instability index | 等电点 Isoelectric point/pI | 亲水性 Hydrophilicity | 脂肪指数 Aliphatic index |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UrSTR1 | 359 | 39 757.77 | 26.91 | 5.44 | -0.196 | 82.79 |
| UrSTR2 | 340 | 37 332.35 | 32.45 | 7.71 | -0.244 | 82.26 |
| UrSTR3 | 419 | 42 301.06 | 33.62 | 6.92 | -0.254 | 86.18 |
| UrSTR4 | 391 | 43 858.54 | 38.06 | 7.59 | -0.179 | 87.77 |
| UrSTR5 | 345 | 37 974.68 | 25.40 | 5.49 | -0.186 | 85.30 |
| UrSTR6 | 301 | 33 662.11 | 34.82 | 7.82 | 0.034 | 101.99 |
| UrSTR7 | 353 | 38 959.17 | 31.16 | 5.22 | -0.119 | 86.69 |
| UrSTR8 | 345 | 37 957.65 | 26.18 | 5.28 | -0.184 | 87.28 |
| UrSTR9 | 397 | 44 083.25 | 28.70 | 5.77 | -0.151 | 92.54 |
| UrSTR10 | 341 | 36 791.16 | 28.91 | 5.71 | 0.085 | 99.18 |
| UrSTR11 | 296 | 32 642.00 | 34.72 | 6.52 | -0.165 | 84.59 |
| UrSTR12 | 191 | 20 798.44 | 20.61 | 4.53 | 0.017 | 95.39 |
| UrSTR13 | 64 | 7 234.31 | 38.38 | 8.55 | -0.331 | 63.75 |
| UrSTR14 | 341 | 36 791.16 | 28.91 | 5.71 | 0.085 | 99.18 |
| UrSTR15 | 175 | 20 227.28 | 27.83 | 9.34 | -0.341 | 86.86 |
| UrSTR16 | 175 | 20 237.32 | 27.40 | 9.38 | -0.346 | 86.86 |
| UrSTR17 | 187 | 20 584.27 | 17.69 | 5.85 | -0.234 | 92.73 |
| UrSTR18 | 175 | 20 295.36 | 27.40 | 9.25 | -0.376 | 86.29 |
| UrSTR19 | 140 | 15 445.99 | 27.56 | 10.01 | -0.013 | 93.36 |
| UrSTR20 | 52 | 5 639.56 | 15.13 | 9.82 | -0.073 | 97.31 |
| UrSTR21 | 81 | 8 790.11 | 11.97 | 10.11 | -0.200 | 90.12 |
| UrSTR22 | 80 | 8 852.30 | 26.24 | 9.58 | -0.129 | 97.37 |
| UrSTR23 | 177 | 19 459.11 | 22.71 | 6.29 | -0.160 | 94.63 |
| UrSTR24 | 153 | 16 949.43 | 19.75 | 9.68 | -0.186 | 88.43 |
| UrSTR25 | 66 | 7 253.40 | 22.19 | 9.99 | -0.255 | 88.48 |
| UrSTR26 | 256 | 27 801.75 | 30.32 | 5.16 | -0.054 | 92.85 |
| UrSTR27 | 381 | 42 185.94 | 26.32 | 5.32 | 0.257 | 107.43 |
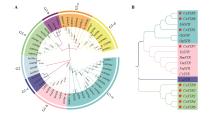
Fig.1
Evolutionary analysis of the UrSTR gene family in U. rhynchophyllaA. Phylogenetic analysis of the complete STR genes family; B. Evolutionary analysis of functionally characterized STR members; the red pentagram markers indicated the previously reported genes; distinct colors corresponded to different experimental groups; outer ring labels(G1, G2, G3) represented major clades of the phylogenetic tree; while secondary labels(G1-a, G1-b, G1-c, G3-a, G3-b, G3-c, G3-d) reflected finer hierarchical classification of genes within these major clades.
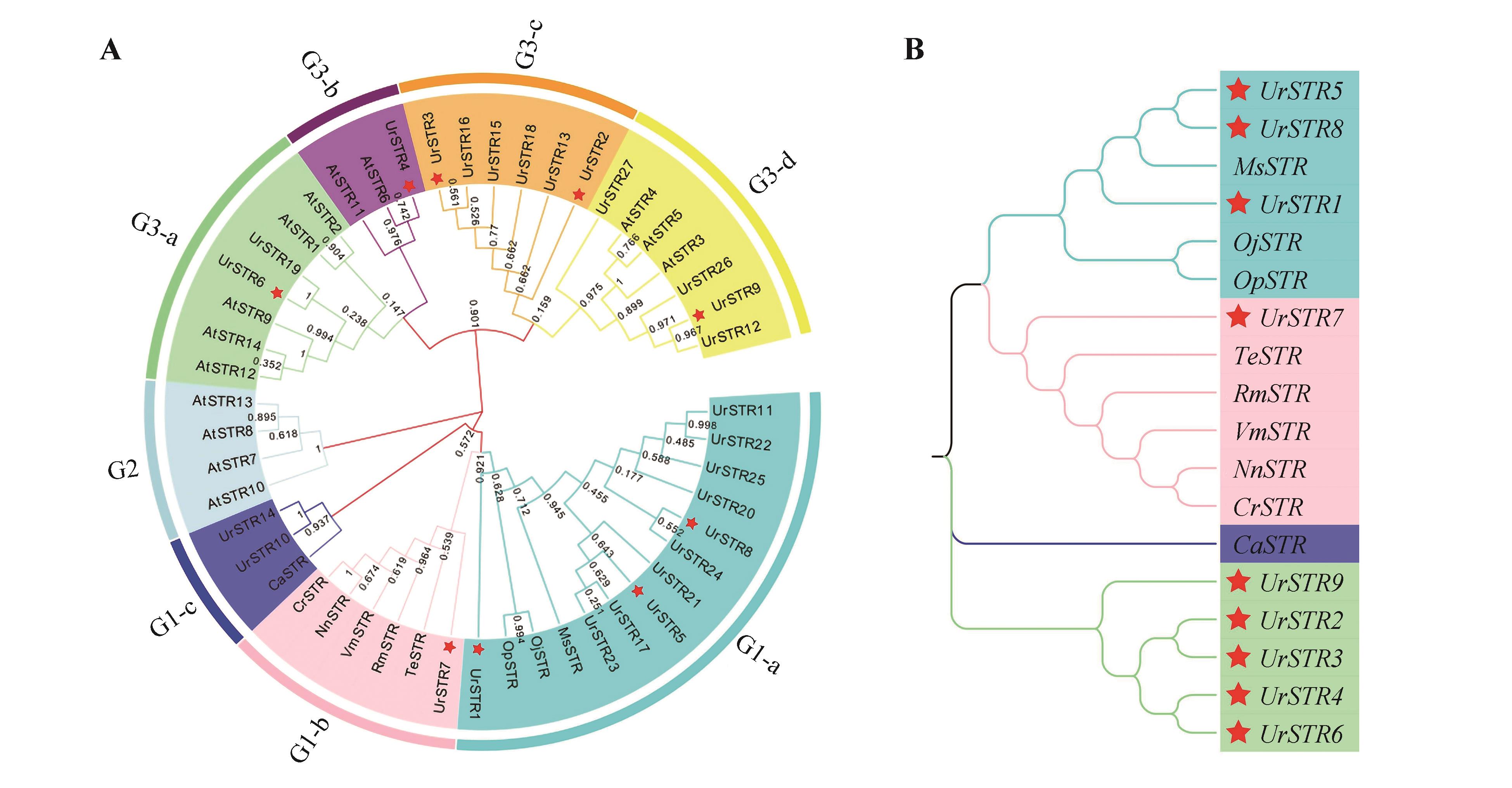

Fig.2
Conservation analysis of catalytic sites inUrSTR proteins family and functionally characterizedSTRMultiple sequence alignment of UrSTR4 withSTRproteins from other plant species and reported STR sequences from U. rhynchophylla. Identical amino acids were displayed in white text on black background, while conserved residues were shown in white text on gray background. The characteristic catalytic residue Glu-309 was marked with a black star.

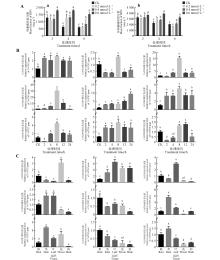
Fig.4
Impact of salicylic acid treatment on monoterpenoid indole alkaloid biosynthesis and UrSTR gene expression in U. rhynchophyllaA. Rhynchophylline and isorhynchophylline mass fraction in SA-treated U. rhynchophylla; B. Expression levels of UrSTR1-UrSTR9 genes in SA-treated U. rhynchophylla; C. Tissue-specific expression profile of UrSTR1-UrSTR9. Error bars represented standard deviation(n=3);different lowercase letters indicated significant differences between different SA concentrations in the same time, between different treatment durations, or between tissues(P<0.05).

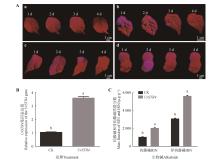
Fig.5
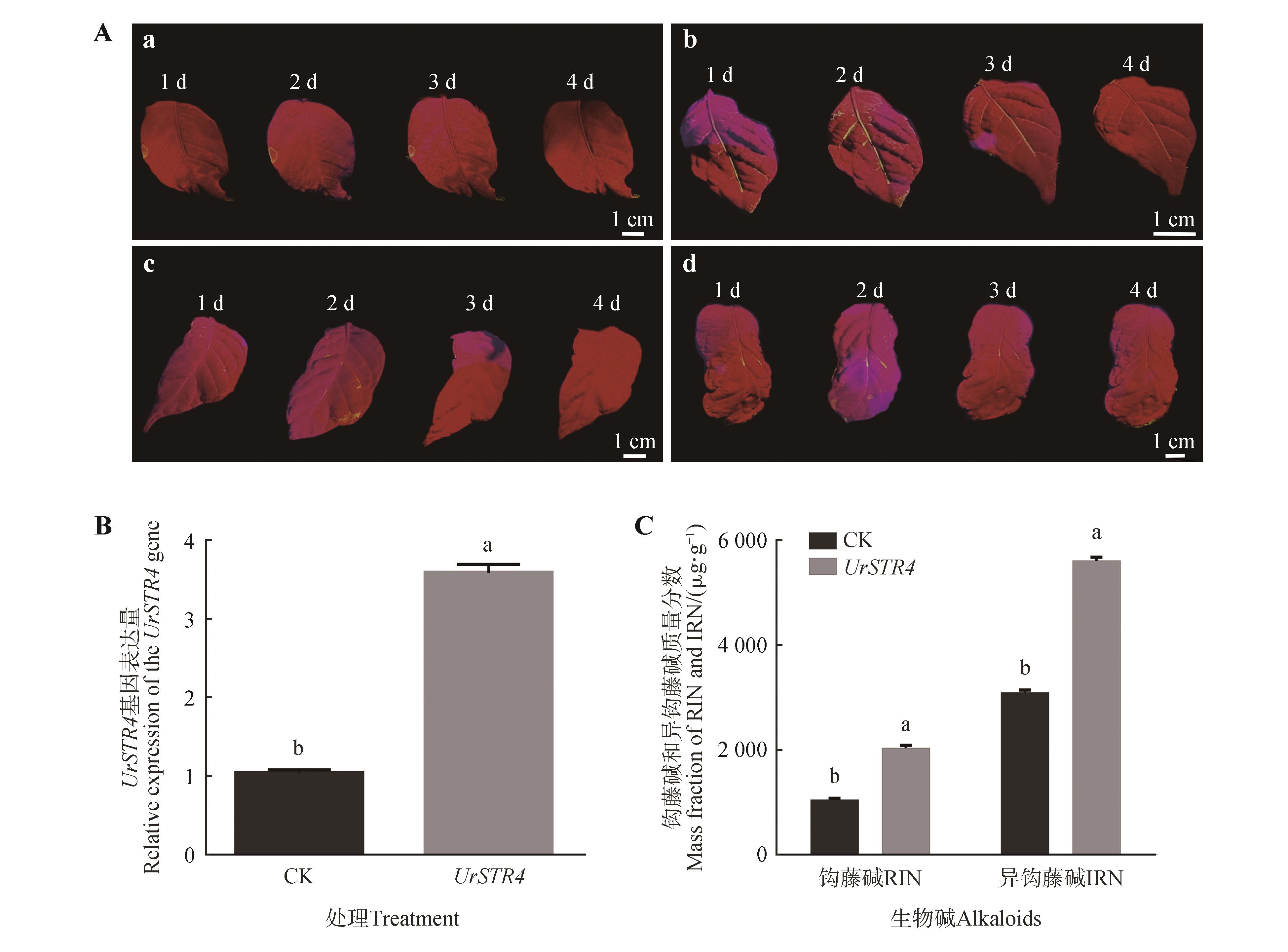
Functional characterization of UrSTR4 in U. rhynchophylla using transient transformationA. GFP fluorescence intensity following Agrobacterium infiltration for 30 s(a), 1 min(b), 2 min(c), or 3 min(d); B. Relative expression levels of UrSTR4 after transient overexpression; C. RIN and IRN mass fraction in overexpression lines; D. Time-course GFP expression from day 1 to 4 post-transformation (after 2-day dark incubation); data represented mean ± SD (n=3);different lowercase letters indicated significant differences between treatments at P<0.01.
| [1] | HEITZMAN M E, NETO C C, WINIARZ E,et al.Ethnobotany,phytochemistry and pharmacology of Uncaria (Rubiaceae)[J].Phytochemistry,2005,66(1):5-29. |
| [2] | ZHANG Q, ZHAO J J, XU J,et al.Medicinal uses,phytochemistry and pharmacology of the genus Uncaria [J].Journal of Ethnopharmacology,2015,173:48-80. |
| [3] | 周浩,路星星,敖雯雯,等.钩藤STR基因及其启动子的克隆与分析[J].药学学报,2022,57(5):1526-1536. |
| ZHOU H, LU X X, AO W W,et al.Cloning and analysis of STR gene and its promoter from Uncaria [J].Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica,2022,57(5):1526-1536. | |
| [4] | LI X, HAN H Q, WEI Y L,et al.Phytochrome interacting factor 3 mediates low light signaling to regulate isorhynchophylline biosynthesis in Uncaria rhynchophylla [J].Scientific Reports,2024,14(1):25032. |
| [5] | YAMAZAKI Y, SUDO H, YAMAZAKI M,et al.Camptothecin biosynthetic genes in hairy roots of Ophiorrhiza pumila:cloning,characterization and differential expression in tissues and by stress compounds[J].Plant and Cell Physiology,2003,44(4):395-403. |
| [6] | KUTCHAN T M.Expression of enzymatically active cloned strictosidine synthase from the higher plant Rauvolfia serpentina in Escherichia coli [J].FEBS Letters,1989,257(1):127-130. |
| [7] | FOUAD A, HEGAZY A E, AZAB E,et al.Boosting of antioxidants and alkaloids in Catharanthus roseus suspension cultures using silver nanoparticles with expression of CrMPK3 and STR genes[J].Plants,2021,10(10):2202. |
| [8] | JUMALI S S, SAID I M, ISMAIL I,et al.Genes induced by high concentration of salicylic acid in Mitragyna speciosa [J].Australian Journal of Crop Science,2011,5(3):296-303. |
| [9] | LU Y, WANG H S, WANG W,et al.Molecular characterization and expression analysis of a new cDNA encoding strictosidine synthase from Ophiorrhiza japonica [J].Molecular Biology Reports,2009,36(7):1845-1852. |
| [10] | SUN Y Z, LUO H M, LI Y,et al.Pyrosequencing of the Camptotheca acuminata transcriptome reveals putative genes involved in camptothecin biosynthesis and transport[J].BMC Genomics,2011,12:533. |
| [11] | SHARMA A, VERMA P, MATHUR A,et al.Overexpression of tryptophan decarboxylase and strictosidine synthase enhanced terpenoid indole alkaloid pathway activity and antineoplastic vinblastine biosynthesis in Catharanthus roseus [J].Protoplasma,2018,255:1281-1294. |
| [12] | CUI L J, NI X L, JI Q,et al.Co-overexpression of geraniol-10-hydroxylase and strictosidine synthase improves anti-cancer drug camptothecin accumulation in Ophiorrhiza pumila [J].Scientific Reports,2015,5:8227. |
| [13] | SINGH S, KAMBLE S N, SATDIVE R K,et al.Heterologous overexpression of Nothapodytes foetida strictosidine synthase enhances levels of anti-cancer compound camptothecin in Ophiorrhiza rugosa [J].Plant Cell,Tissue and Organ Culture,2020,141:67-76. |
| [14] | JIANG C X, YU J X, FEI X,et al.Gene coexpression networks allow the discovery of two strictosidine synthases underlying monoterpene indole alkaloid biosynthesis in Uncaria rhynchophylla [J].International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2023,226:1360-1373. |
| [15] | YANG M Q, YAO B W, LIN R M.Profiles of metabolic genes in Uncaria rhynchophylla and characterization of the critical enzyme involved in the biosynthesis of bioactive compounds-(iso) rhynchophylline[J].Biomolecules,2022,12(12):1790. |
| [16] | GUO E Y, YUAN M T, XU L J,et al.Identification of three key enzymes involved in the biosynthesis of tetracyclic oxindole alkaloids in Uncaria rhynchophylla [J].Bioorganic Chemistry,2023,136:106545. |
| [17] | 穆德添,万凌云,韦树根,等.钩藤不同部位总RNA提取及UrSTR基因的克隆与表达分析[J].农业生物技术学报,2022,30(9):1737-1746. |
| MU D T, WAN L Y, WEI S G,et al.Extraction of total RNA and cloning and expression analysis of UrSTR gene from Uncaria rhynchophylla [J].Journal of Agricultural Biotechnology,2022,30(9):1737-1746. | |
| [18] | 路星星,强玮,付维,等.茉莉酸甲酯对钩藤生物碱合成的影响[J].分子植物育种,2023,21(10):3290-3296. |
| LU X X, QIANG W, FU W,et al.Effects of methyl jasmonate on alkaloids biosynthesis in Uncaria rhyncho-phylla [J].Molecular Plant Breeding,2023,21(10):3290-3296. | |
| [19] | 周浩,强玮,敖雯雯,等.外源脱落酸对钩藤中生物碱合成的影响[J].分子植物育种,2024,22(15):5091-5097. |
| ZHOU H, QIANG W, AO W W,et al.Effect of exogenous abscisic acid on biosynthesis of alkaloids in Uncaria Rhynchophylla [J].Molecular Plant Breeding,2024,22(15):5091-5097. | |
| [20] | 徐磊,胥晓,刘沁松.外源水杨酸对盐胁迫下珙桐幼苗抗氧化系统和基因表达的影响[J].植物研究,2023,43(4):572-581. |
| XU L, XU X, LIU Q S.Effects of exogenous salicylic acid on antioxidant system and gene expression of Davidia involucrata seedlings under salt stress[J].Bulletin of Botanical Research,2023,43(4):572-581. | |
| [21] | JEYASRI R, MUTHURAMALINGAM P, KARTHICK K,et al.Methyl jasmonate and salicylic acid as powerful elicitors for enhancing the production of secondary metabolites in medicinal plants:an updated review[J].Plant Cell,Tissue and Organ Culture,2023,153:447-458. |
| [22] | SÁNCHEZ-ROJO S, CERDA-GARCÍA-ROJAS C M, ESPARZA-GARCÍA F,et al.Long-term response on growth,antioxidant enzymes,and secondary metabolites in salicylic acid pre-treated Uncaria tomentosa microplants[J].Biotechnology Letters,2015,37:2489-2496. |
| [23] | 穆德会,刘艳红,陈漂漂,等.超表达HnCYP82M3和DsTRI基因对颠茄托品烷生物碱合成的影响[J].药学学报,2024,59(3):775-783. |
| MU D H, LIU Y H, CHEN P P,et al.Enhancement of tropane alkaloids biosynthesis in Atropa belladonna hariy root by overexpression of HnCYP82M3 and DsTRI genes[J].Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica,2024,59(3):775-783. | |
| [24] | 王晓红.遮光影响钩藤碱和异钩藤碱生物合成的分子机制[D].贵阳:贵州大学,2022. |
| WANG X H.Molecular mechanisms of shade affecting the biosynthesis of rhynchophylline and isorhynchophylline in Uncaria rhynchophylla [D].Guiyang:Guizhou University,2022. | |
| [25] | 李雪.乙烯促进钩藤生物碱合成的机制研究[D].贵阳:贵州大学,2022. |
| LI X.Study on the mechanism of ethylene promoting the biosynthesis of alkaloids in Uncaria rhynchophylla[D].Guiyang:Guizhou University,2022. | |
| [26] | 张智仙,王晓红,李雪,等.土壤自然干旱处理对钩藤生长与生理特征及主要药用成分积累的影响[J].西北植物学报,2020,40(4):658-666. |
| ZHANG Z X, WANG X H, LI X,et al.Effect of soil natural drought on growth,physiological characteristics and accumulation of main medicinal components of Uncaria rhynchophylla [J].Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica,2020,40(4):658-666. | |
| [27] | YANG M Q, WANG Q, LIU Y N,et al.Divergent camptothecin biosynthetic pathway in Ophiorrhiza pumila [J].BMC Biology,2021,19:122. |
| [28] | MU D T, SHAO Y Y, HE J L,et al.Evaluation of reference genes for normalizing RT-qPCR and analysis of the expression patterns of WRKY1 transcription factor and rhynchophylline biosynthesis-related genes in Uncaria rhynchophylla [J].International Journal of Molecular Sciences,2023,24(22):16330. |
| [29] | GUO Q Q, MA X J, WEI S G,et al. De novo transcriptome sequencing and digital gene expression analysis predict biosynthetic pathway of rhynchophylline and isorhynchophylline from Uncaria rhynchophylla,a non-model plant with potent anti-alzheimer’s properties[J].BMC Genomics,2014,15(1):676. |
| [30] | 邓小红,姬拉拉,熊露露,等.不同海拔对钩藤生长及生物碱含量的影响[J].植物生理学报,2020,56(10):2095-2102. |
| DENG X H, JI L L, XIONG L L,et al.Effects of different altitudes on growth and alkaloid content of Uncaria Rhynchophylla [J].Plant Physiology Journal,2020,56(10):2095-2102. |
| [1] | Lei XU, Xiao XU, Qinsong LIU. Effects of Exogenous Salicylic Acid on Antioxidant System and Gene Expression of Davidia involucrata Seedlings under Salt Stress [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2023, 43(4): 572-581. |
| [2] | Chenjing SHEN, Wenbo WU, Luran GENG, Fulong WANG, Pengzhou ZHAO, Jinhui SONG, Yaguang ZHAN, Jing YIN. Regulatory Effects of Salicylic Acid,Nano-zinc Oxide and Growth-promoting Fungi YZ13-1 on the Resistance to Drought Stress of Fraxinus mandshurica [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2023, 43(3): 388-395. |
| [3] | Jingzhe WANG, Chaokui NIU, Xinyuan LIANG, Chenjing SHEN, Jing YIN. Regulation of Salicylic Acid on Tolerance to Saline Alkali Stress at Seedling Stages of Betula platyphylla [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2023, 43(3): 379-387. |
| [4] | WANG Wan-Qi, QI Wan-Zhu, ZHAO Qiu-Shuang, ZENG Dong, LIU Yi, FU Peng-Yue, QU Guan-Zheng, ZHAO Xi-Yang. Cloning and Expression Analysis of BpJMJ18 Gene Promoter in Betula platyphylla [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2020, 40(5): 751-759. |
| [5] | LIU Jin-Yu, GAO Yue-Hao, HUANG Jin-Shuo, ZHANG Qin. Effects of Exogenous Salicylic Acid on Physiological and Electrical Impedance Parameters of Trollius chinensis Seedlings under High Temperature Stress [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2020, 40(4): 543-551. |
| [6] | FAN Er-Qin, LIU Cai-Xia, FU Peng-Yue, YANG Chuan-Ping, QU Guan-Zheng. Expression Pattern of PagC3H3 Gene in Populus alba×P.glandulosa [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2019, 39(4): 521-528. |
| [7] | DA Qing-Jing, CHEN Xue-Lin, MA Wen-Bing, ZHANG Hai-Xian. Effect of Exogenous SA on Germination and Physiological Characteristics of Meconopsis racemosa Seed [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2017, 37(6): 835-840. |
| [8] | SU Hu, ZHU You-Lin, LI Rong, WU Chao, ZHANG Yun. Cloning the Partial Coding Sequence of ICS Gene and the Influence of ICS Gene on the SA Content in Scutellaria baicalensis Georgi [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2016, 36(3): 421-426. |
| [9] | WANG Ling-Li1,2;LIU Wen-Zhe2*. Induction and Effects of Elicitor on Camptothecin Content in Camptotheca acuminata Callus [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2015, 35(5): 704-709. |
| [10] | YANG Xiao-Jie;ZHANG Hong-Wei. Protection of salicylic acid on Neo-Taraxacum siphonanthum in salt stress [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2006, 26(2): 222-224. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||